Method for facilitating removal of radiation of sulfanilamide antibiotic in waste water by utilizing ferrous ions
A technology of ferrous ions and sulfonamides, which is applied in the field of nuclear technology application and environmental protection, can solve the problems of high pH requirements of solutions and increased processing costs, and achieve the effects of environmental protection, reduced processing costs, and improved processing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
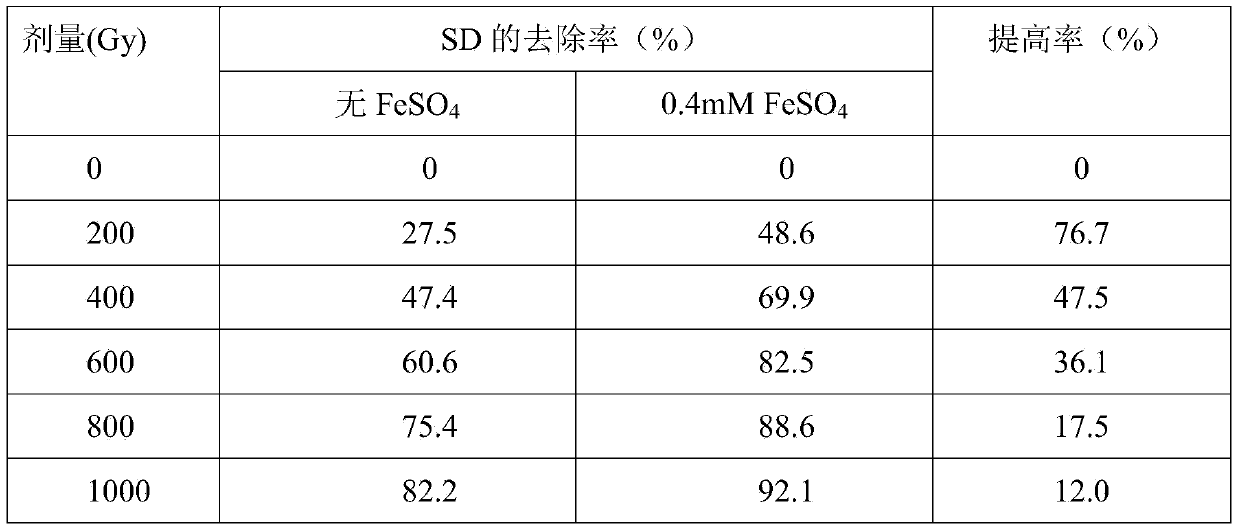
[0023] Sulfadiazine (SD) solution is prepared from analytical reagent and deionized water, the concentration is 20mg / L, the pH is not adjusted (pH5.5-6.5); ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4 ) Using analytical reagents, the mixed solution of sulfadiazine and ferrous sulfate was prepared from deionized water, the concentration of SD was 20mg / L, FeSO 4 The concentration is 0.4mM. The radiation source is from the Institute of Nuclear Energy and New Energy Technology of Tsinghua University. 60 Co radiation device, the central channel dose rate is 320.93Gy / min. In the experiment, 30mL solution was taken each time, put into a 50mL radiation-resistant tube, and placed in the central hole for irradiation. The experiment tested the effect of ion irradiation on the removal of sulfadiazine in two solutions under different absorbed doses (lower dose). The irradiation results are shown in Table 1.
[0024] Table 1 The removal effect of SD under different doses
[0025]
[0026] Detection meth...
Embodiment 2
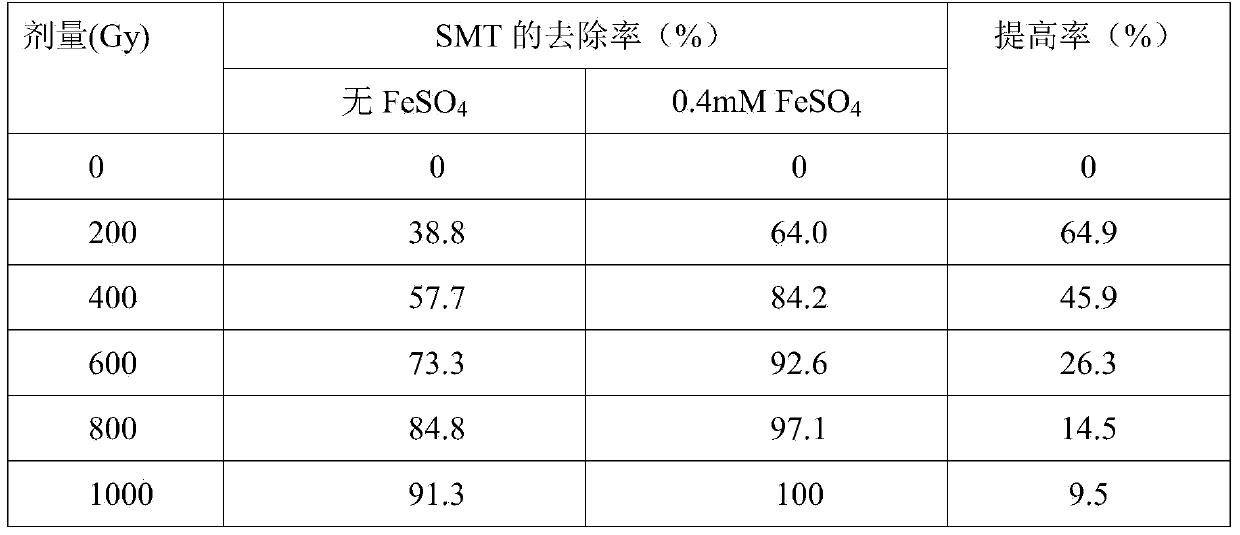
[0029] Sulfamethazine (SMT) solution is prepared from analytical reagent and deionized water, the concentration is 20mg / L, the pH is not adjusted (pH6.0-7.0); ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4 ) using analytical reagents, a mixed solution of sulfamethazine and ferrous sulfate was prepared from deionized water, the concentration of SMT was 20mg / L, FeSO 4 The concentration is 0.4mM. The radiation source is from the Institute of Nuclear Energy and New Energy Technology of Tsinghua University. 60 Co radiation device, the central channel dose rate is 320.93Gy / min. In the experiment, 30mL solution was taken each time, put into a 50mL radiation-resistant tube, and placed in the central hole for irradiation. The experiment tested the effect of ion irradiation on the removal of sulfamethazine in two solutions under different absorbed doses (lower dose). The irradiation results are shown in Table 2.
