Quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (LDPC) code construction method capable of eliminating decoder access conflict
A technology of LDPC codes and construction methods, which is applied in the construction field of quasi-cyclic LDPC codes, can solve problems such as access conflicts, reduce decoder parallelism, and reduce throughput, and achieve the goals of reducing waste, efficient decoding, and reducing redundant delays Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
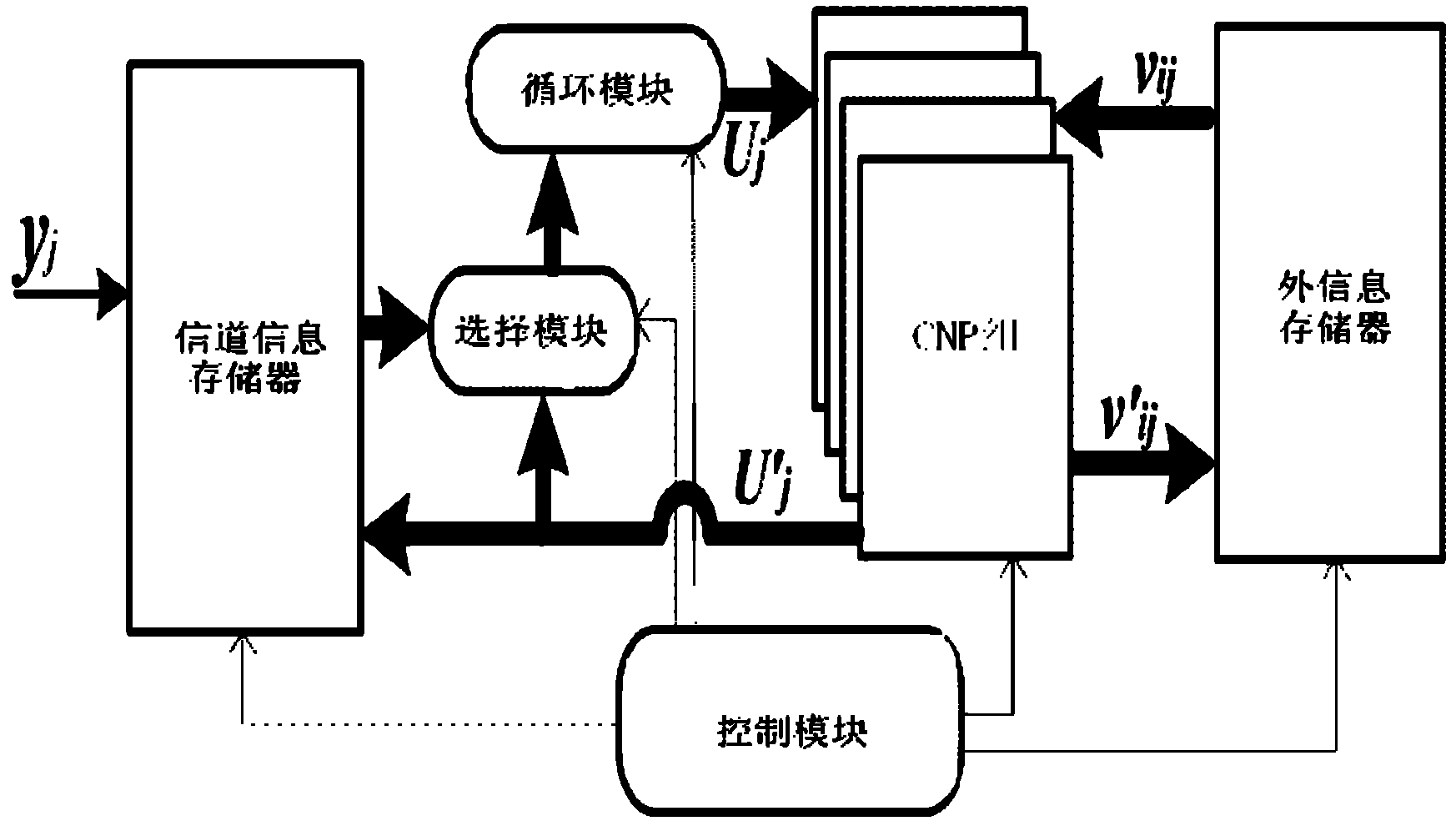
