Heat conducting composite material and heat conducting composite sheet prepared by applying same
A heat-conducting composite material and sheet technology, which is applied in the field of heat-conducting materials, can solve problems such as cumbersome procedures, inability to use, and poor thermal conductivity, and achieve the effects of simple preparation process, increased heat dissipation speed, and reduced interface thermal resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
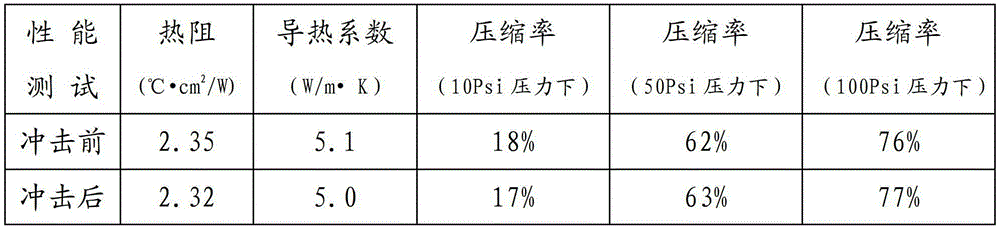
[0019] Weigh 10 kg of simethicone oil with a viscosity of 8000 mPas, 60 kg of spherical alumina powder with a particle size of 65 μm, 10 kg of spherical aluminum powder with a particle size of 0.35 μm, 50 kg of spherical aluminum powder with a particle size of 13 μm, and 0.8 kg of diluent. For example, simethicone oil at 50mPas. Put 10kg of simethicone oil and 0.8kg of diluent weighed into the kneader in sequence for mixing, then put 120kg of heat-conducting powder into the kneader in 4 times and mix for 30-90 minutes, preferably 60 minutes in this example. During mixing, temperature has little effect on the results. After being uniformly mixed by a kneader, the heat-conducting composite material of the present invention is obtained.
[0020] The finished thermally conductive composite material is taken out from the kneader, and the thermally conductive composite material is vacuumized to remove possible air bubbles in the thermally conductive composite material. Finally, th...
Embodiment 2
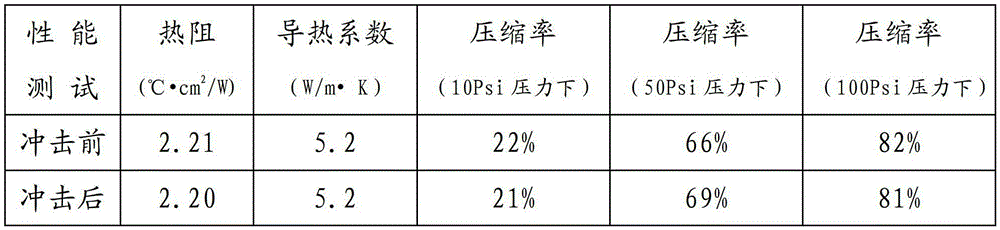
[0028] Weigh 10kg of vinyl silicone oil with a viscosity of 100mPas, 70kg of spherical alumina powder with a particle size of 60μm, 70kg of spherical alumina powder with a particle size of 4μm, 20kg of block aluminum nitride powder with a particle size of 3μm, 0.5 kg thickener, for example with a specific surface area of 280m 2 / g of fumed silica. Put the weighed 10kg vinyl silicone oil and 0.5kg white carbon black into the kneader in turn for mixing, then put 160kg of heat-conducting powder into the kneader successively in 3 times, and mix for 30min-90min, preferably 90min in this example. After being uniformly mixed by a kneader, the heat-conducting composite material of the present invention is obtained. During mixing, temperature has little effect on the results.
[0029] The thermally conductive composite material was taken out from the kneader, and then the thermally conductive composite material was calendered into a sheet covered with a protective film on both uppe...
Embodiment 3
[0035]Weigh 10kg of long-chain alkyl methyl silicone oil with a viscosity of 980mPas, 80kg of massive alumina powder with a particle size of 20μm, 30kg of flake graphite powder with a particle size of 5μm, and 20kg of flaky nitride powder with a particle size of 1μm. Boron powder, 0.8kg silane coupling agent A171. Put the weighed 10kg of long-chain alkyl methyl silicone oil and 0.8kg of silane coupling agent into the kneader for mixing, and then put 130kg of heat-conducting powder into the kneader in 5 times and mix for 30min to 90min. , preferably 80min. After being uniformly mixed by a kneader, the heat-conducting composite material of the present invention is obtained. During mixing, temperature has little effect on the results.
[0036] The finished thermally conductive composite material is taken out from the kneader, and the thermally conductive composite material is vacuumized to remove possible air bubbles in the thermally conductive composite material. Finally, the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com