Rapid composting method of water plant by utilization of biomass charcoal
A biomass charcoal and aquatic plant technology, which is applied in the preparation of organic fertilizers, the treatment and application of biological organic parts, etc., can solve the problems of a large amount of aquatic plant waste, high moisture content, and reduced compost productivity, etc. The effect of biological dehydration rate, less ammonia volatilization, and enlargement of site area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
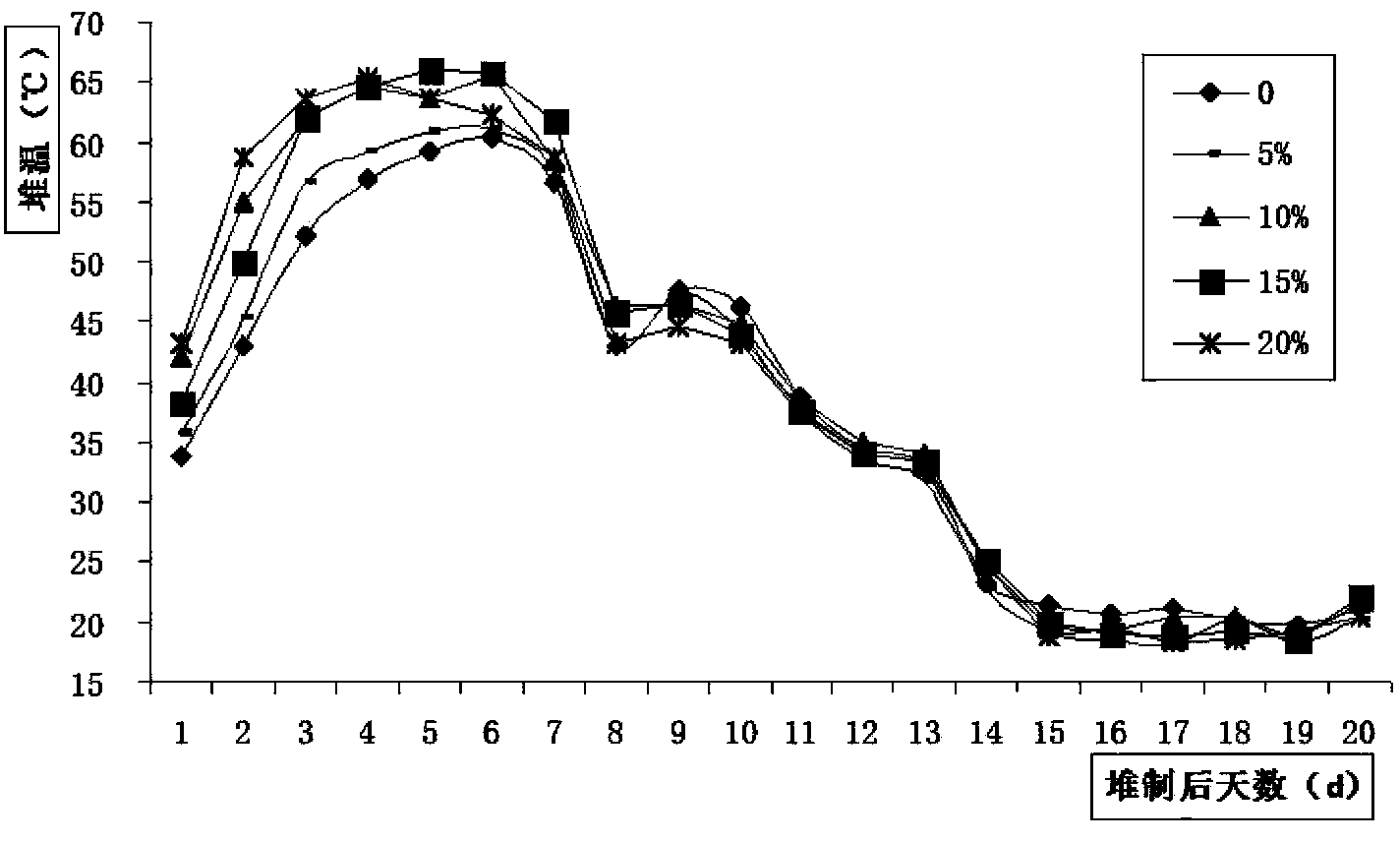
[0054] Example 1: A method of using biochar to quickly compost aquatic plants
[0055] The method of this fast composting is made up of following steps successively:
[0056] The first step is to weigh the raw materials required for composting. The raw materials are composed of basic compost and biochar (purchased from Henan Sanli New Energy Co., Ltd., straw bio-black carbon with a particle size of less than 0.25 mm), of which , the basic stacking material refers to the mixture formed by chopped fresh Elodea (moisture content 90%, CN ratio 13) and straw (moisture content 13.5%, CN ratio 72); the fresh Elodea and straw The ratio is based on the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio on a dry basis of the basic stock being 25, and the natural weight obtained by conversion according to the actual moisture content of fresh Elodea and straw; the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio on a dry basis refers to Under the state of water content, the content ratio of carbon and nitrogen in carbohydrates in plants...
