Preparation method of composite anode material of lithium-ion power battery
A composite cathode material and power battery technology, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of poor conductivity and rate performance, affecting applications, etc., and achieve excellent conductivity, high specific capacity, and good rate performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0021] With Li(CH 3 COO)·2H 2 O is Li source, Ni(CH 3 COO) 2 4H 2 O, Co(CH 3 COO) 2 4H 2 O, Mn(CH 3 COO) 2 4H 2 O is Ni source, Co source, Mn source respectively. According to the molar ratio Li:(Ni+Co+Mn)=1.1:1 (the molar ratio of Ni:Co:Mn is 1:1:1), weigh the corresponding raw materials in 50ml deionized water, and use this mixed solution as liquid A . Then weigh citric acid and ethylene glycol (the molar ratio of citric acid and ethylene glycol is 1:3) with the amount of total metal ions and other substances and dissolve it in 50ml of alcohol as solution B. Slowly add liquid A to liquid B dropwise, and use a water bath to stir magnetically at about 60°C to allow citric acid to coordinate with metal ions. After the dropwise addition is complete, heat up to 95°C to cause esterification between the citric acid complex and ethylene glycol, and the solution becomes viscous at this time. Next, the viscous liquid was dried in a vacuum oven at 120° C. to obtain a xerog...
example 2
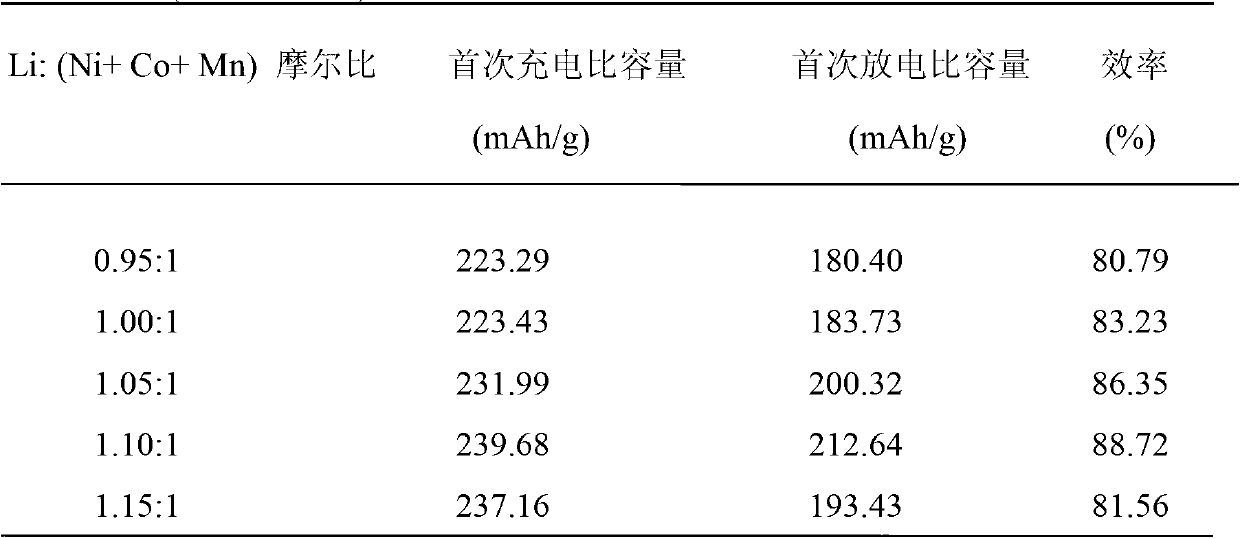
[0024] This example investigates the effect of the molar ratio Li:(Ni+Co+Mn) on the electrochemical performance of the material. The results of 0.2C constant current charge and discharge are shown in Table 1. Except that the molar ratio Li:(Ni+Co+Mn) is different from Example 1, other conditions are consistent with Example 1.
[0025] Table 1Li: (Ni+Co+Mn) molar ratio versus LiNi 1 / 3 co 1 / 3 mn 1 / 3 o 2 The influence of the electrochemical performance of the material
[0026]
example 3
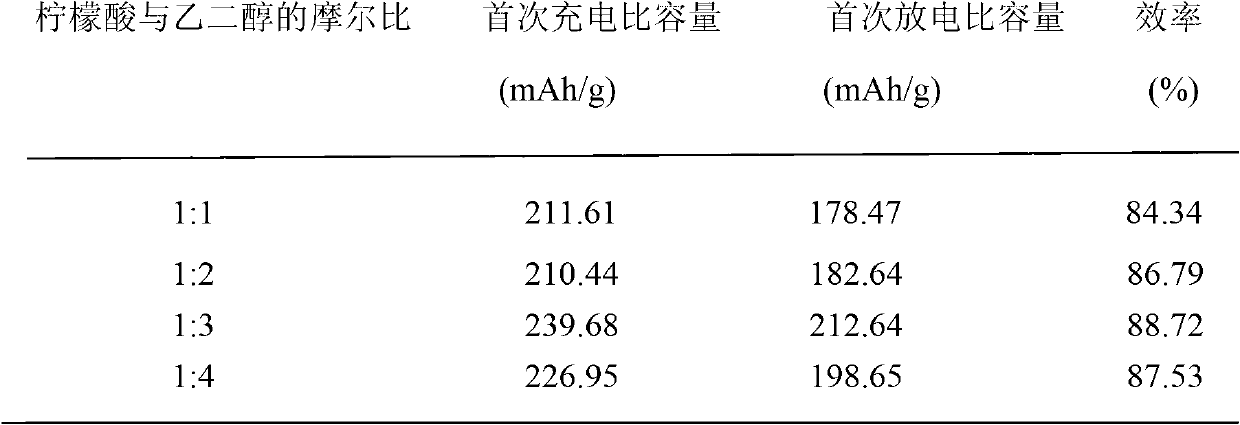
[0028] This example investigates the effect of the molar ratio of citric acid to ethylene glycol on the electrochemical performance of the material. The results of 0.2C constant current charge and discharge are shown in Table 2. Except that the mol ratio of citric acid and ethylene glycol is different from example 1, other conditions are all consistent with example 1.
[0029] Table 2 The molar ratio of citric acid to ethylene glycol versus LiNi 1 / 3 co 1 / 3 mn 1 / 3 o 2 The influence of the electrochemical performance of the material
[0030]
[0031]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com