An epstein-barr-virus vaccine
A Barr virus and vaccine technology, applied in the direction of viruses, viral peptides, antiviral agents, etc., can solve the problems that it cannot be applied to humans, cannot trigger EBV-specific immune cells, and CD4+ cells cannot be regarded as vaccines, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
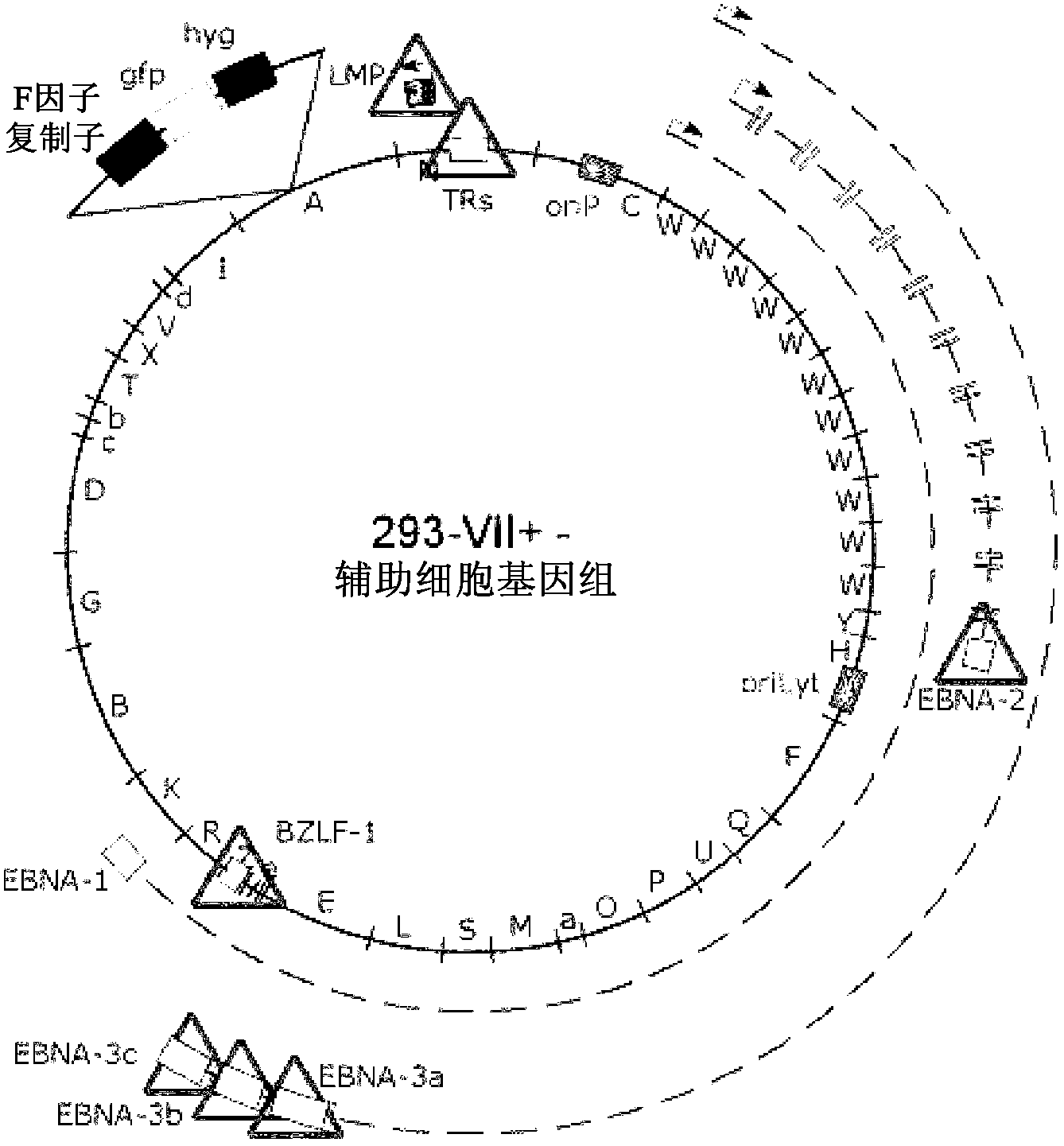
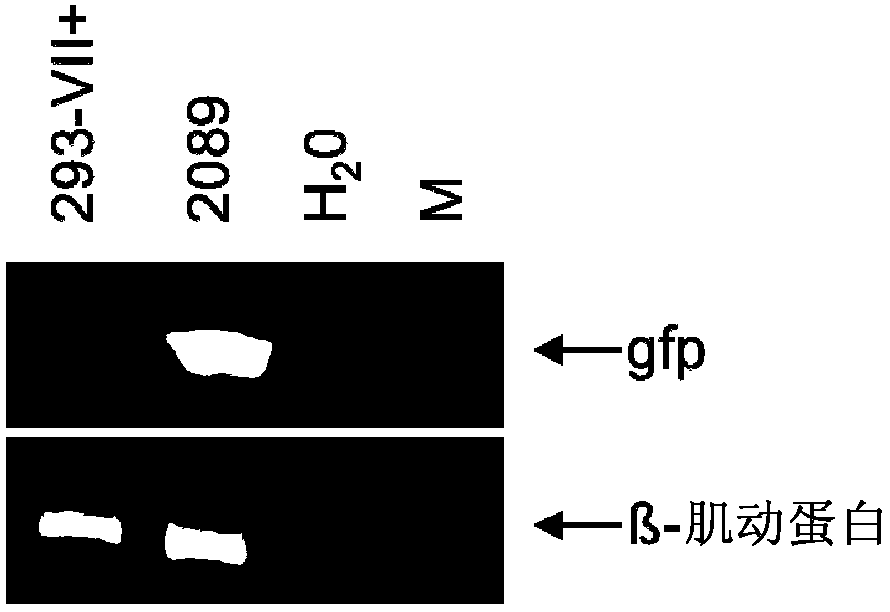
[0100] Example 1 : 293-VII+ cells release VLPs when induced to lack viral DNA but contain various EBV proteins
[0101] The inventors have recently described the construction of two helper cell lines for the encapsulation of EBV-derived vectors into recombinant virus particles (Delecluse et al., 1999; Hettich et al., 2006). These cell lines contain an EBV helper genome that lacks terminal repeats (TRs), but instead contains the gfp gene for the packaging signal of this virus. Thus, these helper cell genomes cannot be packaged into viral particles, but instead deliver in trans all the proteins required for packaging a suitable viral vector as well as assembly and release of recombinant and infectious EBV particles. The first generation cell