Method of assisting to identify irradiated lipid-containing foods
A technology for assisting identification and food, applied in material excitation analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of a large number of organic solvents, expensive instruments, long extraction and purification time, etc., and achieve the effect of satisfying the detection range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0063] Preparation of epsilon subunit polyclonal antibody:
[0064] Using the purified ε subunit as the immune antigen, 2 rabbits of 2 kg were immunized. Quantitatively take out according to the immunization dose (0.5mg antigen per rabbit), add an equal volume of Freund’s (in)complete adjuvant, pump back and forth with a syringe, and make a water-in-oil (W / O) emulsion, back , Multi-point injection under the skin of the neck. The established immunization procedure was as follows: for the first immunization, the antigen was emulsified with complete Freund's adjuvant, 0.5ml / mouse, and the leg muscle was injected; for the second immunization two weeks later, the antigen was emulsified with incomplete Freund's adjuvant. The third immunization was carried out at an interval of 10 days. 10 days after the third immunization, the ear vein blood was collected to separate the serum, and the serum antibody titer was detected by indirect ELISA method.
[0065] Preparation of 2-oxo-cyclo...
Embodiment 1
[0076] Embodiment 1, the selection of extraction solvent
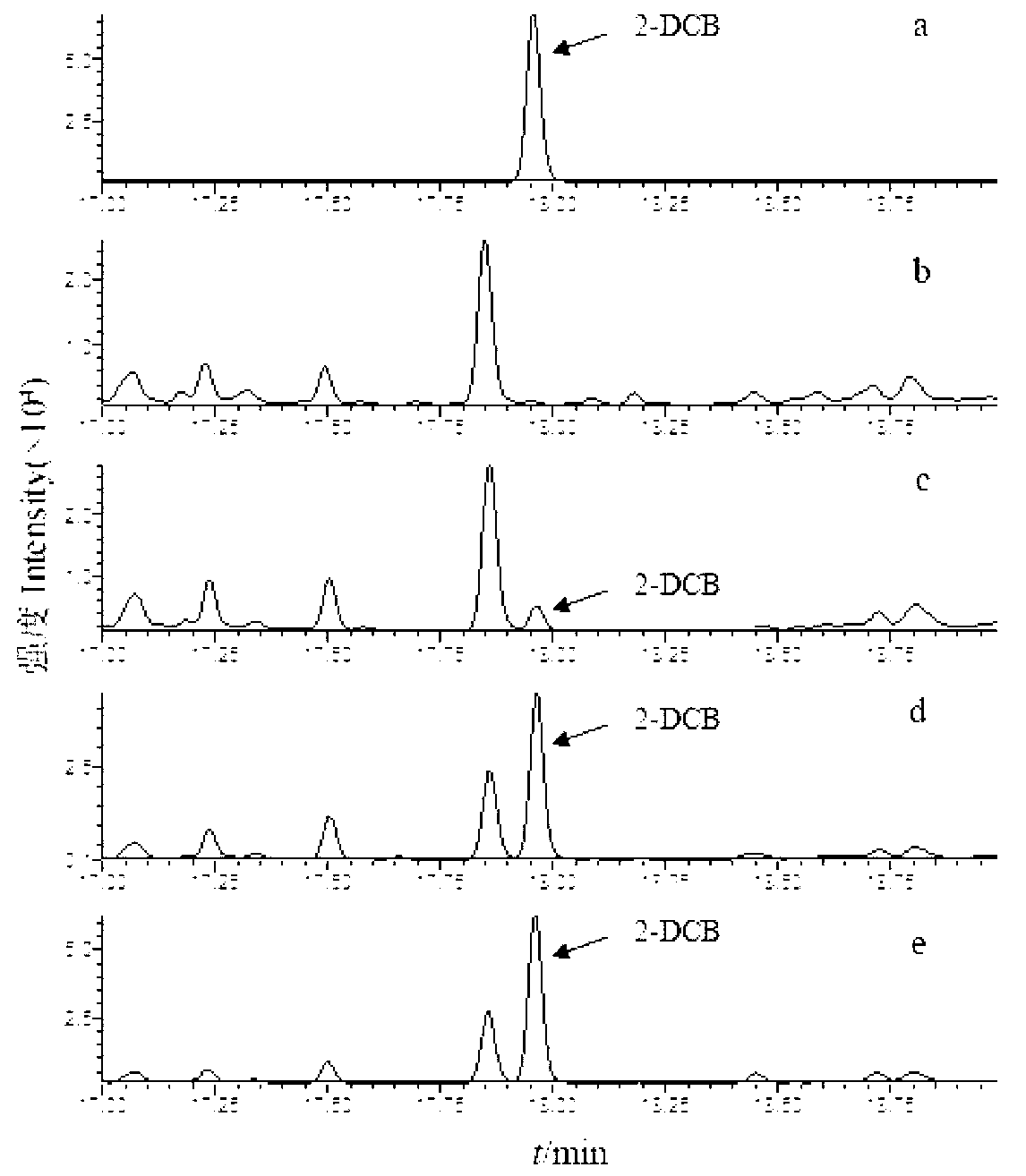
[0077] Most of the reported sample pretreatment methods use the traditional Soxhlet extraction method. Using n-hexane as the extractant to extract the fat in fat-containing irradiated food, and after purification by homemade Florisil column, GC-MS analysis and determination were carried out. This method takes a long time to extract and purify and consumes a large amount of organic solvent; The critical fluid extraction (SFE) method is fast and convenient for extracting 2-ACBs, and the extraction time is 30 to 60 minutes, but the SFE equipment is expensive and not widely used; the accelerated extraction method (ASE) method uses an accelerated solvent extractor, and ethyl acetate is used as The extractant extracts fat under high temperature and high pressure. The extract is added to acetonitrile and placed at -20°C to filter the fat, and then purified with a 1g silica gel column. The content of 2-ACBs is analyzed by GC-M...