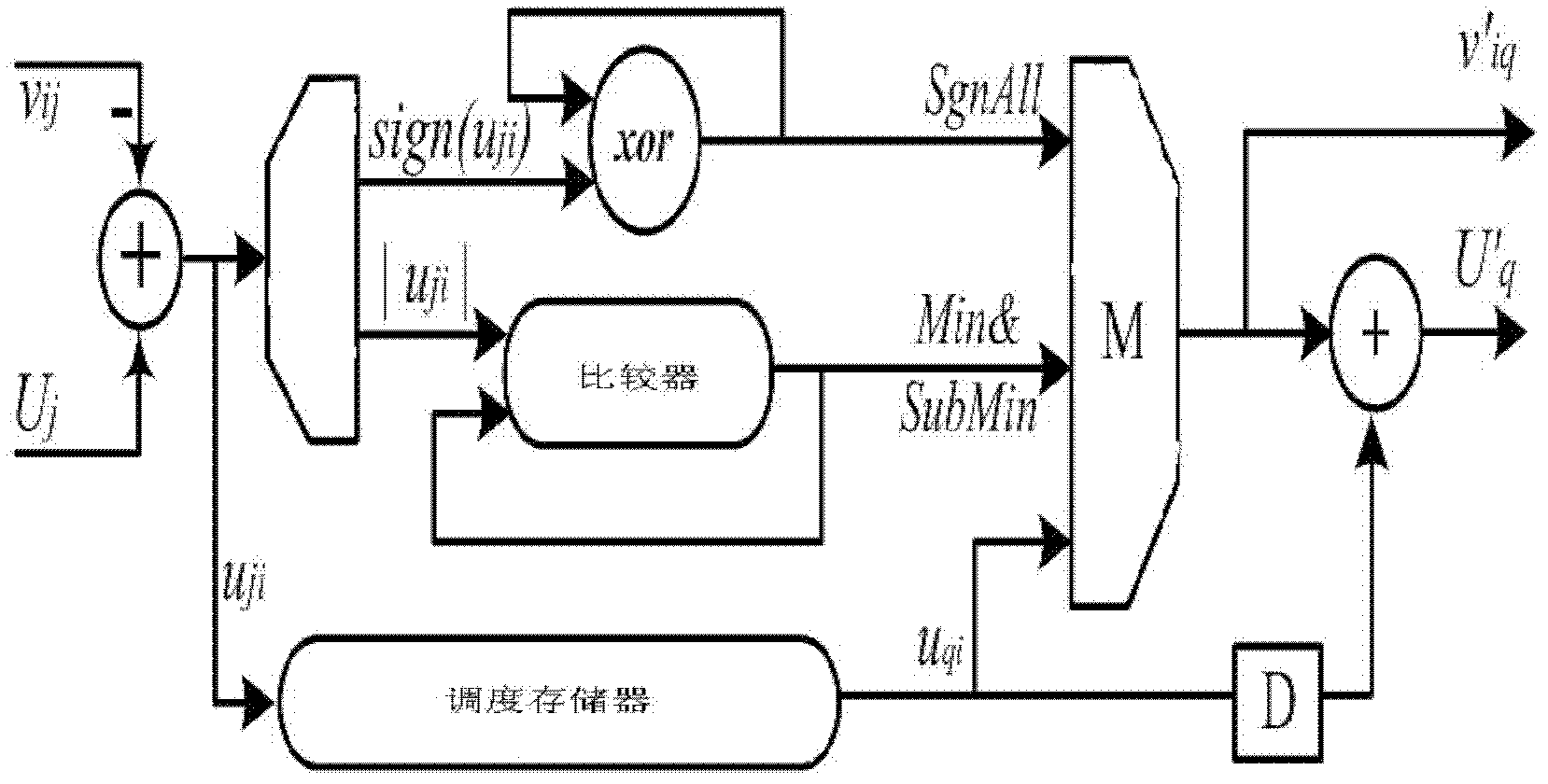
[0075] According to the previous analysis, in order to avoid U j Access conflict, the ADeg constraint that the base matrix of the quasi-cyclic LDPC code needs to satisfy is as follows: in any row of the base matrix (Hb), there must be at least ADeg non-zero elements in different columns from all non-zero elements in the previous row, and the degree of avoidance The typical value of ADeg is 5 or 8. This section presents the corresponding construction algorithm.