line, TR-2, contains an additional complete EBV genome that retains the full transformation capacity of primary human B-cells (Delecluse et al., 1999). To deal with the rare irrational packaging of helper cell genomes and the unintended r...
Embodiment 2
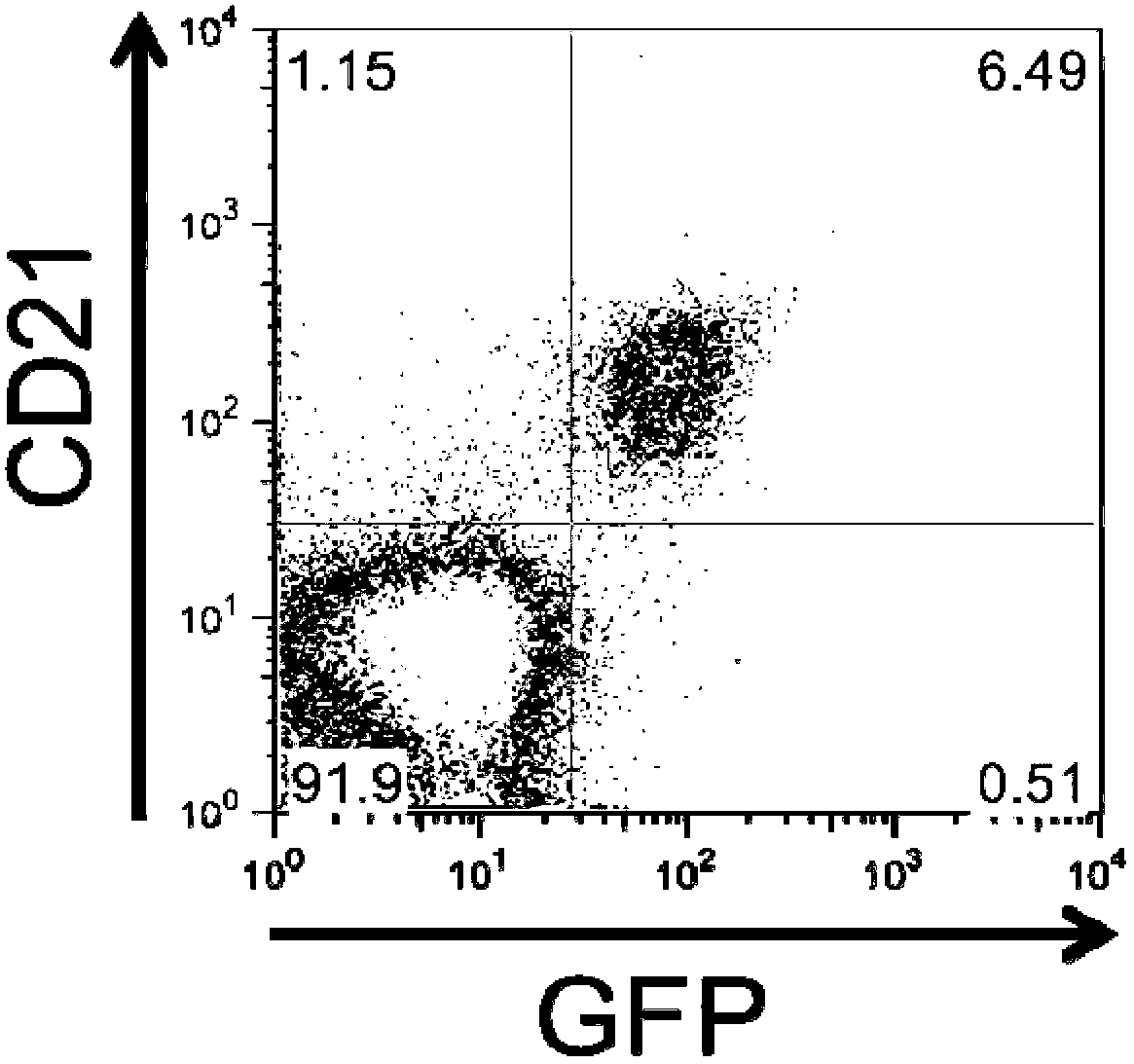
[0104] Example 2: 293-VII+-VLP has EBV-like B-cell tropism
[0105] One protein found to be incorporated into the VLP is gp350 / 220, the major viral envelope protein that mediates virion binding to human B-lymphocytes by interacting with CD21. Therefore, the inventors wanted to elucidate whether VLPs have a B-cell tropism similar to wild-type EBV. To do this, they incubated freshly isolated PBMCs overnight with concentrated VII+ VLPs and analyzed VLP binding by FACS. For these experiments, they took advantage of the fact that enhanced GFP expressed from the genome of VII+ helper cells was also incorporated into VLPs. as in Figure 3a As shown in , binding of VLPs was restricted to CD21+ cells, most likely B-cells, as judged by the fact that only CD21+ cells became GFP-positive. In contrast, VLP binding to CD21-negative cells could not be observed. To study the interaction of VLPs with B-cells in more detail, the inventors performed confocal microscopy on VLP-cultured PBMC...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Example 3 : VII+-VLPs induce neutralizing EBV-specific antibodies in naive hosts
[0108] The results of the previous sections demonstrate the potential of VLPs to stimulate EBV-specific awakening of immune responses. In the next series of experiments, the inventors therefore evaluated whether VLPs were also able to induce EBV-specific immune responses in naive hosts in vivo, which is of course a prerequisite for prophylactic vaccines. For this purpose, the inventors vaccinated BALB / C mice twice intraperitoneally with 10 μg VLP (n=4) over a period of 14 days and immunized control mice with the same amount of exosomes isolated from the 293 supernatant. Rats (n=2). Four weeks after the second immunization, sera were collected and analyzed for the presence of EBV-specific antibodies, and splenocytes were tested for EBV specificity. To this end, the inventors coated a collection of 96-well plates with serial lysates of HEK293 cells that had been transiently transfected ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com