Embodiment 2
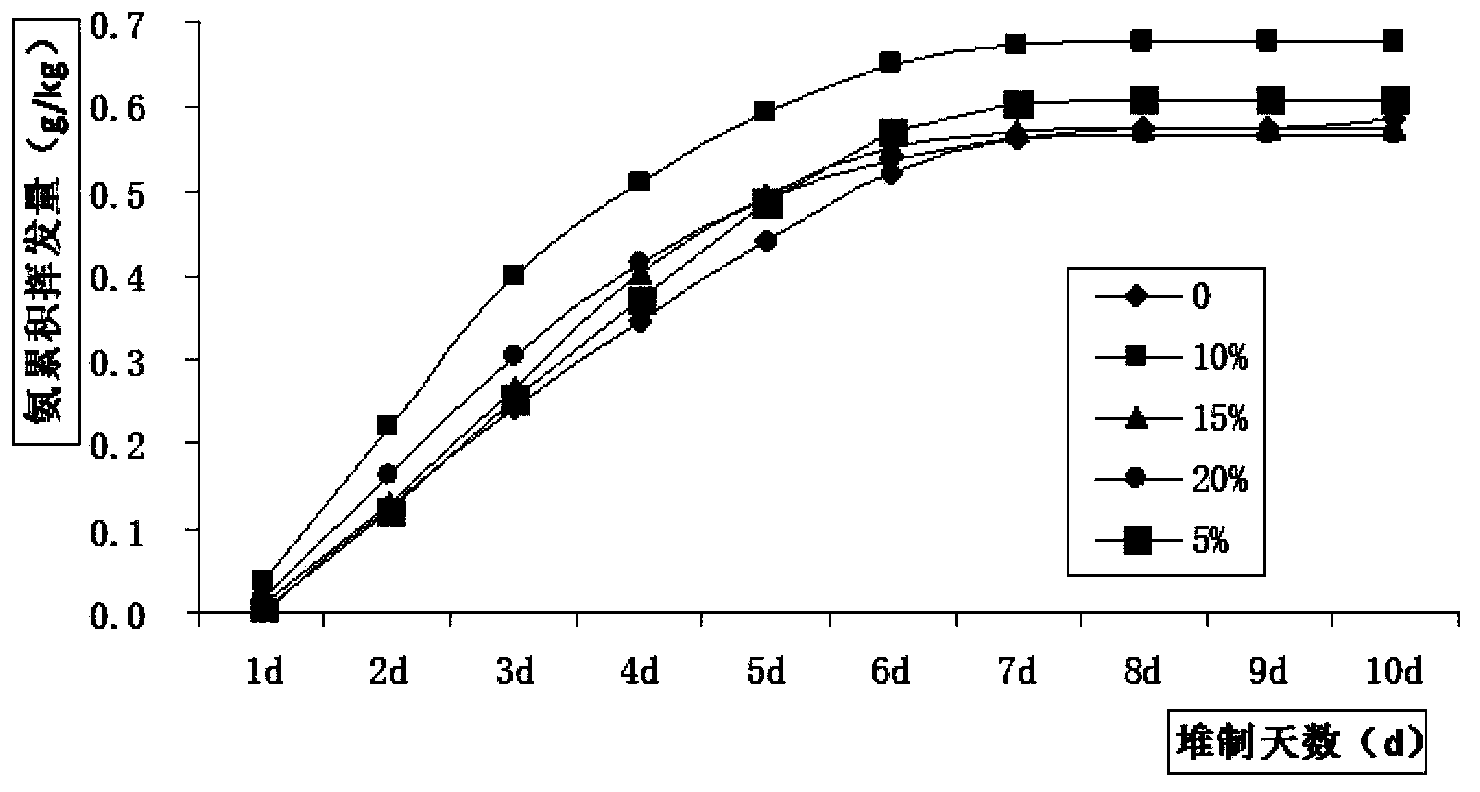
[0061] Embodiment 2: A method of using biochar to quickly compost aquatic plants
[0062] The method of this fast composting is made up of following steps successively:
[0063] The first step is to weigh the raw materials required for composting. The raw materials are composed of basic compost and biochar (purchased from Henan Sanli New Energy Co., Ltd., straw bio-black carbon with a particle size of less than 0.25 mm), of which , the basic stacking material refers to the mixture formed by chopped fresh Elodea (moisture content 90%, CN ratio 14) and straw (moisture content 13.5%, CN ratio 70); the fresh Elodea and straw The ratio is based on the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio on a dry basis of the basic stock being 22, and the natural weight obtained through conversion according to the actual moisture content of fresh Elodea and straw; the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio on a dry basis refers to Under the state of water content, the content ratio of carbon and nitrogen in the carbohydrat...
