Initial alignment detecting method of rotor position in permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and rotor position technology, applied in the permanent magnet synchronous motor servo drive control, permanent magnet synchronous motor field, can solve the problem that the motor is difficult to stand still, not suitable, etc., to achieve simple and fast detection process, improve Effect of improving reliability and starting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] In order to understand the technical content of the present invention more clearly, the following examples are given in detail.
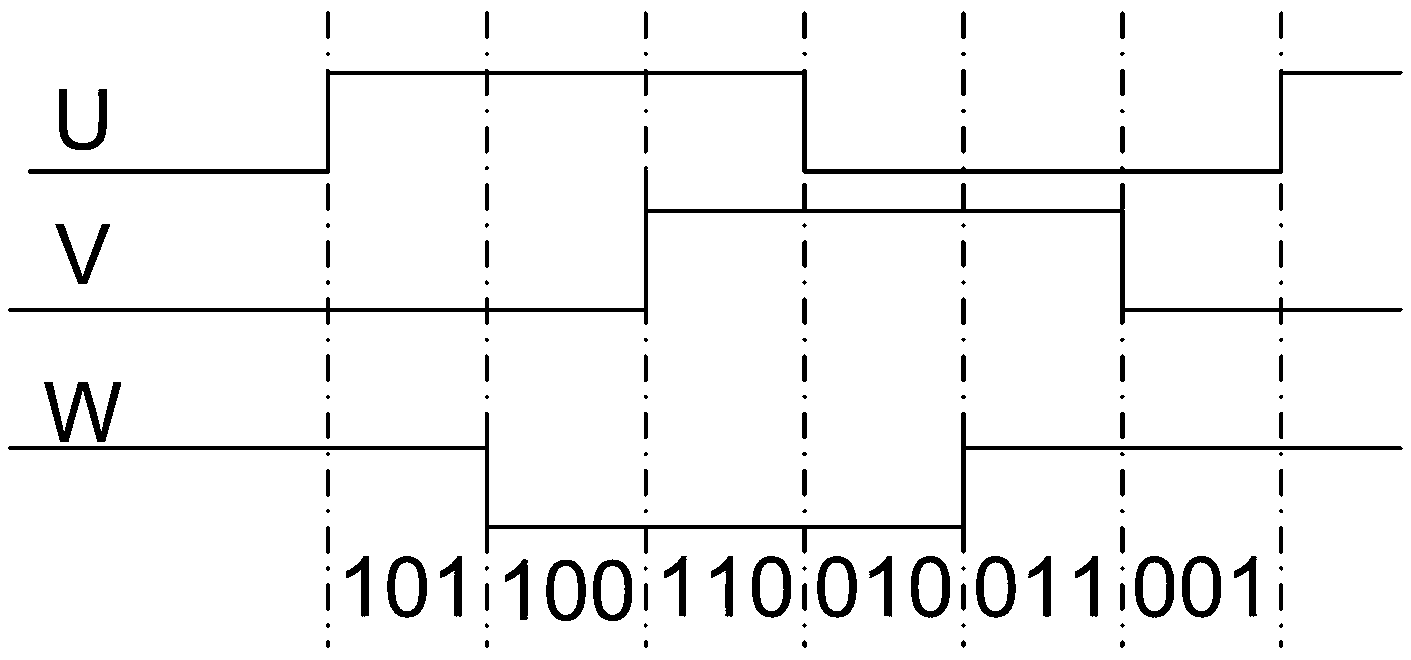
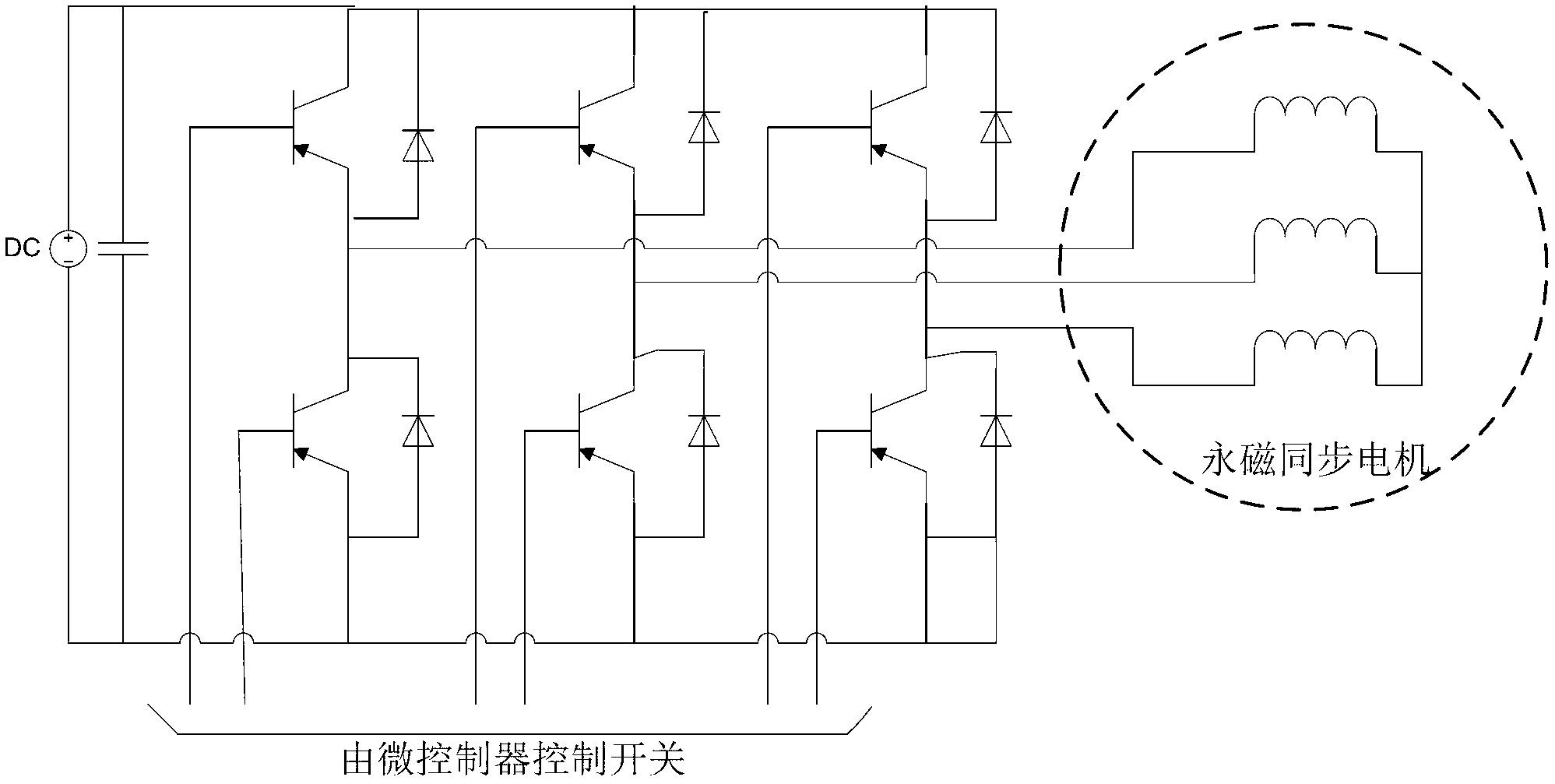
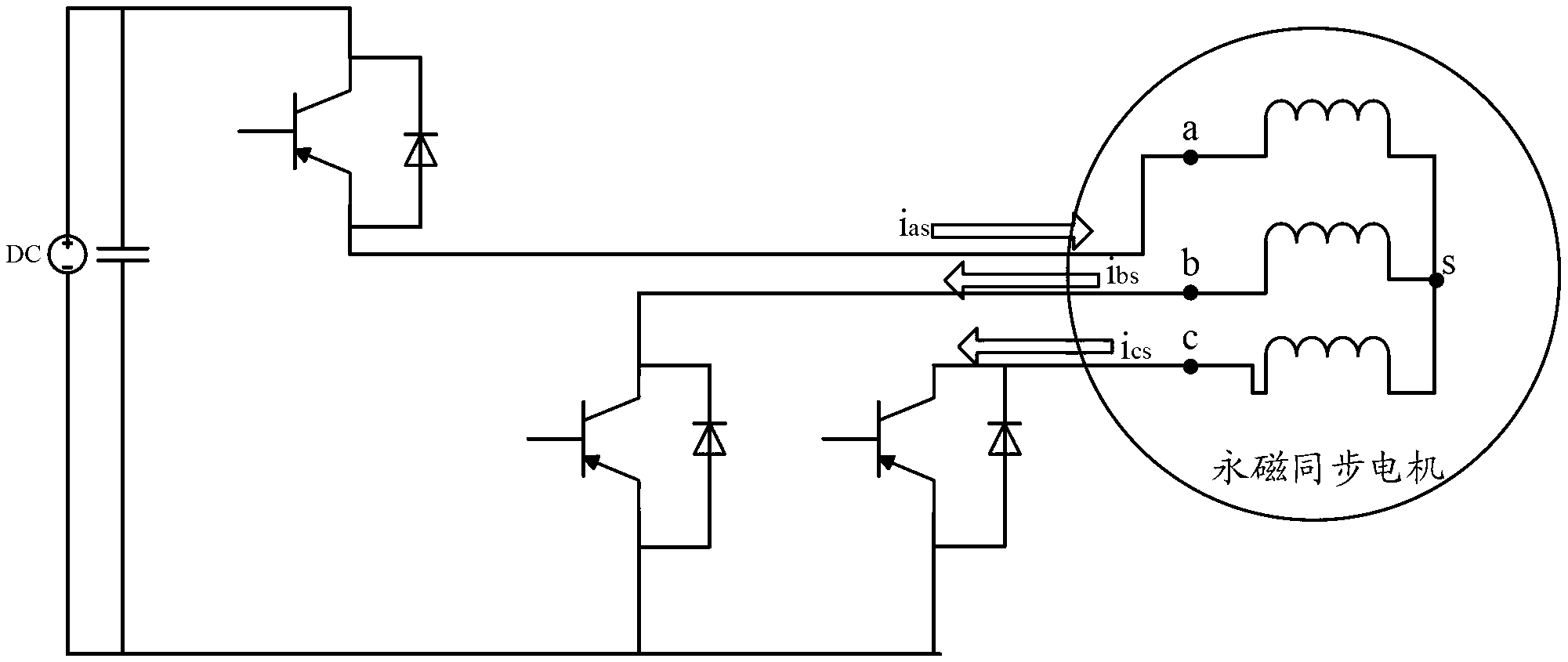
[0043] see Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown, the rotor position initial positioning detection method in the permanent magnet synchronous motor includes the following steps:
[0044] (1) The angle interval of the spatial position of the motor rotor is deduced through the three pulse signals U, V, W with a phase difference of 120° in the encoder on the motor, and the corresponding initial angle is obtained; the inferred motor rotor The angle interval of the spatial position includes the following steps:
[0045] (11) According to the state combination of pulse signals U, V, and W when the motor is initially powered on, the 360° space of the motor rotor angle value is equally divided into the following 6 angle intervals:
[0046] 0°~60°;
[0047] ●60°~120°;
[0048] ●120°~180°;
[0049] ●180°~240°;
[0050] ●240°~300°;
[0051] ●300°~360°. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com