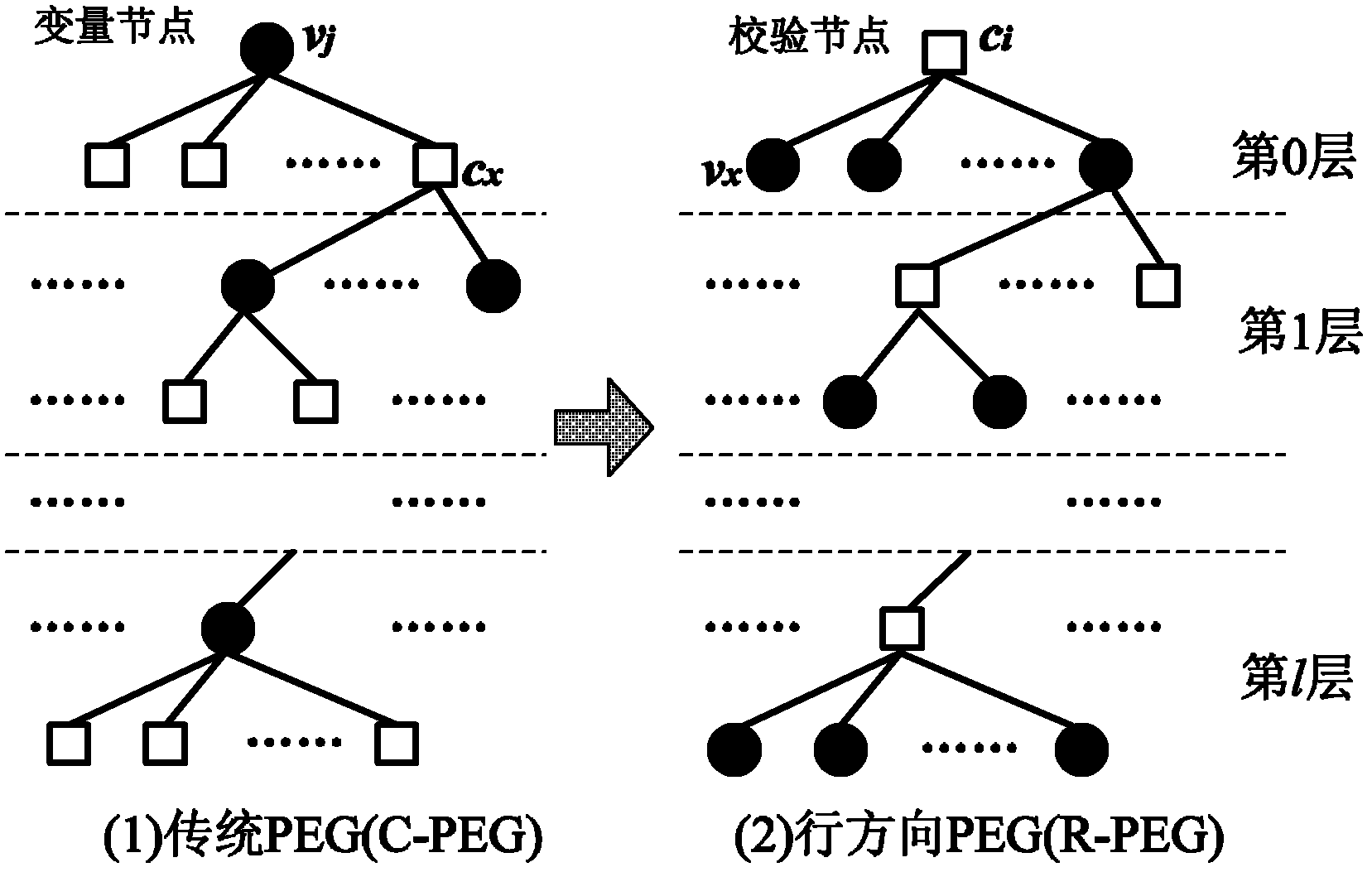
[0076] Block Progressive Edge Growth (Block-PEG, BPEG) construction algorithm is a generalized PEG algorithm, which can construct QC-LDPC codes. Combining the R-PEG algorithm with the BPEG algorithm, and adding ADeg constraints in the construction algorithm, the process of constructing the Row Direction Conflict Avoidance Block PEG algorithm (RCAB-PEG) can be obtained. For the sake of simplicity, check nodes and rows are not distinguished in the algorithm flow expression, and variable nodes and columns are not distin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com