Embodiment 3
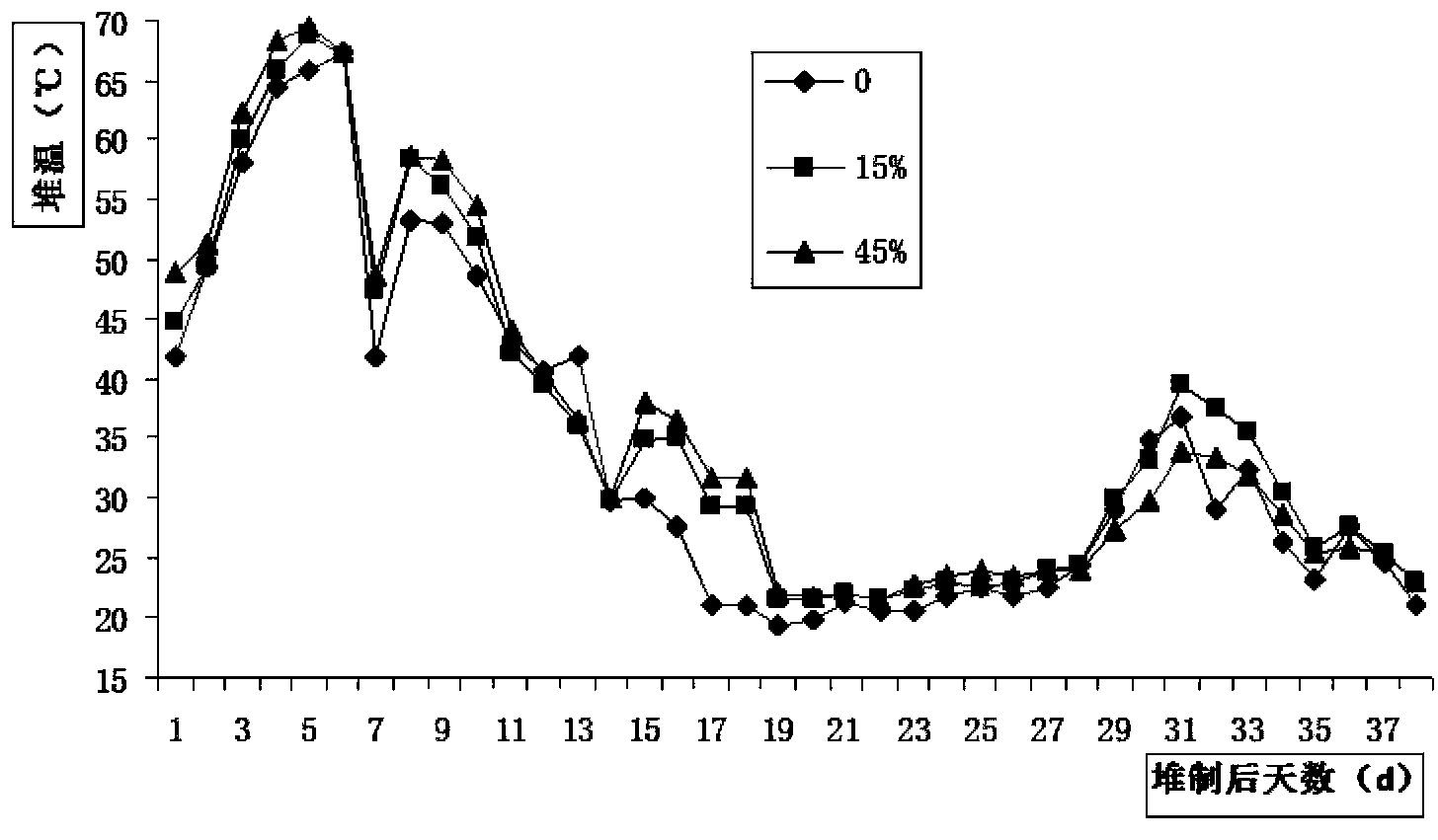
[0068] Embodiment 3: A kind of method that utilizes biomass charcoal to compost quickly to aquatic plants
[0069] The method of this fast composting is made up of following steps successively:
[0070] The first step is to weigh the raw materials required for composting. The raw materials are composed of basic compost and biochar (purchased from Henan Sanli New Energy Co., Ltd., straw bio-black carbon with a particle size of less than 0.25 mm), of which , the basic stacking material refers to the mixture formed by chopped fresh water hyacinth (alias water hyacinth, water content 90%, CN ratio 9) and wheat straw (moisture content 13.5%, CN ratio 85); the fresh The proportioning of water hyacinth and wheat straw is based on the fact that the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio on a dry basis of the basic stack is 28, and according to the actual moisture content of fresh water hyacinth and wheat straw, the natural weight obtained by conversion; Nitrogen ratio refers to the content ratio o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com