Heat transfer bridge sensor for measuring scour and silt depth around steel pipe piles of bridges
A technology of bridge-type sensors and steel pipe piles, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices and instruments, can solve problems such as the inability to realize automatic monitoring, unfavorable large-scale promotion of technologies, and complicated sensor installation, and achieve simple and reliable measurement principles, good economic benefits, The effect of broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
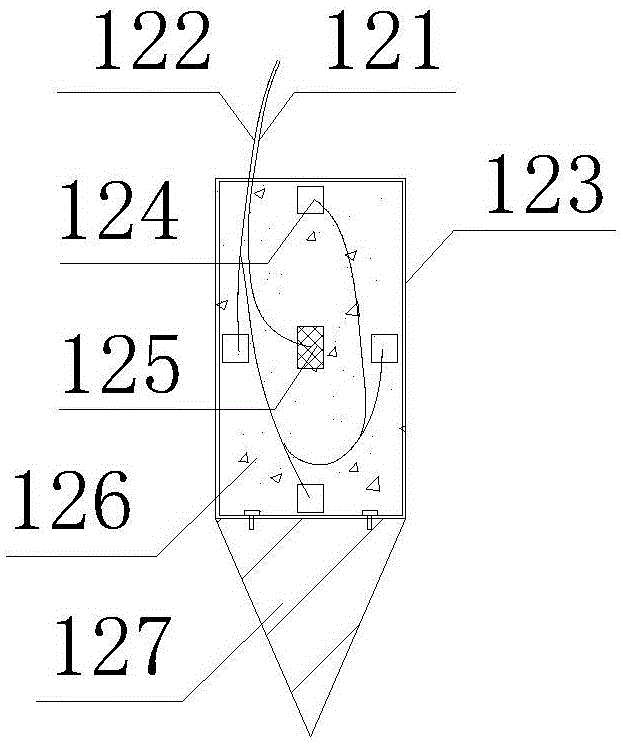
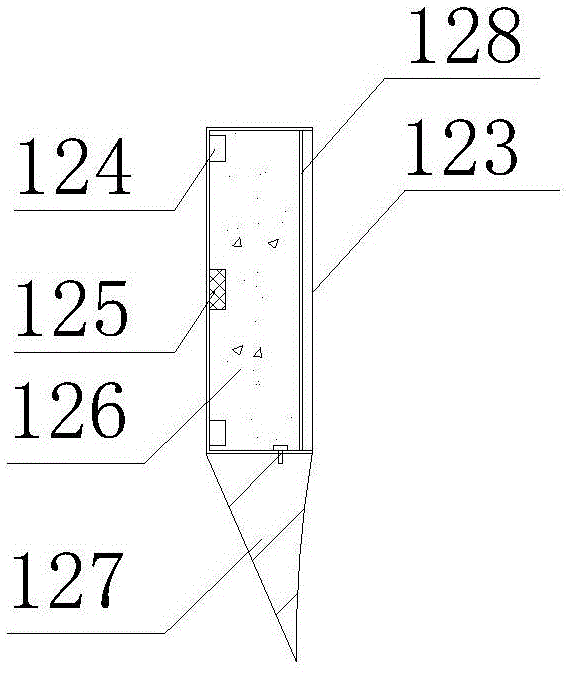
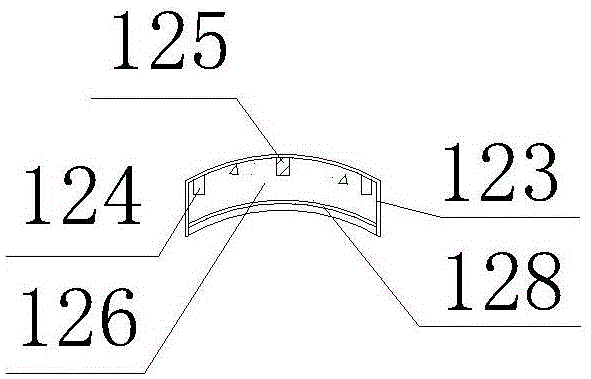
[0027] Combining Figure 1 and figure 2 , The sensor 12 includes a power line 121 , a signal line 122 , a housing 123 , a temperature probe 124 , a heating block 125 , a heat insulating material 126 , a cone 127 , and a sealing plate 128 . The housing 123 is welded by stainless steel sheets with tile-shaped side walls and semicircular ends. The pointed cone 127 is half a solid cone, and the top surface of the pointed cone 127 is connected to the bottom surface of the housing 123 by bolts. The center of the inner side wall of the casing 123 is a heating block 125, and a temperature probe 124 is located at the midpoint of each of the four sides. The power line 121 of the heating block 125 and the signal line 122 of the temperature probe 124 are drawn out from the top of the casing 123 . The rest of the space in the casing 123 is filled with a heat insulating ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com