Preparation method of bismuth oxyhalide/ titanium dioxide composite photocatalyst
A technology of titanium dioxide and bismuth oxyhalide is applied in the field of preparation of new photocatalytic materials, which can solve the problems of easy deactivation and low performance of photocatalytic materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
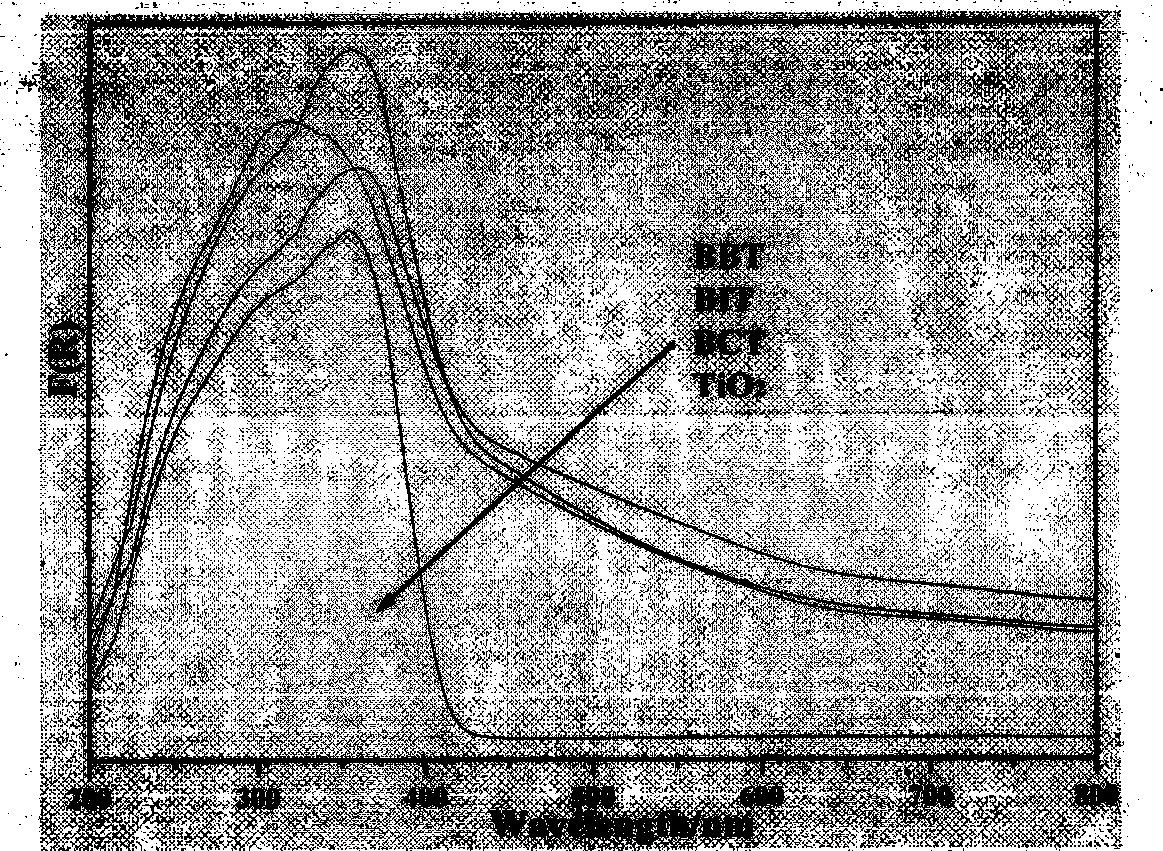
[0017] Bismuth oxyhalide / titanium dioxide composite photocatalyst for degradation of benzene. The gas-phase degradation reaction of organic pollutants is carried out on a continuous reaction device, using benzene (purge generation) as a simulated reactant, the flow rate is set to 20ml / min, and the concentration is adjusted to 200ppm. The loading amount of the catalyst in the quartz reactor is about 0.85g, and the light source is Porphyra PLS-XE300C (installed with a 420nm ultraviolet filter), and the distance between the lamp port and the reactor is fixed at about 10cm. Reactants and products were monitored online by gas chromatography (HP4890, Porapak R packed column, TCD, FID). Turn on the light after the adsorption is saturated, and automatically inject samples every 30 minutes to analyze organic pollutants and product CO 2 The concentration was calibrated by external standard method. The result is as figure 2 Shown, TiO 2 The visible light photocatalytic efficiency is...
example 2
[0019] Bismuth oxyhalide / titanium dioxide composite photocatalyst for degradation of ethylene, acetone and toluene. The specific experimental procedure is as described in Example 1. The simulated organic matter was successively replaced by ethylene, acetone and toluene, and the concentrations were all adjusted to 200 ppm. The result is as image 3 As shown, the four catalysts all showed high degradation ability to acetone and toluene, but the degradation to ethylene was not ideal. This is because, although the molecular structure of ethylene is the simplest and the penetration is strong, the adsorption amount on the catalyst is very small. Experiments have found that its dark adsorption speed is very fast, basically reaching saturation in 2 hours. In this case, the reactant and the catalyst cannot be fully contacted, and the reaction effect is naturally greatly reduced. In contrast, acetone has a simple structure and strong polarity, and is easier to combine with catalytic m...
example 3
[0021] Activity stability of bismuth oxyhalide / titania composite photocatalysts. Catalyst deactivation generally occurs in photocatalytic reactions. The main reasons are the shedding of loads and the deposition of intermediate products. Traditional organic photosensitization (RhB) and inorganic photosensitization (CdS), although can significantly improve TiO 2 The ability to respond to visible light, but the dopant itself is extremely unstable, prone to photocorrosion and loss of activity; on the other hand, due to its own surface characteristics, some catalysts are very easy to attach intermediate products during the reaction, resulting in the occupation of active sites . In the experiment, 10h was set as a cycle, and a total of 5 cycles of cyclic photoreaction were carried out. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that from the beginning of the reaction, TiO 2In the process of continuous deactivation, the degradation rate is only 5% after 30 hours, and at this time the dop...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com