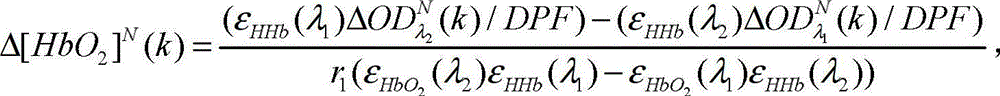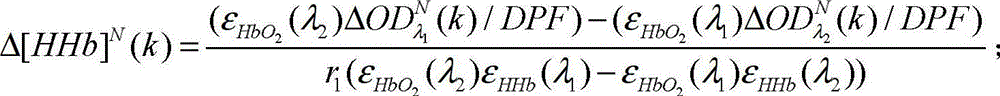Near-infrared brain-machine interface signal detection method integrating independent component analysis and least square method
A technology of independent component analysis and least squares method, applied in the field of hemoglobin concentration detection, which can solve the problems of inaccurate change in reduced hemoglobin concentration and accurate extraction of signals affecting brain function activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
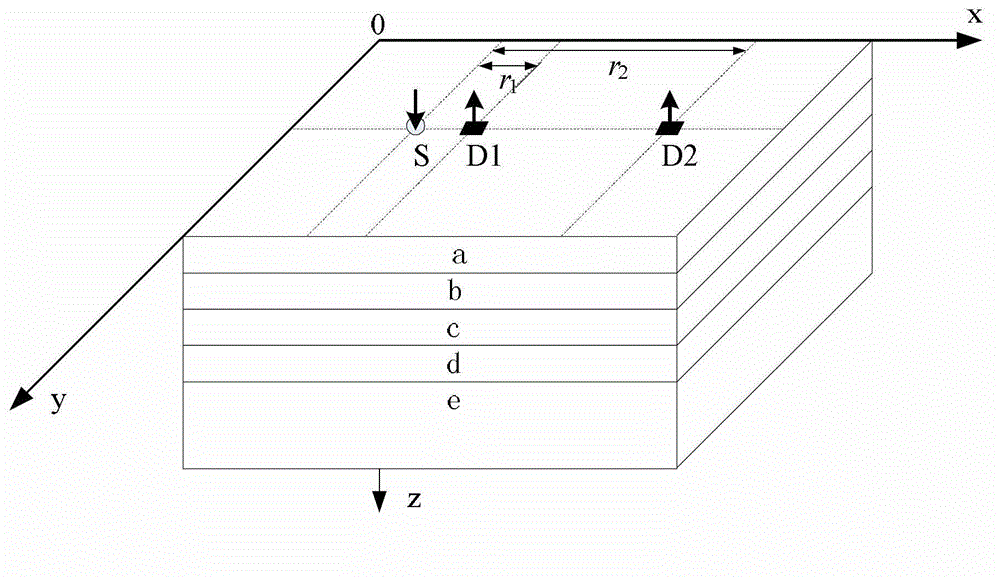
[0068] Specific implementation mode 1: the following combination figure 1 In this embodiment, the method for detecting signals of a near-infrared brain-computer interface based on independent component analysis and least squares method described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0069] Step 1: Use a near-infrared probe close to the scalp surface of the head to be tested, so that the near-infrared light emitted by the near-infrared probe is incident on the brain tissue to be tested. The near-infrared probe consists of a dual-wavelength light source S, a detector D1, and a detector D2 Structure, in which the linear distance between the dual-wavelength light source S and the detector D1 is r 1 , 5mm≤r 1 ≤15mm, the linear distance between the dual-wavelength light source S and the detector D2 is r 2 , 30mm≤r 2 ≤45mm; detector D1 is used to sense hemodynamic changes in the outer brain tissue, and detector D2 is used to sense hemodynamic changes in the cerebral cortex;...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0103] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment further explains the first embodiment. The two wavelengths emitted by the dual-wavelength light source S in this embodiment are respectively λ 1 =760nm, λ 2 = 850nm.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0104] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment further explains the first or second embodiment, the linear distance r between the dual-wavelength light source S and the detector D1 in this embodiment 1 10mm, the linear distance r between the dual-wavelength light source S and the detector D2 2 It is 40mm.
[0105] The distance between the two detectors set in this embodiment is about twice the detection depth of the near-infrared light. This setting enables the near-infrared light detected by the detector D2 to effectively penetrate the cerebral cortex, and the near-infrared light detected by the detector D1 is only Penetrate into the outer brain tissue of the head. Then the obtained optical density change is converted into a time series of changes in oxyhemoglobin concentration Δ[HbO 2 ] N (k), Δ[HbO 2 ] F (k) and the time series of changes in the concentration of reduced hemoglobin Δ[HHb] N (k), Δ[HHb] F (k). The time series Δ[HbO 2 ] N (k), Δ[HbO 2 ] F (k) or time series Δ[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com