[0030] The removal effect of SMT under the different doses of table 2
[0031]
[0032] ...
Embodiment 3
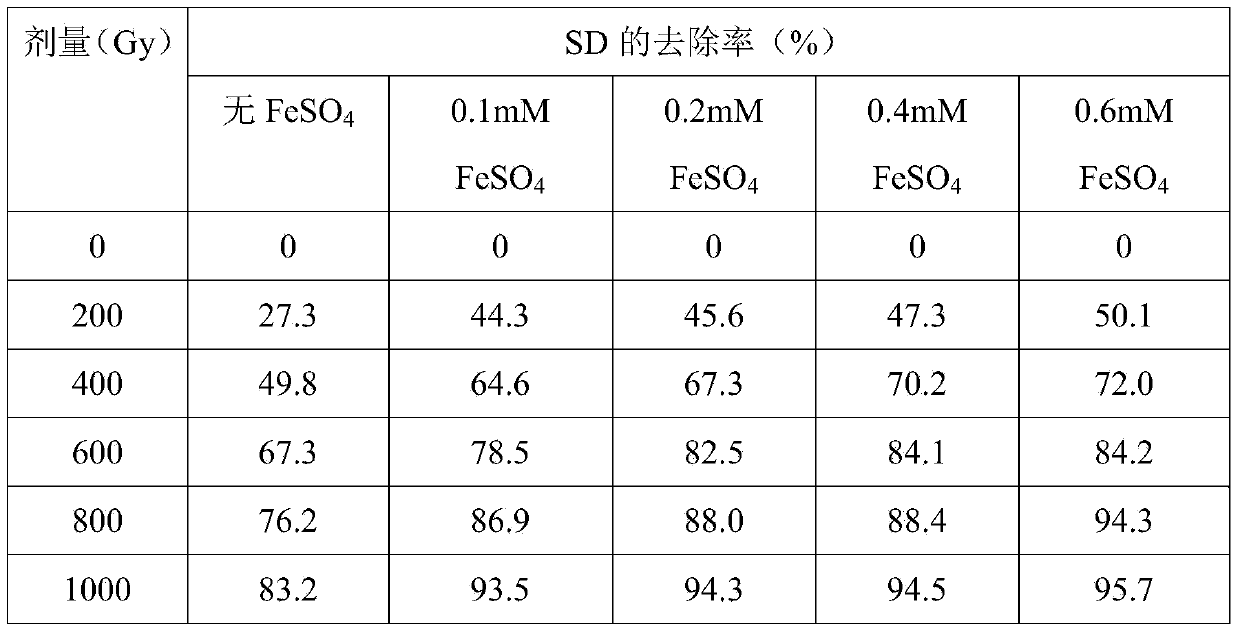
[0035] Sulfadiazine (SD) solution is prepared from analytical reagent and deionized water, the concentration is 20mg / L, the pH is not adjusted (pH5.5-6.5); ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4 ) Using analytical reagents, the mixed solution of sulfadiazine and ferrous sulfate was prepared from deionized water, the concentration of SD was 20mg / L, FeSO 4 The concentrations were 0.1 mM, 0.2 mM, 0.4 mM and 0.6 mM, respectively. The radiation source is from the Institute of Nuclear Energy and New Energy Technology of Tsinghua University. 60 Co radiation device, the central channel dose rate is 320.93Gy / min. In the experiment, 30mL solution was taken each time, put into a 50mL radiation-resistant tube, and placed in the central hole for irradiation. The experiment tested the effect of ion irradiation on the removal of sulfadiazine in solution under different conditions (lower dose) under different absorbed doses. The irradiation results are shown in Table 3.
[0036] The removal effect of SD...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com