Near-infrared spectrum technology based method for rapidly identifying wheat grains with FHB (Fusarium Head Blight)
A technology of near-infrared spectroscopy and scab, which is applied in the direction of color/spectral characteristic measurement, material analysis through optical means, and measuring devices, etc., to improve the quality of flour, ensure the safety of humans and animals, and reduce the effect of impurities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] a) Sample pretreatment: collect 25 scab-affected wheat, and remove impurities such as stones, soil clods, and grass seeds in the sample. For each wheat sample, one portion of common grains and one portion of scab grains were picked out, 100 g each, and stored in mesh bags. Naturally dry until the moisture content of the wheat grains is stable at 10% to 13%. Then draw 2 / 3 of the samples as the calibration set samples, and 1 / 3 as the validation set samples.
[0033] b) Spectral data collection: scan range 950nm ~ 1650nm, room temperature 0°C ~ 42°C, repeat scanning of the sample 4 times, and calculate the average spectrum. For each sample, one spectrum of ordinary wheat grains and one spectrum of head blight wheat grains were collected. The spectrum of ordinary wheat grains was represented by adding 0 to the sample code, and the spectrum of grains of scab diseased wheat grains was represented by adding 1 to the sample code.
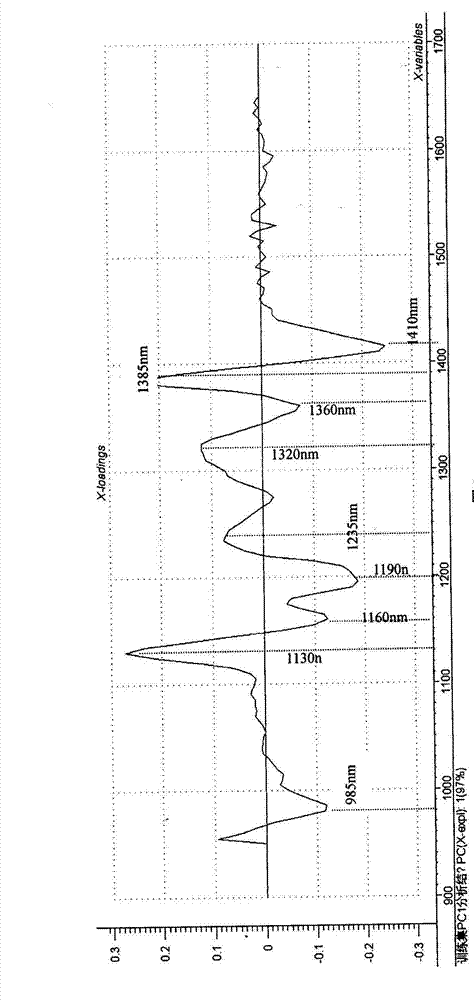
[0034] c) Spectral preprocessing: Unscramble...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Collect 25 scab-affected wheat, and remove impurities such as stones, soil clods, and grass seeds in the samples. The scanning range is 950nm to 1650nm, the room temperature is 0°C to 42°C, the sample is scanned 4 times repeatedly, and the average spectrum is calculated. For each wheat sample, one portion of common grains and one portion of scab grains were picked out, 100 g each, and stored in mesh bags. Naturally dry until the moisture content of the wheat grains is stable at 10% to 13%. The near-infrared spectrometer scans and collects the spectrum. The spectrum of common wheat grains is represented by adding 0 to the sample code, and the spectrum of scab grains is represented by adding 1 to the sample code. Then draw 2 / 3 of the samples as the calibration set samples, and 1 / 3 as the validation set samples. Without any processing on the spectra, the original spectra were systematically clustered and analyzed using the centroid connection method provided by SPSS soft...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Collect 25 scab-affected wheat, and remove impurities such as stones, soil clods, and grass seeds in the samples. The scanning range is 950nm to 1650nm, the room temperature is 0°C to 42°C, the sample is scanned 4 times repeatedly, and the average spectrum is calculated. For each wheat sample, 10 common grains and 10 scab grains were selected. Naturally dry until the moisture content of the wheat grains is stable at 10% to 13%. The near-infrared spectrometer scans and collects the spectrum. The spectrum of ordinary wheat grains is represented by adding 0 to the lowercase letter of the sample code, and the spectrum of scab wheat grains is represented by adding 1 to the lowercase letter of the sample code. Then draw 2 / 3 of the samples as the calibration set samples, and 1 / 3 as the validation set samples. First, the software Unscrambler7.8 was used to preprocess the spectral data by Norris derivation spectrum, and then the WARD method provided by SPSS software was used t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com