A multi-cell filtering method for pose positioning of mobile robot in production workshop
A mobile robot and robot technology, which is applied in the field of multi-cell filtering, can solve the problem of low pose positioning accuracy, and achieve the effects of improving computational efficiency, avoiding the increase of dimension, and reducing the conservativeness of identification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
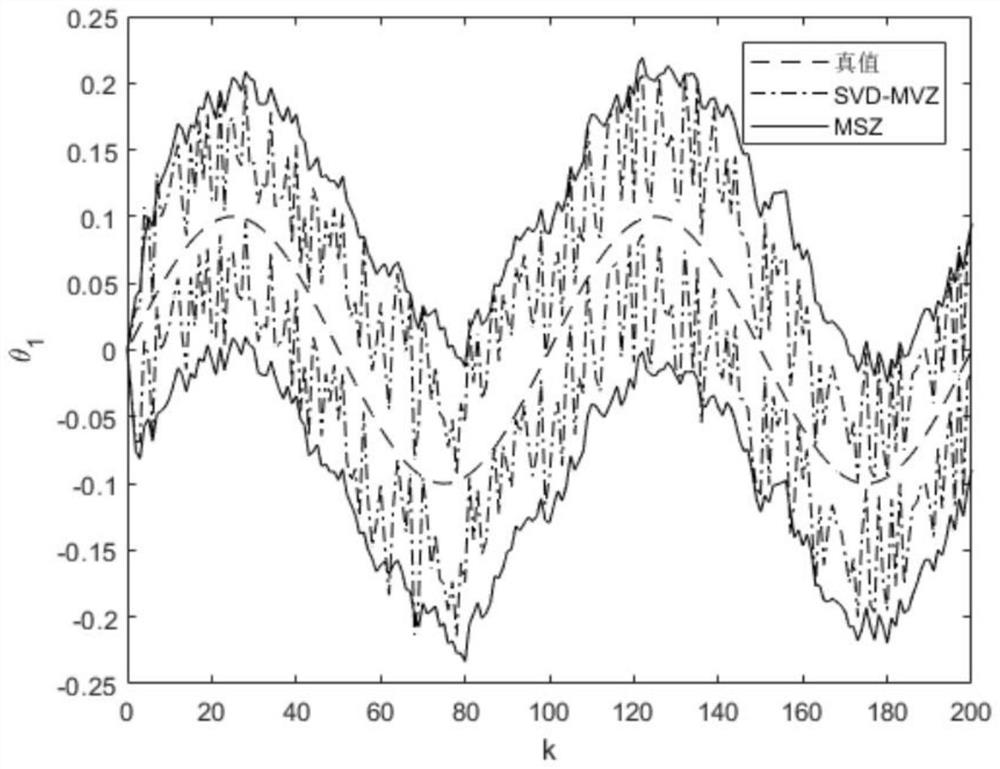
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] This embodiment provides a mobile robot pose positioning method, the method comprising:
[0044] Step1: Discretize the kinematics model of the mobile robot into a discrete continuous model y k = φ k T θ * +e k , where φ k is the observation vector, θ is the pose positioning parameter, e k Indicates the bounded noise of the system;
[0045] Step2: Under the given unknown but bounded noise and external excitation signal, obtain the observation vector φ according to the kinematics model of the mobile robot k and the output sequence y k , and by observing the vector φ k and the output sequence y k Obtain the constraints of the kth step parameter feasible set;
[0046] Step3: According to the constraints of step k and the fully symmetrical polyhedron of step k-1, the fully symmetrical polyhedron with the smallest volume in step k is obtained;
[0047] Step4: Extend the fully symmetrical polyhedron obtained in Step3 to obtain the expanded fully symmetrical polyhedr...
Embodiment 2
[0050] In this embodiment, the application of the mobile robot pose positioning method provided in this application to a crawler mobile robot in a production workshop is introduced as an example:
[0051] Step 1: Go through the typical kinematics model of the crawler mobile robot in the production workshop, and then discretize it into a discrete continuous system y k = φ k T θ * +e k ;
[0052] A typical kinematic model of a crawler mobile robot in a production workshop:
[0053]
[0054] where (x k the y k ) T Indicates the current position of the robot, ψ k Indicates the robot angle, the current position of the robot and the robot angle can be measured by the sensor. ω 1,k , ω 2,k Respectively represent the rotational angular velocity of the left and right driving wheels, r represents the radius of the wheel, b represents the distance between the left and right wheels, ΔT represents the time interval, s 1,k , s 2,k Indicates the slip rate of the robot, (x k...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com