Multi-focus femtosecond laser scribing method applied to separation of light emitting diode (LED) device
A LED device, femtosecond laser technology, applied in laser welding equipment, welding equipment, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of reduced light transmittance, complicated light-emitting diode preparation process, difficult sapphire substrate, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
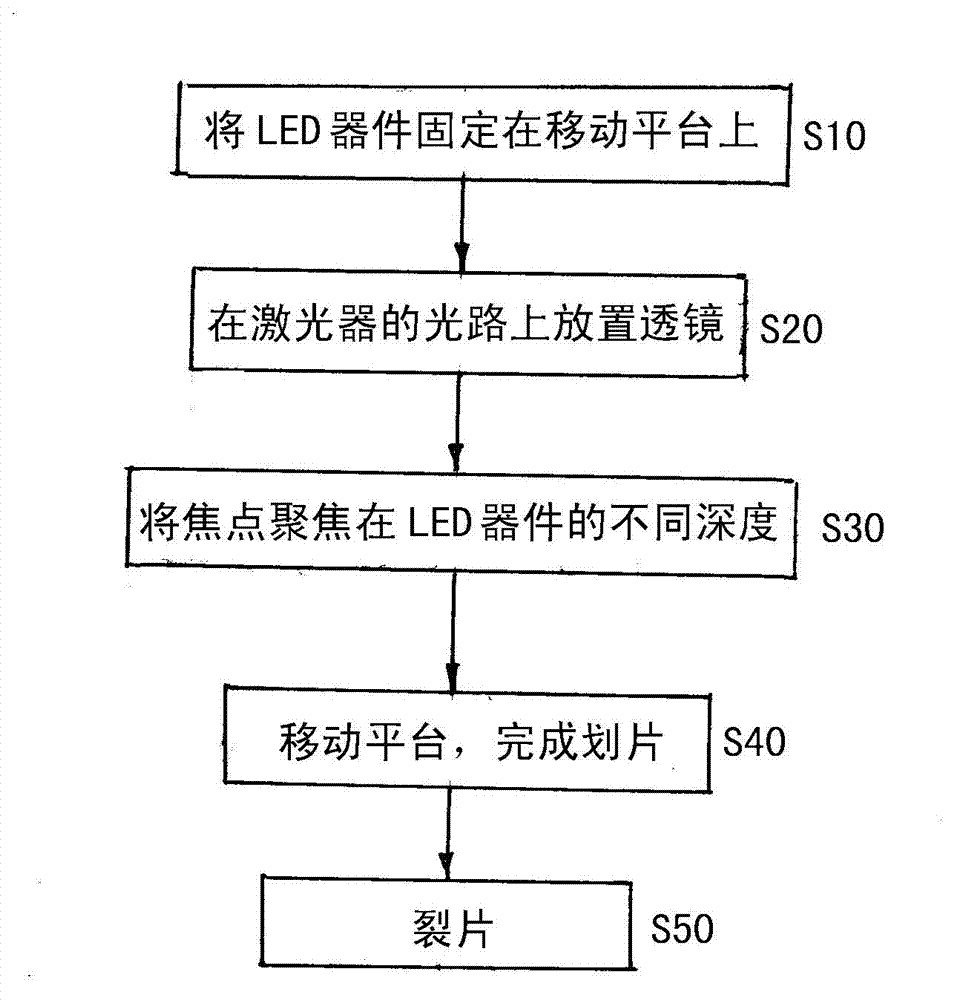
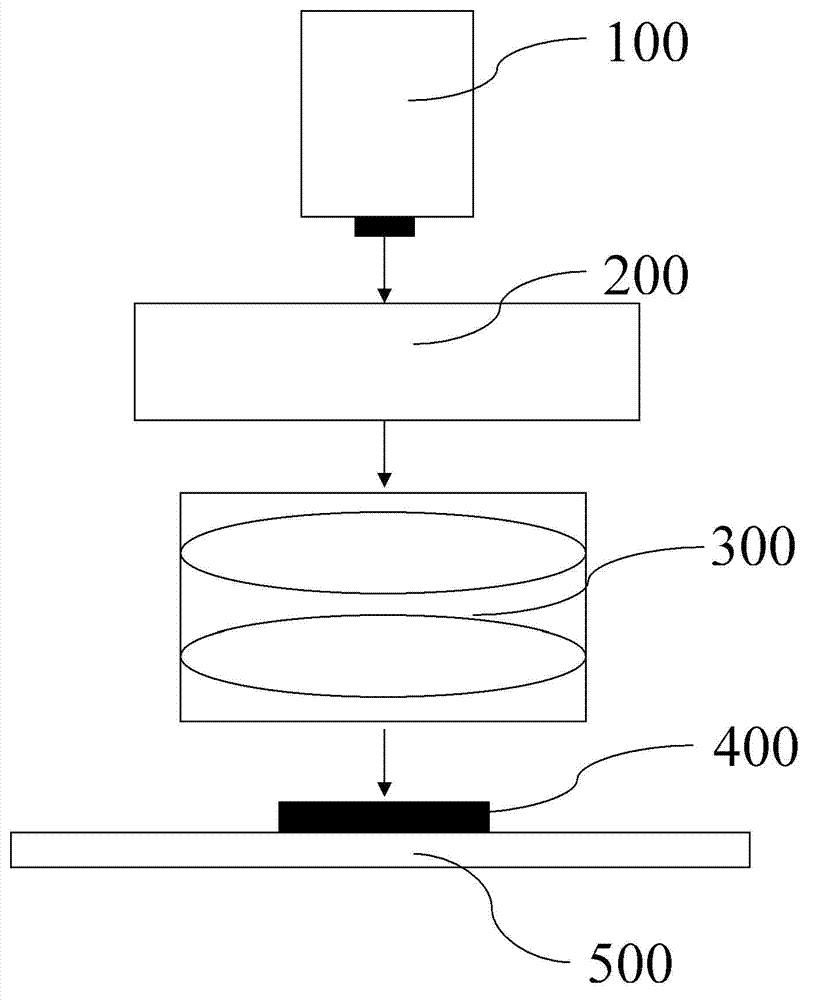
[0019] Please refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, the present invention provides a multi-focus femtosecond laser scribing method applied to the separation of LED devices, including:
