Constant-speed constant-frequency wind turbine low-voltage riding-through device and control method
A low-voltage ride-through technology and wind turbine technology, applied in wind power generation, control systems, control generators, etc., can solve the cost of low-voltage ride-through devices, control complexity, difficulty in implementing engineering transformation, increase device cost and floor area, Increased difficulty of DC voltage regulation control and other issues, achieving both economical and practical, enhanced power supply reliability, and low cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
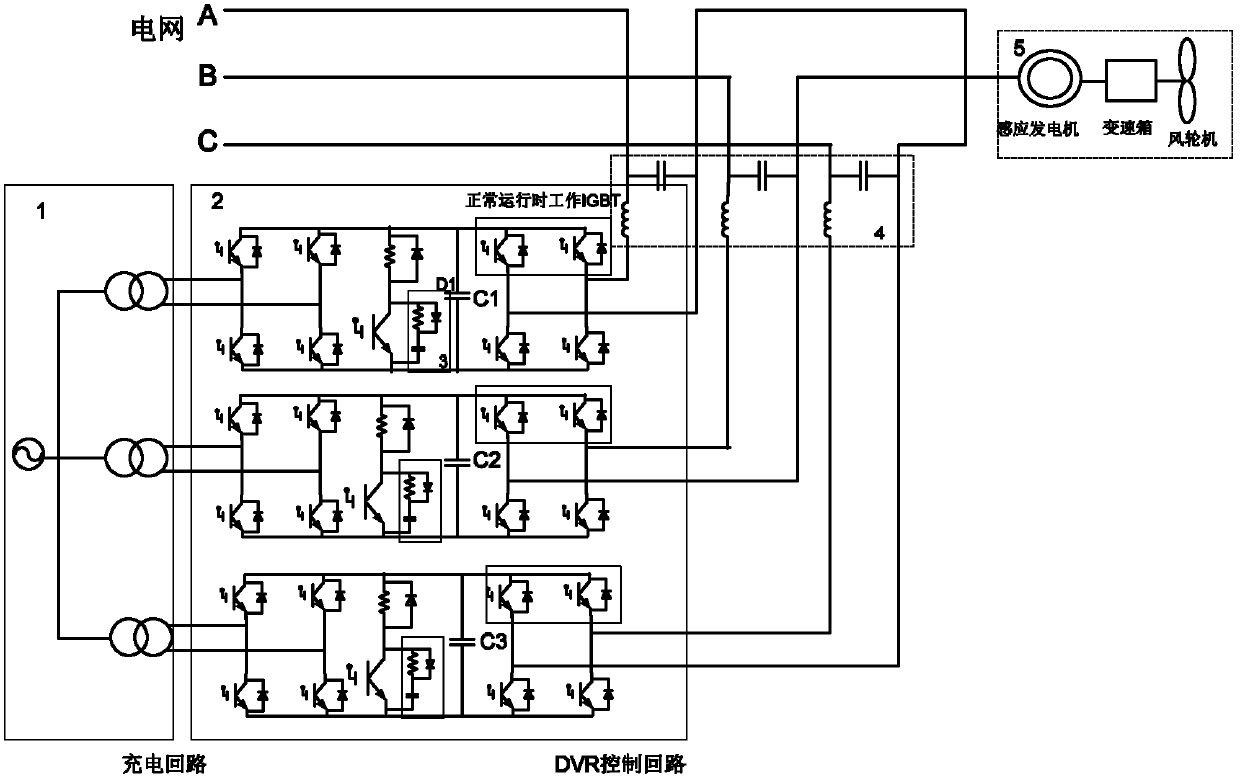
[0039] Such as figure 2As shown, the low voltage ride-through device of this embodiment connects a switch in series between the grid system and the wind turbine; connects a series contactor and a reactive power compensation module in parallel between the switch and the wind turbine; The active power absorption circuit is connected in parallel between the contactor and the reactive power compensation module; the switch is an electronic switch or a mechanical switch, and the electronic switch includes an anti-parallel thyristor or an anti-parallel GTO. This embodiment takes the anti-parallel thyristor valve of electronic switch as an example, which is used to cut off the channel for the wind turbine to feed active power to the grid system when a voltage sag occurs in the grid system, and quickly connect the wind turbine to the grid system after the grid system voltage recovers. Grid system connectivity. The reactive power compensation module is a parallel capacitor bank, which...
