RAFT (reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer) preparation method of polylysine derivative
A technology of polylysine and its derivatives, which can be used in pharmaceutical formulations, genetic material components, gene therapy, etc. It can solve problems such as poor DNA burden capacity, poor molecular weight and distribution control, and achieve excellent biocompatibility , the effect of extensive application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
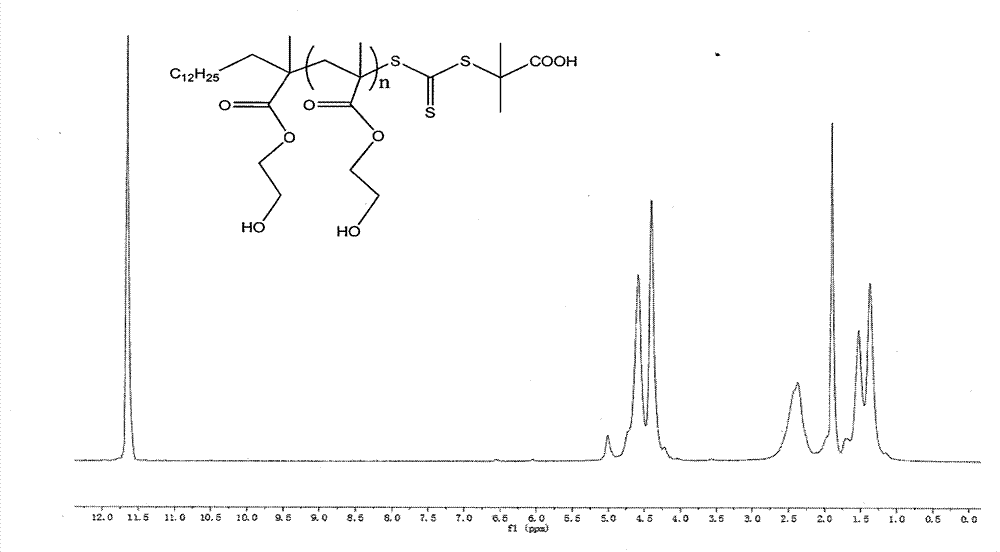
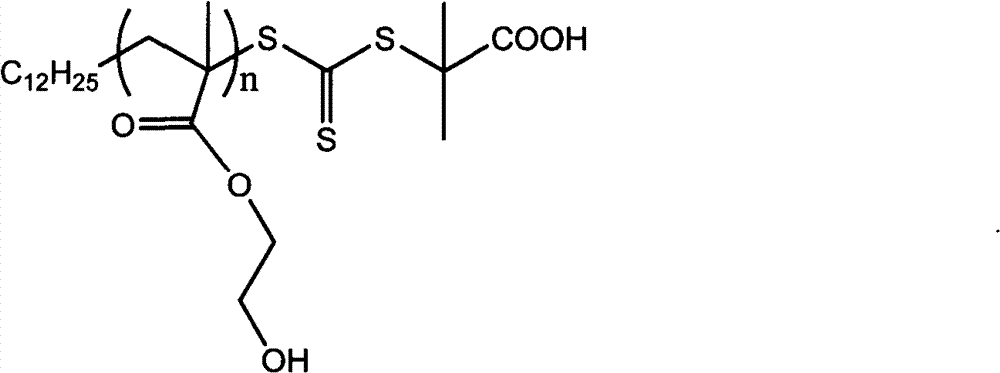
[0014] Weigh 1.00g of hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) (7.684×10 -3 mol), trithiocarbonate 0.0839g (2.305×10 -4 mol), AIBN0.0128g (7.684×10 -5 mol), 4ml of tert-butanol, added to a 50ml reactor, protected by nitrogen gas for 30min before the reaction, heated up to 75°C under magnetic stirring, after 5h of reaction, cooled with ice water to stop the reaction, precipitated with cold ether three times, and then Under constant temperature drying to obtain homopolymer PHEMA, the product is white, molecular weight M n(GPC) =5.4×10 4 , the molecular weight distribution is 1.52.
Embodiment 2
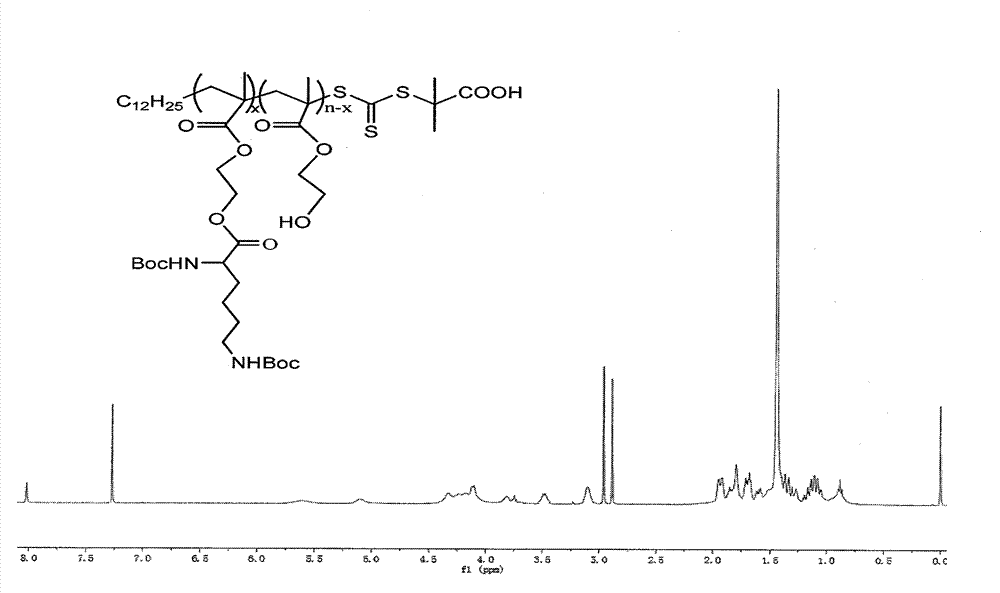
[0016] Weigh Boc-protected lysine (Boc-L-lysine) 1.010g (2.15×10 -2 mol), PHEMA0.38g (7.6×10 -6 mol), DCC 0.793g (3.84×10 -3 mol), DMAP 0.0202g (1.65×10 -4 mol), DMF15ml, added to a 50ml reactor, kept the temperature at 25°C under magnetic stirring, after 24 hours of reaction, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, and precipitated in ether to obtain PHEMA-co-PHEMA-Boc-L-lysine copolymer , the product is pale yellow.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com