[0020] Step S10: Fix the prepared LED device 400 on the horizontal moving platform 500, then adjust the CCD focus of the optical path system, so that the back of the LED device 400 is located at the imaging center of the CCD imaging device 200 (see figure 2 ); adjust the horizontal moving platform 500 to be parallel to the runway of the LED device 400 .
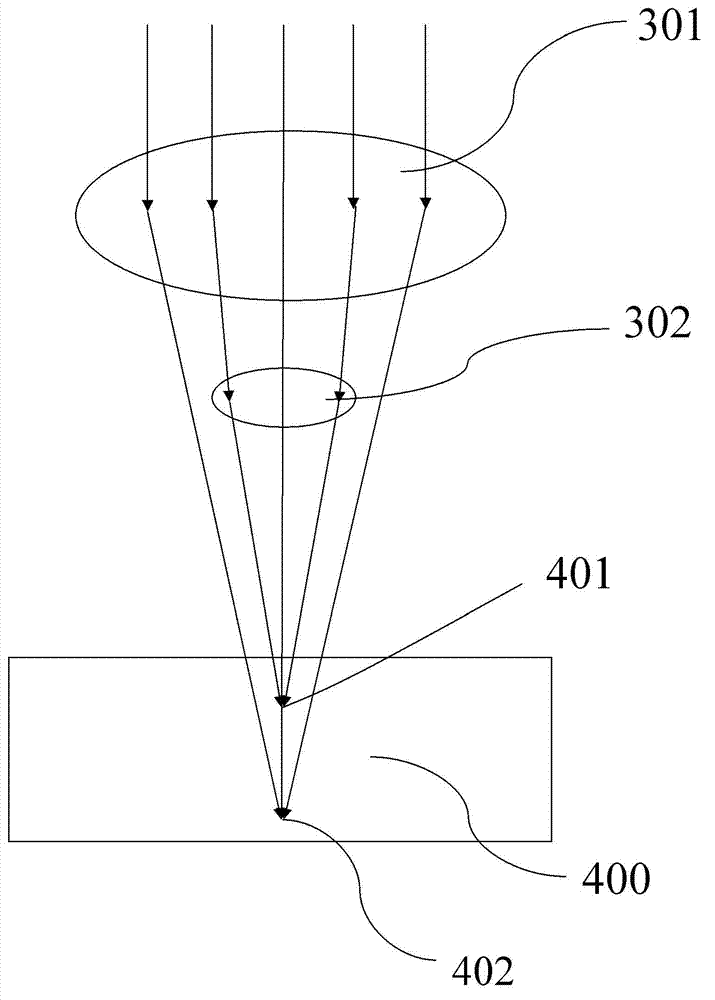
[0021] Step S20: placing a plurality of lenses 300 on the laser optical path of the femtosecond laser 100 to divide the laser light into multiple focal points, the central wavelength range of the laser output by the femtosecond laser 100 is 200nm-1600nm, and the pulse width range is 1fs-1000fs, The repetition frequency is 1MHz-1000MHz, the average power range is 1mw-100W, the number of the lens 300 and the focal point is 1-10 (the number ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com