Preparation method of tissue engineering scaffold material
A technology of tissue engineering scaffold and solution, which is applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., and can solve problems such as poor connectivity between pores, poor mechanical strength of scaffolds, difficulty in controlling the diameter and density of channels between pores, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] A kind of preparation method of tissue engineering scaffold material provided by the present invention comprises:
[0034] a) mixing the biocompatible polyester with a non-polar solvent to obtain a first solution;
[0035] b) adding a phase inversion solvent into the first mixed solution to obtain a second solution;
[0036] c) placing the second solution in a mold, removing the non-polar solvent and phase inversion solvent through a liquid-gas phase or liquid-solid phase inversion process, and drying the solute. Obtain tissue engineering scaffold materials.
[0037] In order to solve the problems of the prior art and make the tissue engineering scaffold material have high strength and controllable porosity and void size, the present invention uses a phase inversion method to prepare the first biocompatible polyester for preparing the tissue engineering scaffold material by dissolving solution, and then add a phase inversion solvent to the first solution to obtain a s...
Embodiment 1
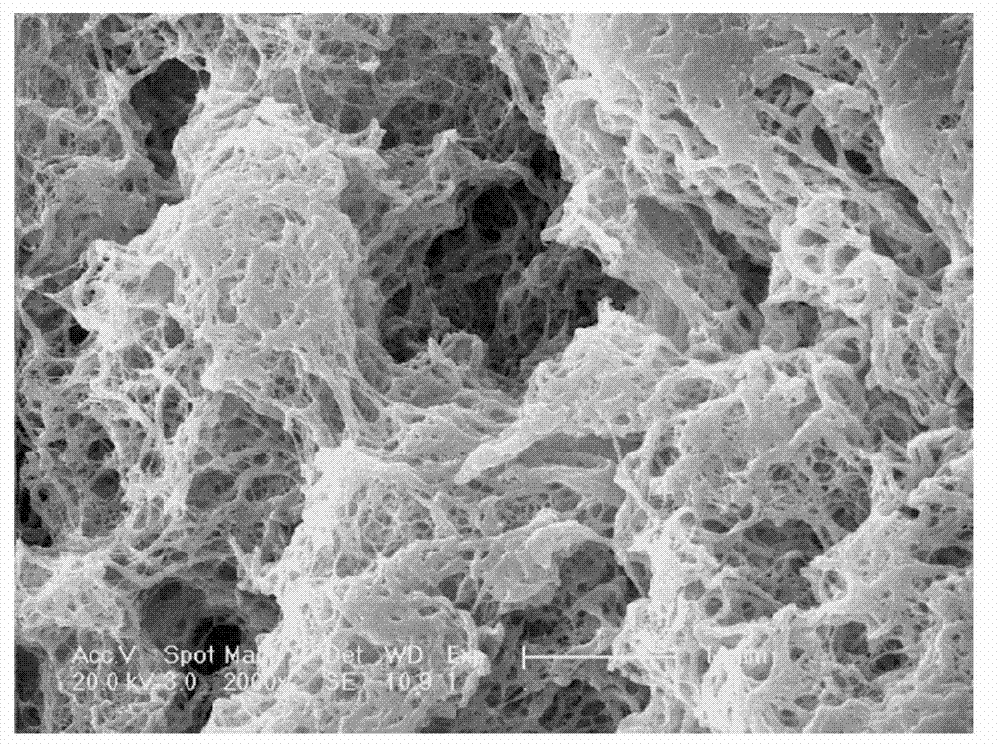