Embodiment 2
[0052] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is:
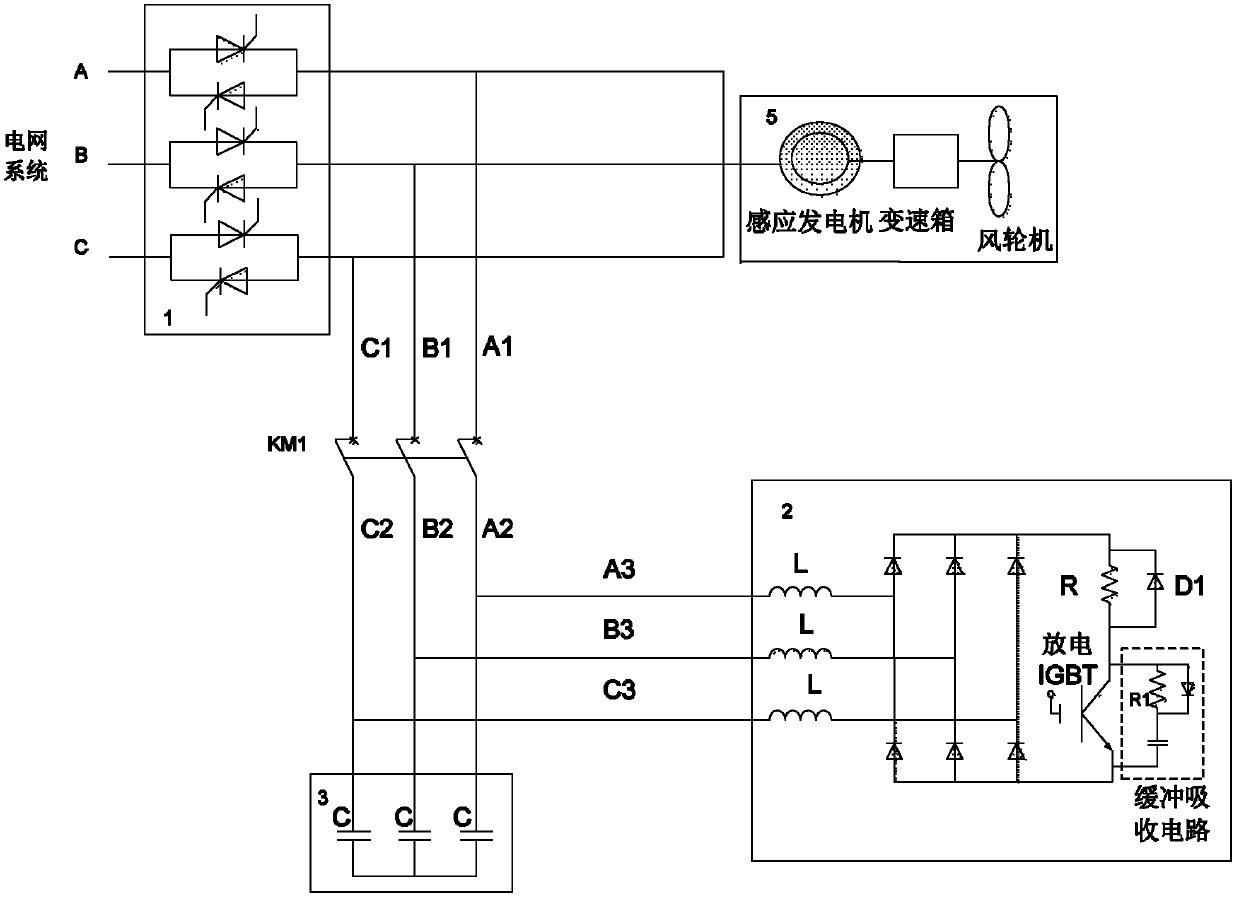
[0053] The active absorption circuit of this embodiment has another form, such as image 3 shown. That is, it includes a reactor, a three-phase uncontrollable rectifier bridge, a discharge resistor, a discharge IGBT and an IGBT snubber snubber circuit; three reactors, each of which is connected in series with the discharge resistor and the three-phase uncontrollable rectifier bridge in sequence, so The three-phase uncontrollable rectifier bridge is connected in parallel with the discharging IGBT, and the discharging IGBT is connected in parallel with the IGBT snubbing circuit.
[0054] The control method of the device is the same as that in the first embodiment.
