Stratus cloud and convective cloud automatic recognition method based on Doppler radar data
A Doppler radar and automatic identification technology, which is applied in the field of meteorological information processing and identification, can solve problems such as heavy workload, large subjective components, and inability to automate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
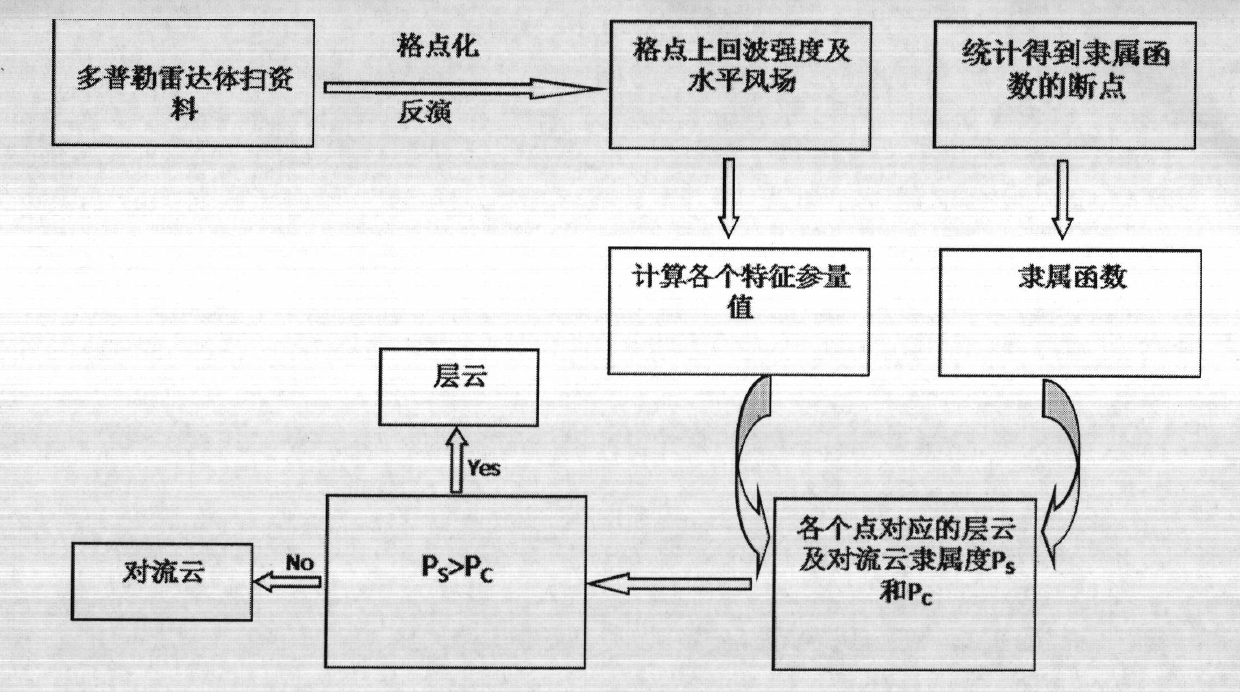
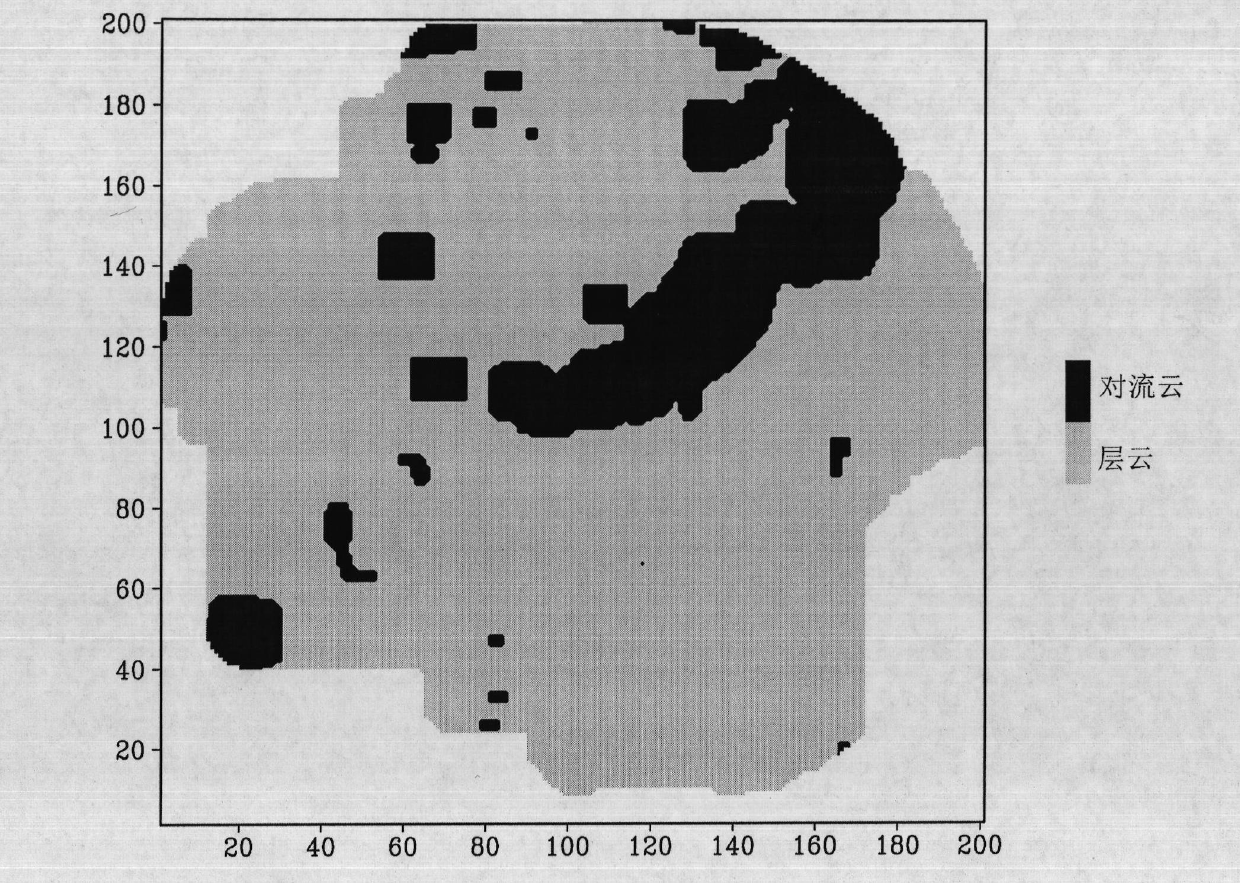
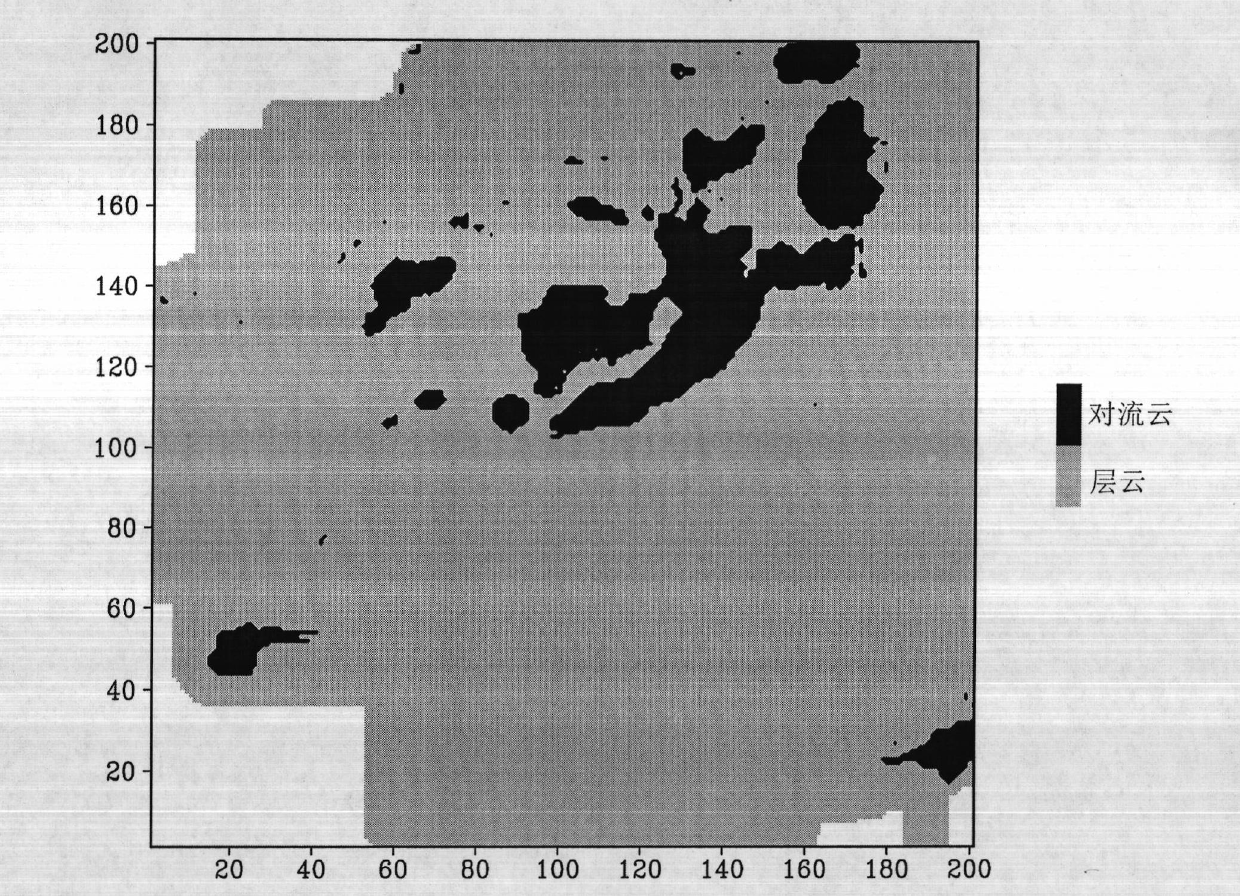
[0057] The present invention provides relevant processing and the example of detection below, and its detected radar data is Nanjing Doppler radar measured data on July 19th, 2006, relevant characteristic parameter and intermediate data are as follows, utilize prior art according to this data simultaneously And the present invention has been processed respectively, and its result has been carried out comparative inspection. The present invention has been compared with the "peak value" method (or called "SHY95" method) commonly used in the world, but the technology of Xiao Yanjiao, Liu Liping and others is not adopted, because their technology has a large subjective component.
[0058] from Figure 2 to Figure 3 It can be seen that the SHY95 method of the prior art and the dynamic fuzzy logic algorithm design result of the present invention are more consistent on the whole and are more consistent with the echo band distribution, especially in figure 2 within the black area of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com