Super resolution moving grating confocal imaging device and confocal imaging method
A technology of moving gratings and imaging devices, which is applied in the direction of using optical devices, measuring devices, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as super-resolution moving grating imaging methods that have not yet appeared
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
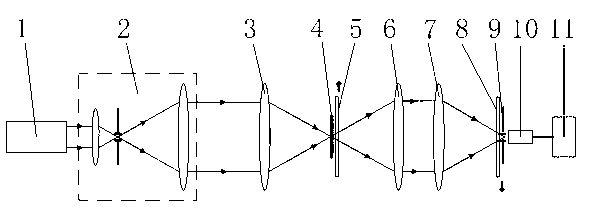
[0024] Both the modulation moving grating 5 and the demodulation moving grating 8 are one-dimensional sinusoidal gratings with diffraction orders of 0 and ±1, and they move at a constant speed at the same and opposite speeds at the conjugate positions of the object space and the image space. The converging angles of the objective lens 3 and the first collecting objective lens 6 are equal, that is, the numerical apertures in the air are equal, and NA=0.1 is selected in this embodiment.
[0025] In this example, in order to prevent the CTFs after the frequency band extension from overlapping, the spatial frequency of the grating used must satisfy
[0026] v 0 ≥4sin(α 0 ) / λ
[0027] Among them, v 0 is the spatial frequency of the grating, that is, the reciprocal of the spatial period of the grating; α 0 is the converging angle between the focusing objective lens 3 and the first collecting objective lens 6; λ is the wavelength of the illuminating light;
[0028] After filteri...
specific Embodiment 2
[0034] The difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment 1 is that both the modulation moving grating 5 and the demodulation moving grating 8 are two-stage Dammann gratings with diffraction orders of 0, ±1 and ±2.
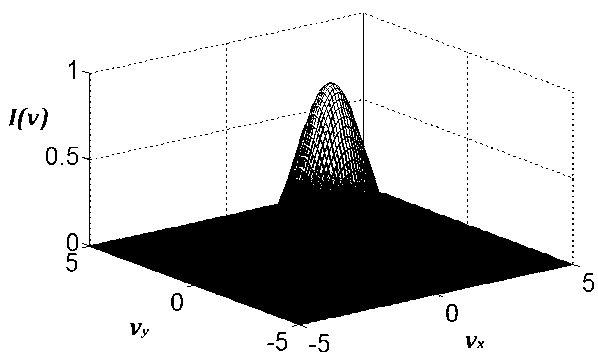
[0035] After filtering or integrating the signal processing, the normalized light intensity is:
[0036] I ( v , v x , v y ) = | [ 1 + 2 cos ( 4 v x ) + 2 cos ( 8 v x ) ...
specific Embodiment 3
[0041] The difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment 1 and the specific embodiment 2 is that the modulation moving grating 5 and the demodulation moving grating 8 adopted are two-dimensional sinusoidal gratings whose diffraction orders on the x-axis and y-axis are 0 and ±1, The two-dimensional sinusoidal grating has the same spatial frequency in the direction of the x-axis and the direction of the y-axis, and moves at a constant speed at the same and opposite speeds at the conjugate positions of the object space and the image space, and the speed in the y-axis direction is the x-axis direction 3 times the above.
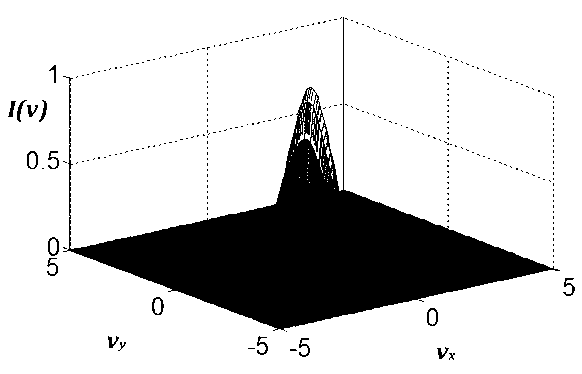
[0042] After filtering or integrating the signal processing, the normalized light intensity is:
[0043] I ( v , v x , v y ) = | ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com