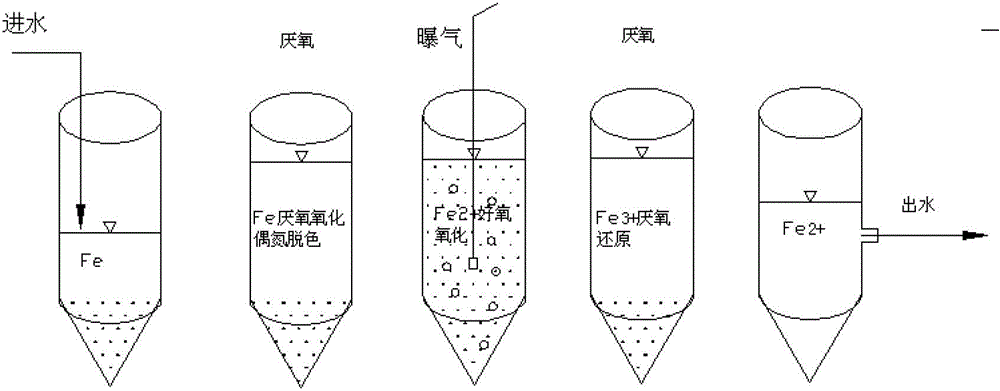
Method for strengthening azo dye biodegradation by utilizing zero-valent iron
An azo dye, biodegradation technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of microbial reaction rate limitation, inability to achieve complete mineralization of azo dyes, etc. Achieve the effect of rapid COD removal, rapid degradation, and promotion of recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
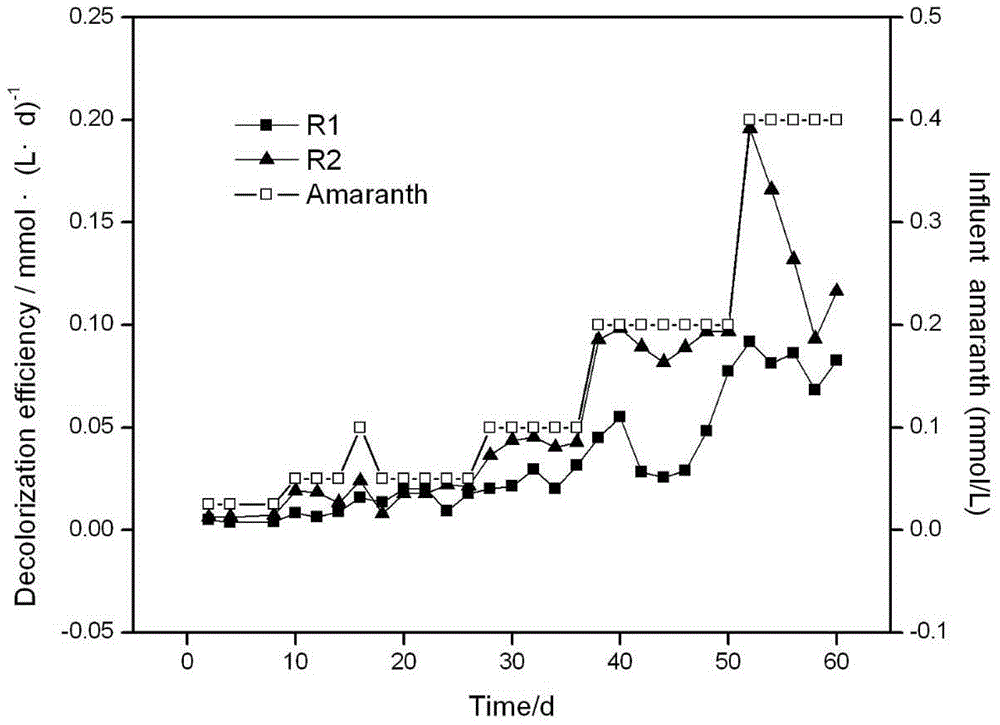
[0015] Example 1: Effect of adding zero-valent iron on the removal of amaranth in reactor
[0016] Artificially prepared azo dye wastewater was used as reaction influent. With sucrose-C, (NH4) 2 SO 4 -N, KH 2 PO 4 -P is used as carbon source, nitrogen source and phosphorus source, its COD:N:P ratio is 200:5:1, the initial influent COD is 500mg / L; the trace element is CoCl 2 .6H 2 O:0.5g·L -1 , NiCl.6H 2 O:0.05g·L -1 、CuSO 4 .5H 2 O:0.0465g·L -1 , ZnSO 4 :0.0893g·L -1 、H 3 BO 3 :0.05g·L -1 , MnCl 2 .4H 2 O:0.5g·L -1 , (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 .2H 2 O:0.01g·L -1 ; Amaranth concentration from 0.025mmol L -1 Gradually increase to 0.4mmol·L -1 , pH8.0, the balance is water. See the run time for each amaranth concentration gradient figure 2 . The anoxic-aerobic-anoxic sequencing batch reactor process is adopted, and the process parameters are: hydraulic retention time is 48h: anaerobic section 24h, aerobic section 12h, anaerobic section 10h, idle 2h, and the...
