Method by adopting molecular marker-assisted backcross to improve gibberellic disease expansion resistance of wheat
A molecular marker-assisted, scab-blight technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, plant genetic improvement, application, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and labor-intensive resistance, hinder the effective use of resistance sources, etc., to speed up the promotion and improve the breeding. Choose efficient, efficient effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
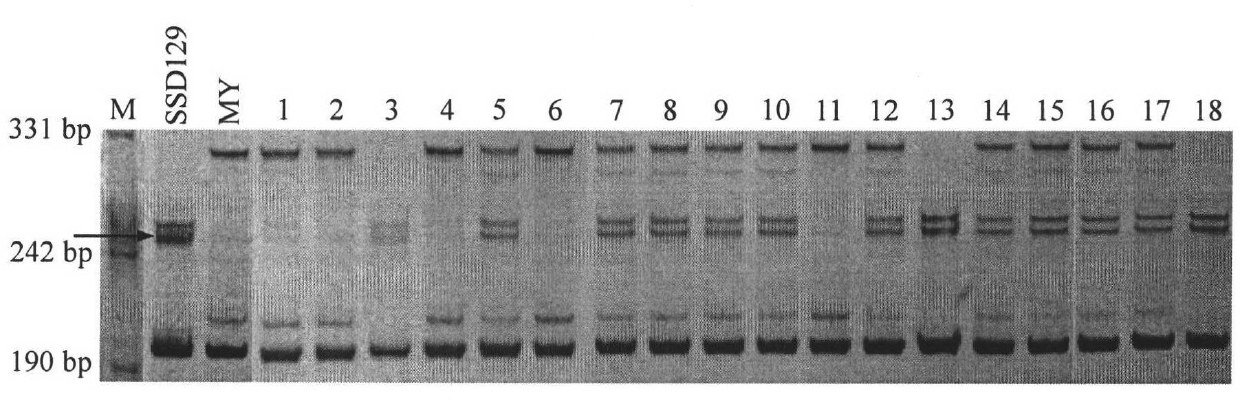
[0050] Example 1 Using SSR markers closely linked to target QTLs to assist backcrossing to improve expansion resistance of wheat lines
[0051] F 1 ; Then use Mianyang 99-323 as the reincarnation parent to backcross and get BC 1 f 1 . Will BC 1 f 1 The isolated population is planted in the field as a single plant, listed at the seedling stage, and the DNA of each individual plant is extracted, and the genotype is analyzed using the SSR markers closely linked to the target QTL, and the heterozygous individual plants carrying the target QTL are selected to continue backcrossing to obtain BC 2 f 1 . Use a similar method to select individual plants and continue backcrossing to obtain BC 3 f 1 . in bc 3 f 1 In the segregation population, the homozygous individual plants carrying the target QTL were selected according to the marker genotypes to obtain near-isogenic lines by selfing. A total of 1 generation of crossing, 3 generations of backcrossing and 2 generations of s...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2 Select SSR markers throughout the wheat genome to analyze the background recovery rate
[0063] In order to speed up the restoration of recurrent parents in areas other than the target QTL, the genetic map constructed using the Nanda 2419×Wangshuibai recombinant inbred line population (Xue SL, Zhang ZZ, Lin F, Kong ZX, Cao Y, Li CJ, Yi HY, Mei MF, Zhao DM, Zhu HL, Xu HB, Wu JZ, Tian DG, Zhang CQ, Ma ZQ (2008) A high-density intervarietal map of the wheat genome enriched with markers derived from expressed sequence tags. Theor Appl Genet 117:181-189) selected a marker every 20-30cM, and a total of 150 pairs of SSR markers distributed on 21 chromosomes were selected for the background recovery rate analysis of each generation.
[0064] Results show: in BC 2 f 1 In this generation, 97 pairs of markers were randomly selected from 150 pairs of markers to evaluate the genetic background of 19 heterozygous individuals with Qfhs. , much higher than the 87.5% theore...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: Identification of Field Scab Resistance Expansion of Near-Isogenic Lines
[0066] Field resistance evaluation was carried out in Jiangpu experimental field and Pailou experimental field of Nanjing Agricultural University in 2010 and 2011, respectively. Random block design was adopted, with 2 rows per plot, row length 1.5m, row spacing 0.25m, plant spacing 0.1m, and 15 plants per row. In the flowering stage, the single-flower drip method was used to inoculate, and the Gibberella used was a mixture of strong pathogenic bacteria F4, F15, F17 and F34 strains, and the concentration of the spore liquid was 1×10 5 spores / ml. The number of diseased spikelets (NDS) and the length of diseased rachis (LDR) were investigated 21 days after flowering, and the spreadability of the bred near-isogenic lines against scab was evaluated.
[0067] The results showed that compared with the recurrent parents, the number of diseased spikelets and the length of the diseased axis of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com