Observability constraint-based random planet landing track optimizing method
A stochastic optimization, trajectory technique, applied in instrumentation, adaptive control, control/regulation systems, etc., which can solve problems such as poor estimation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
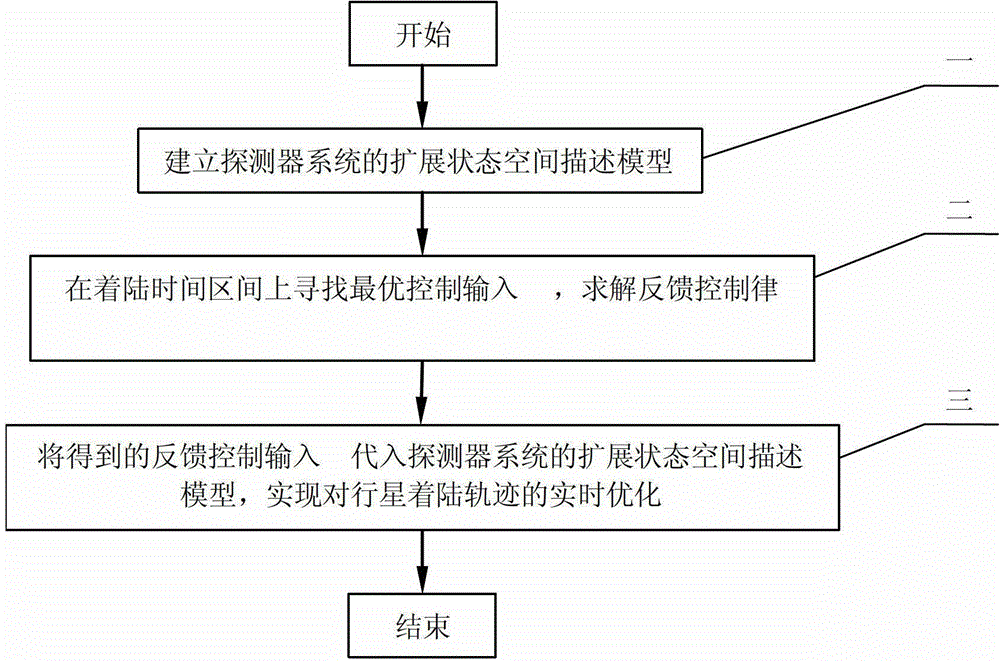
[0024] In order to further illustrate the purpose and advantages of the present invention, the content of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
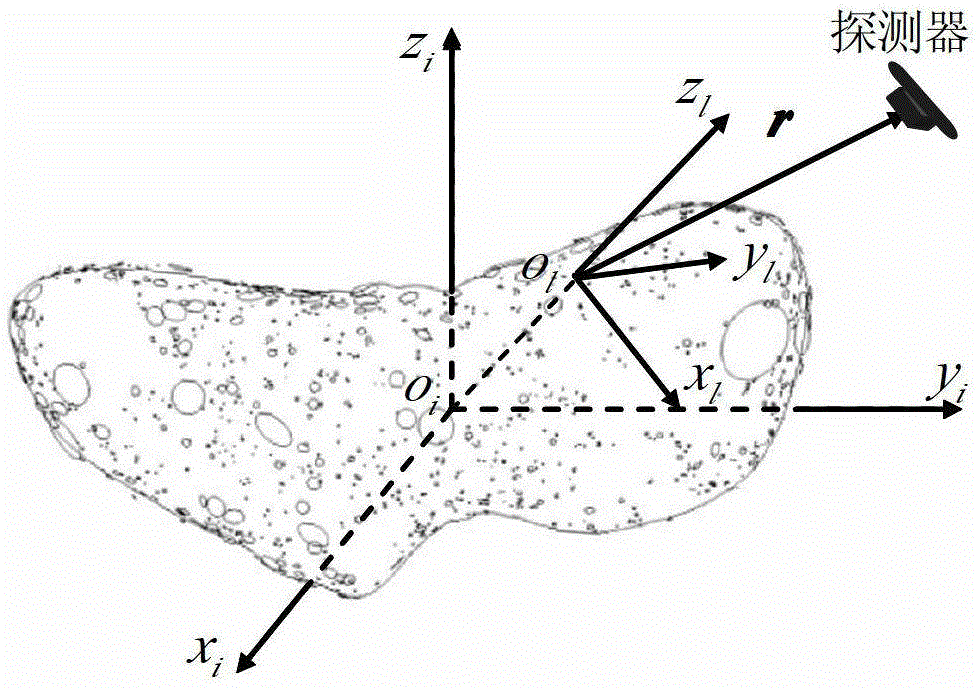
[0025] ①Establish the dynamic equation of the detector under the fixed coordinate system of the landing point
[0026] r · = v ·
[0027] v · = u + g - a e - a k + a Δ
[0028] Among them, r, v are the position vector and velocity vector of the probe relative to the predetermined landing point, u is the control input of the probe, g is the gravitational acceleration of the planet, a e ,a k are the centrifugal inertial acceleration and Coriolis accele...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com