Method for separating positive electrode, negative electrode and diaphragm of LiFePO4 battery
A diaphragm separation and battery technology, applied in battery recycling, recycling technology, recycling by waste collectors, etc., to achieve good separation effect and simplified recycling steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
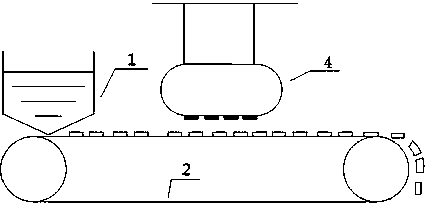
[0020] like figure 1 As shown, a LiFePO 4 The method for separating positive and negative poles and separators of batteries comprises the following steps:
[0021] a. LiFePO with shell removed 4 The core of the aluminum-plastic soft pack battery (including positive, negative and separator mixture), mechanically crushed into a size of 1cm 2 fragments of
[0022] b. If figure 1 As shown, place a large amount above 1cm 2 The fragments are uniformly fed to the conveyor belt 2 by the feeder 1, and the width of the conveyor belt 2 is 1m, so that the fragments are flattened on the conveyor belt 2 and advance at a constant speed. A circular magnet with a magnetic field strength of 15,000 gauss and a diameter of 1m is set above the conveyor belt. The suspended magnet 4 is 5cm away from the surface of the conveyor belt. During work, the positive electrode material is adsorbed by magnetic force. The conveyor belt advances to the end to be collected. When the feeding and transmis...
Embodiment 2
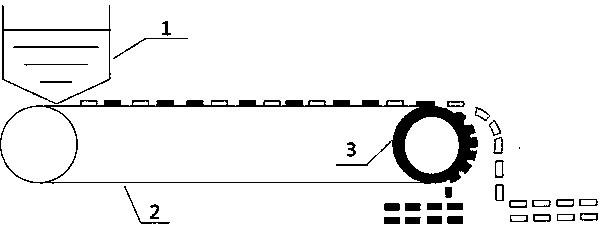
[0025] like figure 2 As shown, a LiFePO 4 The method for separating positive and negative poles and diaphragms of batteries comprises the following steps:
[0026] a. LiFePO with shell removed 4 The cell of the aluminum shell battery (including positive, negative and diaphragm mixture), mechanically crushed into a size of 100cm 2 fragments of
[0027] b. Put a large amount of the above 100cm 2 The fragments are evenly fed to the conveyor belt 2 by the feeder 1, and the width of the conveyor belt 2 is 1m. The fragments are spread on the conveyor belt and advance at a constant speed. At the end of the conveyor belt is a magnetic roller 3 with a magnetic field strength of 10,000 gauss. When the conveyor belt is driven by rotation, it absorbs the positive pole material. The negative pole and the diaphragm have no adsorption force and are separated from the conveyor belt by gravity. The positive pole rotates to the back with the magnetic roller and then detaches. conveyor bel...
Embodiment 3
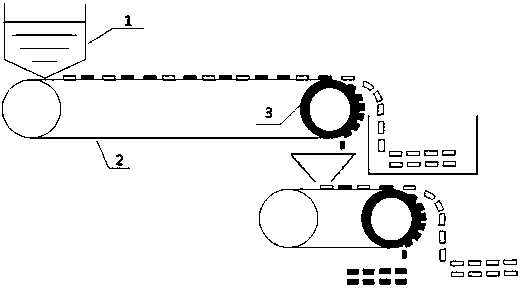
[0030] like image 3 As shown, a LiFePO 4 The method for separating positive and negative poles and diaphragms of batteries comprises the following steps:
[0031] a. LiFePO with shell removed 4 The cell of the steel shell battery (including positive, negative and diaphragm mixture), mechanically crushed into a size of 50cm 2 fragments of
[0032] b. Put a large amount of the above 100cm 2 The fragments are evenly fed to the conveyor belt 2 by the feeder 1, and the width of the conveyor belt 2 is 1m. The fragments are spread on the conveyor belt and advance at a constant speed. At the end of the conveyor belt are two magnetic rollers 3 with a magnetic field strength of 5000 gauss. While the conveyor belt is driven by rotation, the positive electrode material is adsorbed. The negative electrode and the diaphragm have no adsorption force and are detached from the conveyor belt by gravity. The absorbed positive electrode material passes through a conveyor belt again. And the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetic flux density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com