[0050] Dissolve polyester polymer polylactic acid (PLA) in chloroform; add DMF with a volume ratio of 3:2 to chloroform into the polymer solution; wait for the polymer solution to evaporate at room temperature for several days to form a relatively dry solid; The block was placed in three-distilled water with a negative pressure of 10 MP and washed several times until there was no solvent or porogen in the aqueous solution after washing; it was dried in vacuum, and the morphology of the scaffold was detected by field emission scanning electron microscopy (ESEM). Such as figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
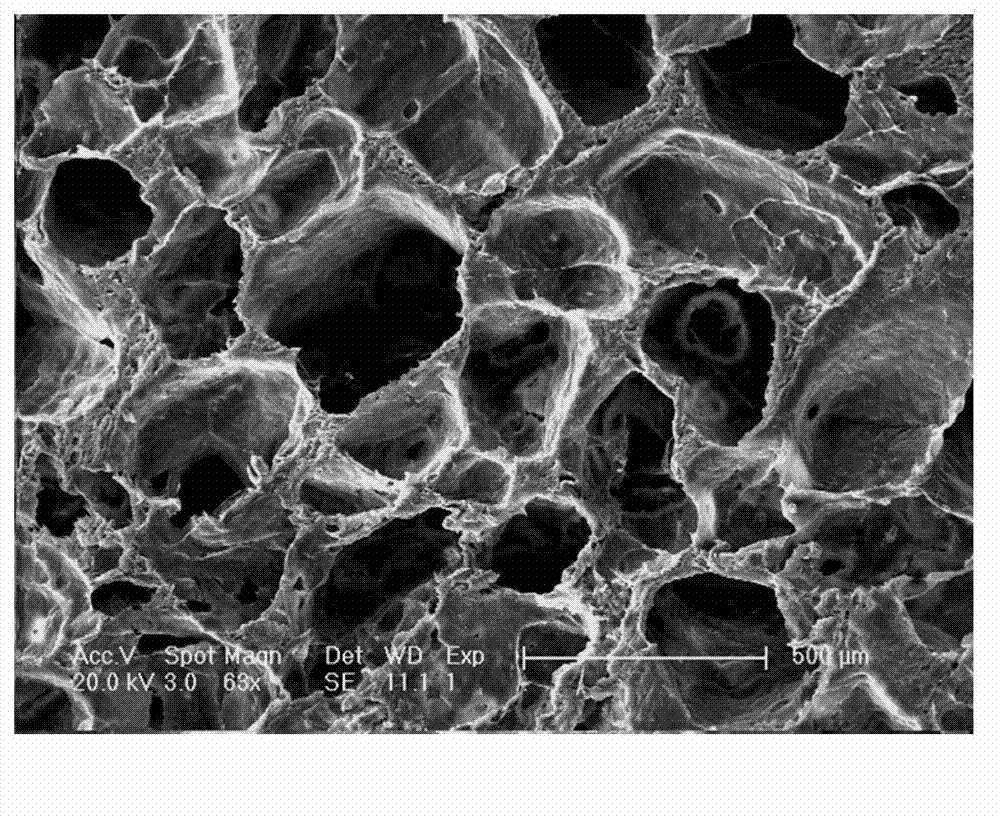
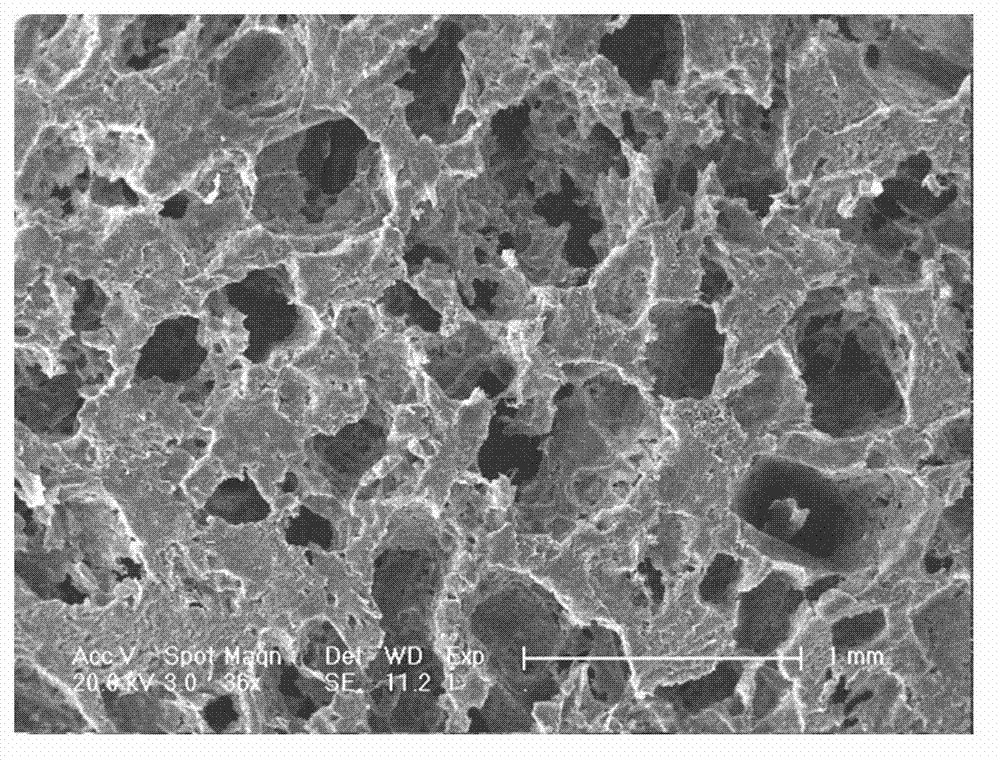
[0052] Dissolve polyester polymer polylactic acid (PLA) in chloroform; add DMF with a volume ratio of 2:3 to chloroform to the polymer solution; add a particle size of 200 μm with a mass ratio of 9:1 to PLA in the mold sucrose granules; pour the dual-solvent polymer solution into the mold filled with sucrose granules; wait for the polymer solution to evaporate at room temperature for several days to form a relatively dry solid; put the solid block into three-distilled water with a negative pressure of 10MP and wash it several times , until there is no more solvent or porogen in the aqueous solution after washing; vacuum drying, and field emission scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) to detect the morphology of the scaffold. Such as figure 2 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com