Thermal treatment process for improving deformed magnesium alloy strength
A technology for deforming magnesium alloys and magnesium alloys, which is applied in the field of heat treatment of magnesium alloy materials, can solve the problems of improved mechanical properties and weak strengthening effect of deformed magnesium alloys, and achieves the effects of improving production efficiency, wide application and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A heat treatment process for improving the strength of a deformed magnesium alloy, the heat treatment process comprising the following steps:
[0029] 1) Magnesium alloy raw material: ordinary AZ61 deformed magnesium alloy ingot is used as raw material, the alloy composition (weight percentage) is: 6.64% Al, 1.01% Zn, 0.25% Mn, impurity elements are less than 0.01%, and the rest is Mg.
[0030] 2) Homogenization treatment of magnesium alloy ingots: perform homogenization treatment of magnesium alloy ingots in a heat treatment furnace at a temperature of 400°C for 12 hours.
[0031] 3) Extrusion plastic deformation: Extrude the homogenized magnesium alloy ingot on an extruder at an extrusion temperature of 390°C and an extrusion ratio of 11.7.
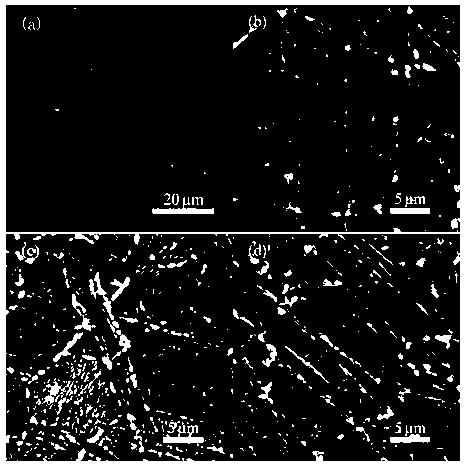
[0032] image 3 (a) is the scanning structure photo of the AZ61 magnesium alloy extruded sheet. It can be seen from the figure that in the AZ61 magnesium alloy extruded sheet, there is very little second phase, which has...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The magnesium alloy raw material and homogenization treatment, extrusion plastic deformation, cold rolling plastic deformation, and artificial aging heat treatment temperature are the same as those in Example 1, except that the AZ61 magnesium alloy aging holding time is 60 hours.
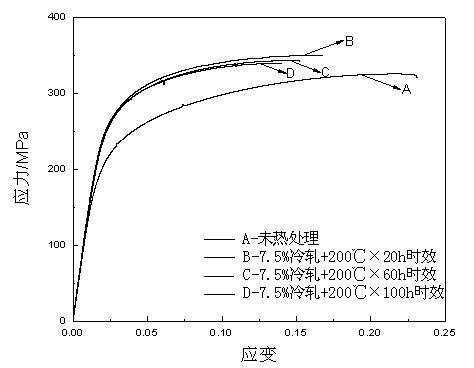
[0038] image 3 (c) is the scanning structure photo of AZ61 magnesium alloy after extrusion, 7.5% cold rolling, aging at 200°C for 60h, and air cooling. It can be seen from this that the relative image 3 (b) The number of second phase precipitation is more, and the second phase precipitation is more obvious at grain boundaries and twins, and the volume is larger. The AZ61 magnesium alloy obtained by this process has a yield strength of 231MPa, a tensile strength of 345MPa and an elongation of 12.7% at room temperature.
Embodiment 3
[0040] The magnesium alloy raw material and homogenization treatment, extrusion plastic deformation, cold rolling plastic deformation, and artificial aging heat treatment temperature are the same as those in Example 1, except that the AZ61 magnesium alloy aging holding time is 100 hours.
[0041] image 3 (d) is the scanning structure photo of AZ61 magnesium alloy after extrusion, 7.5% cold rolling, aging at 200°C for 100h, and air cooling. It can be seen from the figure that the second phase is obviously coarsened at the grain boundaries and twins. The AZ61 magnesium alloy obtained by this process has a yield strength of 219MPa, a tensile strength of 343MPa and an elongation of 11.6% at room temperature.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com