Embodiment 3
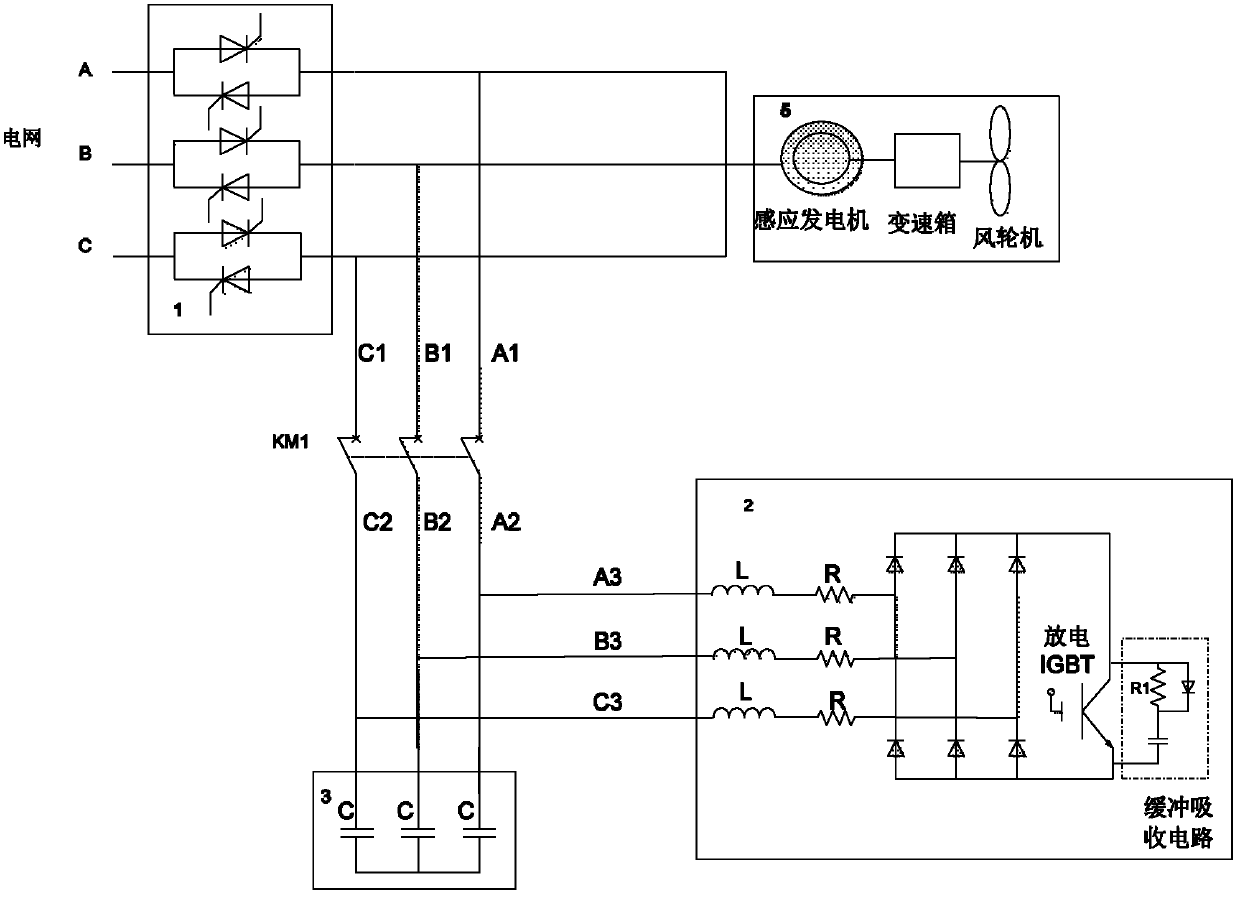
[0056] In order to suppress the overvoltage at the terminal of the wind turbine, in this embodiment, on the basis of Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2, a lightning arrester is connected in parallel between the contactor and the parallel capacitor, such as Figure 4 (Taking the form of the active absorption circuit of Embodiment 1 as an example) as shown. When the terminal of the wind turbine is overvoltage, the lightning arrester is connected to the ground to avoid overvoltage at the terminal of the wind turbine and burn out the hardware. The arrester is placed in the circuit and connected to the three-phase contactor through the power lines A2, B2, and C2. The reactive power compensation capacitor and the active power absorption circuit are connected to the power lines A2, B2, and C2 through the power lines A3, B3, and C3. Other control methods for the circuit are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com