Cloning and application of major gene Chalk5 for chalkiness rate of paddy rice
A major gene, chalky rate technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as QTL phenotypic trait interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
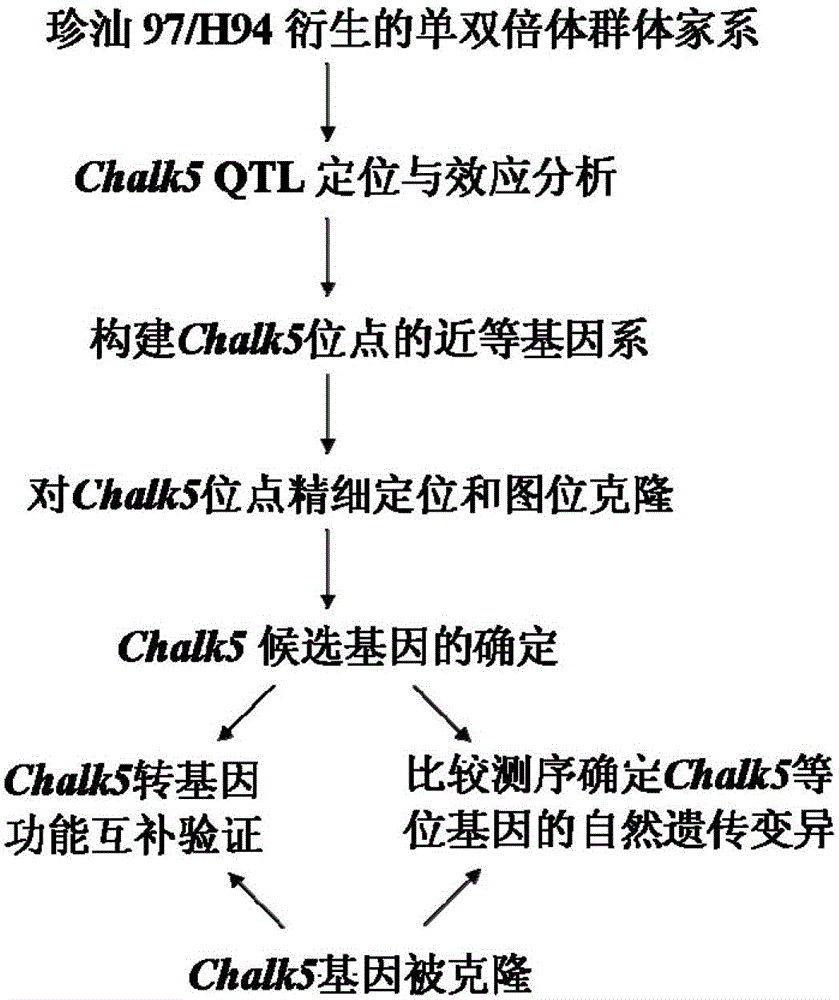
[0032] Example 1: Construction of Chalk5 near-isogenic lines
[0033] 1 Backcross and selection
[0034] as attached figure 1 As shown, a family containing the Chalk5 gene and 55% of the genetic background was selected from the double haploid population derived from the combination of the rice variety Zhenshan 97B with a high chalkiness rate and the variety H94 with a low chalkiness rate. Hybridization, with Zhenshan 97B as the recurrent parent, backcrossed continuously for 3 generations, in BC 1 f 1 and BC 2 f 1 In each generation, only forward selection was performed on Chalk5, that is, individual plants whose target segment was Zhenshan 97B / H94 heterozygous genotype were selected for the next round of backcrossing. The target segment refers to the previous QTL mapping results (Fan Chuchuan, 2006, Ph.D. dissertation, Huazhong Agricultural University Library) identified two SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) markers RM593 and RM574 (see: ( http: / / www.gramene.org / ) within ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Fine mapping and map-based cloning of Chalk5
[0039] 1 Phenotypic measurement of chalkiness
[0040] The grains of each transgenic and near-isogenic line were dried naturally and placed at room temperature for at least 3 months to ensure that the grains were dry and the water content of the lines was relatively consistent. The chalkiness rate is expressed by the percentage of chalky rice grains among 100 randomly selected brown rice grains.
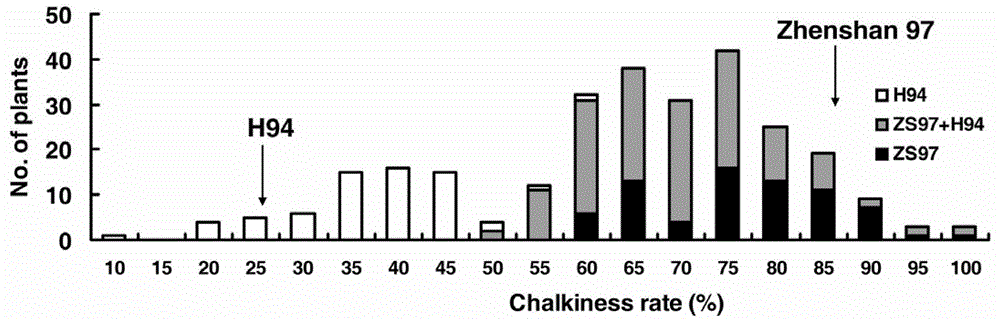
[0041] from BC 3 f 1 single plant derived BC 3 f 2 288 individuals were randomly selected from the population to form a random population. The grain chalkiness rate of each individual plant in Zhenshan 97B, H94 and random populations was investigated, and the genotypes of each plant were determined by molecular markers RM593 and RM574 at both ends (see Table 4 for the sequence). There were significant differences in the white rate between the two parents. In random populations, the grain chalkiness rate showed a ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3: Transgene complementation test of Chalk5
[0050] 1 Chalk5 transgenic technology route:
[0051] Real-Time PCR expression profiling analysis found that the Chalk5 gene was specifically expressed in the endosperm tissue during the whole growth period, and the expression level of the high chalky variety (Zhenshan 97B) was higher than that of the low chalky variety (H94) in the endosperm tissue 5 days after fertilization high( Figure 5 ). Therefore, according to the predicted full-length ORF2 sequence of the candidate gene, a pair of PCR-specific primers Chalk5 ORF2 (Table 4) with restriction endonuclease KpnI and PstI adapters were designed to amplify the ORF2 fragment of Zhenshan 97B and ligated to the TA clone Promega On the T vector, select the correct clone containing the candidate gene without mutation, use the restriction endonuclease KpnI and PstI to digest the positive clone, carry out subcloning, and then connect it to the binary overexpression v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com