Embodiment 2
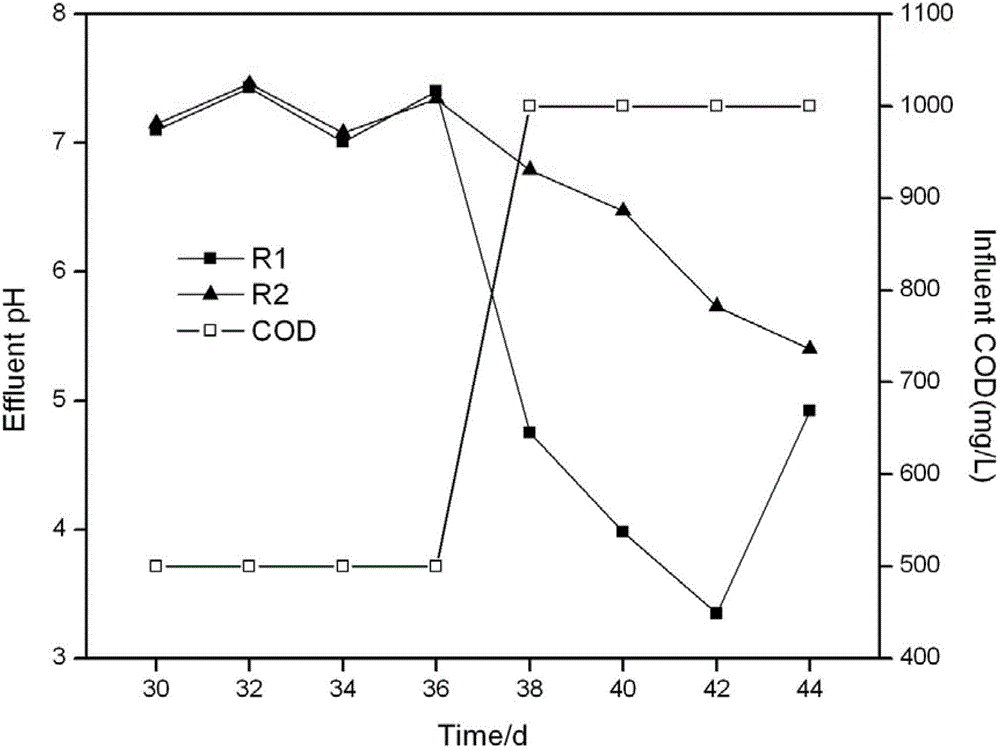
[0017] Example 2: The effect of adding zero-valent iron on the pH of the effluent under the condition of high COD load in the reactor
[0018] Artificial water distribution formula, reactor design (reactor R1 is only inoculated with activated sludge, and reactor R2 is inoculated with activated sludge based on adding zero-valent iron, and the dosage is 6mmol L -1 ), the operating parameters were the same as those in Example 1, when running for 38 days, the COD of the influent was adjusted from 500mg / L to 1000mg / L, and the pH changes of the effluent of the reactor with added parts iron and zero-valent iron were compared. The result is as image 3 As shown, when the COD is 500mg / L, the pH of the effluent from reactors R1 and R2 is about 7.0, and the COD removal rate is 85%. When the COD rises to 1000mg / L, the effluent from the reactor is acidic, the pH of the effluent from the reactor R1 is 3.3-5.0, and the pH of the effluent from the reactor R2 is 5.4-6.8. At the same time, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com