Embodiment 2
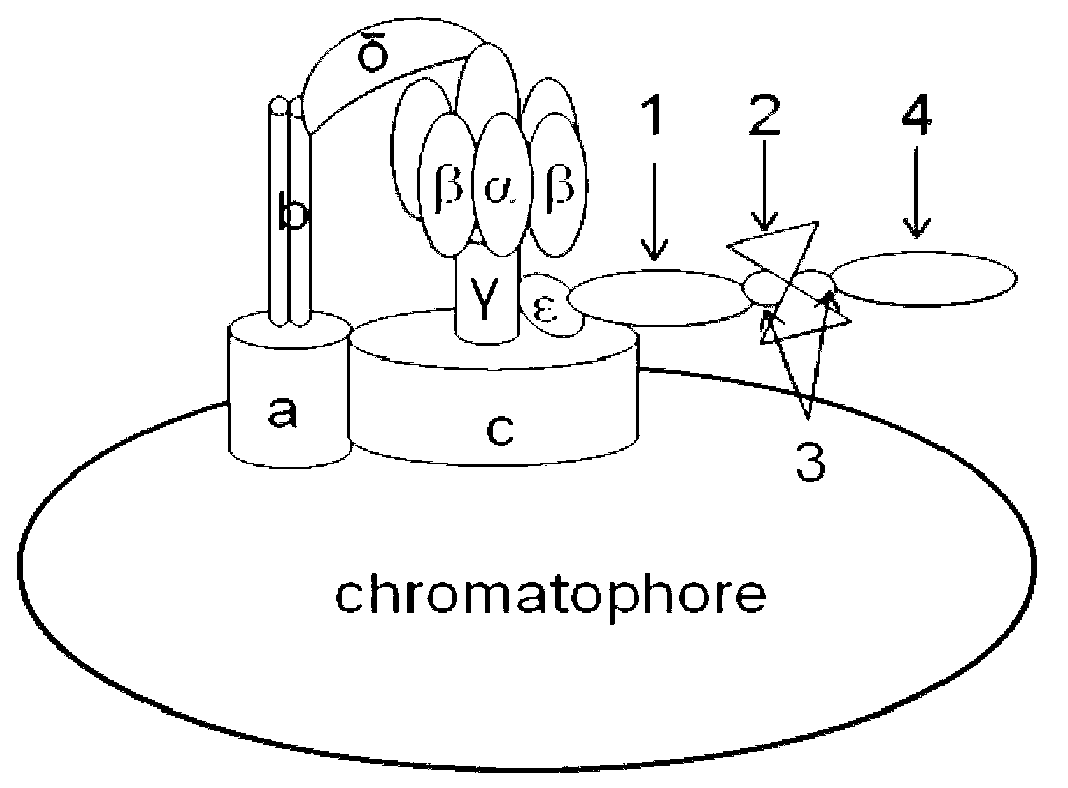
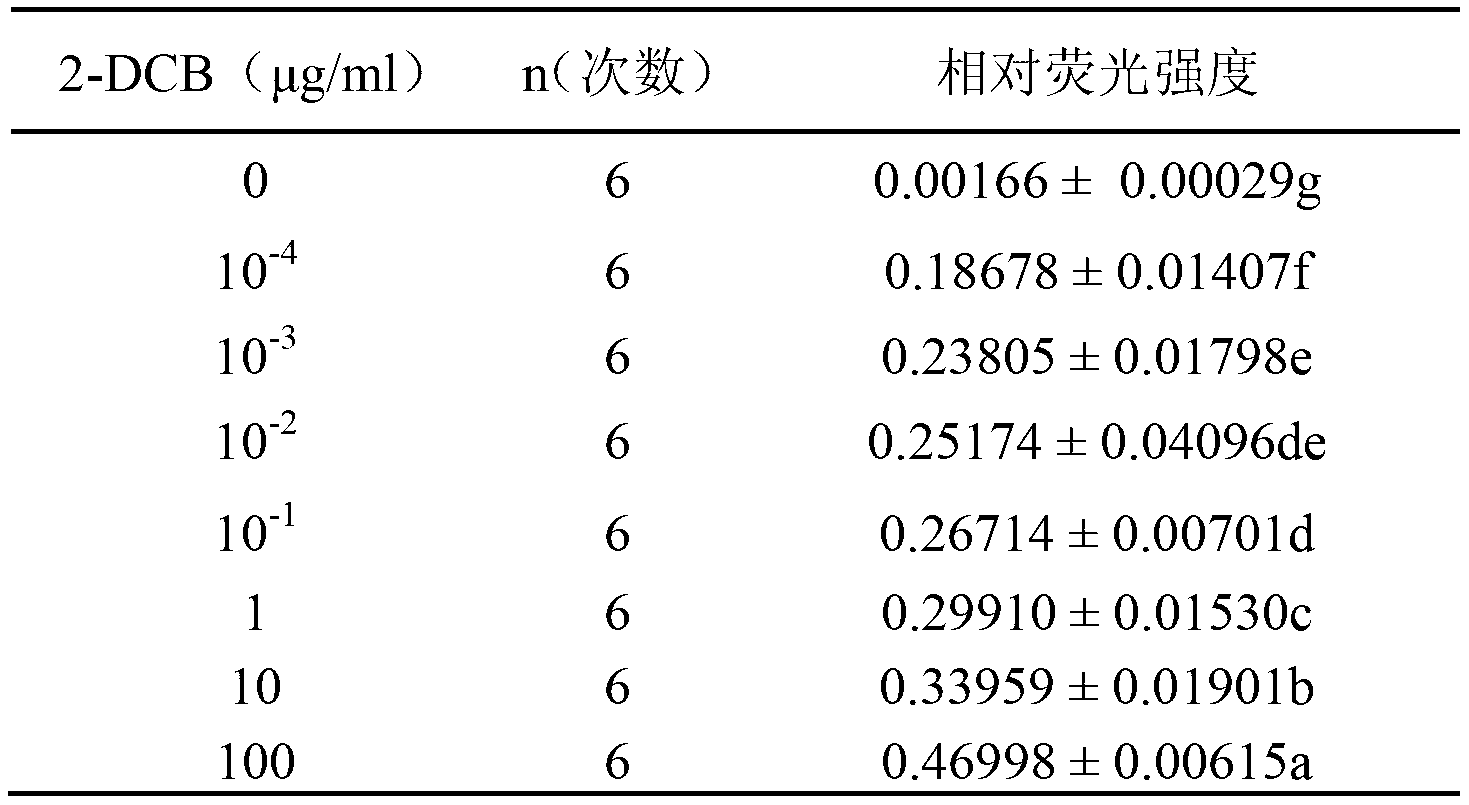
[0090] Embodiment 2, construction of molecular motor biosensor
[0091] 15 μL of photosynthetic chromophores (chromatophores with F 0 f 1 -ATP synthase) (50mg / mL) mixed with 8μL (0.5mg / ml) biotinylated ε subunit polyclonal antibody, diluted to 1mL with PBS buffer, then incubated at 37°C for 60min, the excess The epsilon subunit polyclonal antibody was removed by centrifugation at 40,000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C; the precipitate was redissolved with 500 μL of PBS buffer, then 7.5 μL (0.1 mg / mL) of streptavidin was added, and diluted to 1 mL with PBS buffer, Incubate at 37°C for 10 minutes, remove excess streptavidin by centrifuging at 40,000 rpm for 20 minutes at 4°C; reconstitute the pellet with 500 μL of PBS buffer, and then add 28 μl (0.036 mg / ml) of biotinylated 2- DCB polyclonal antibody, and diluted to 1mL with PBS buffer, incubated at 37°C for 10min, excess 2-DCB polyclonal antibody was removed by centrifugation at 40,000 rpm at 4°C for 20min; then the precipitate was rec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com