Method for establishing xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease model for NOD/SCID (non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient) mice
A graft-versus-host and method-establishing technology is applied in the establishment of NOD/SCID mouse xenograft-versus-host disease models, which can solve the problems of increasing implanted cell niches, limiting the wide application of the model, and achieving the modeling process. Simple, efficient, and repeatable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Example 1 Preparation of activated human PBMCs
[0014] 1. Add 5ml of lymphocyte separation medium into a 15ml centrifuge tube;
[0015] 2. Take 10 ml of heparin anticoagulated human peripheral venous blood and mix it with the same amount of Hank's solution, and slowly superimpose it on the layered liquid surface along the tube wall with a dropper, pay attention to keep a clear interface, and centrifuge horizontally at 600g×20 minutes;
[0016] 3. After centrifugation, the tube is divided into three layers, the upper layer is plasma and Hank's solution, the lower layer is mainly red blood cells and granulocytes, the middle layer is lymphocyte separation fluid, and there is a white cloud layer mainly composed of mononuclear cells at the interface of the upper and middle layers narrow band;
[0017] 4. Use a dropper to insert into the cloud layer, absorb mononuclear cells, put them into another 15ml centrifuge tube, add 5 times the volume of Hank's solution, centrifuge a...
Embodiment 2
[0019] Example 2 Modeling of NOD / SCID mice
[0020] 1. Pretreat NOD / SCID mice on -3 to -1 days, the pretreatment program is: intraperitoneal injection on -3 days and -2 days
[0021] Inject (or perfuse) cyclophosphamide 50mg / kg / day, intraperitoneally inject anti-mouse CD122 monoclonal antibody 100μg / mouse on day -1;
[0022] 2. On the 0th day, each mouse in the experimental group was infused (or perfused) with activated human PBMCs prepared from the tail vein 1×10 7 A total of 0.2ml, each mouse in the control group was infused (or perfused) with 0.2ml of phosphate buffered saline from the tail vein;
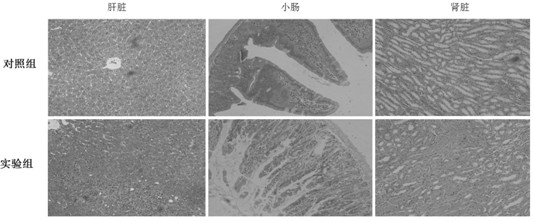
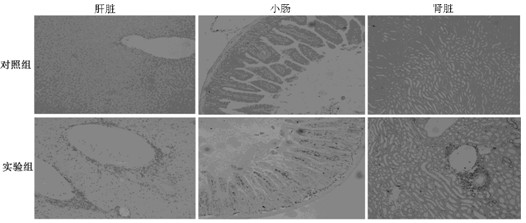
[0023] 3. Regularly observe the mouse weight, diarrhea, skin GVHD manifestations (hair loss, erythema, etc.), activity, etc. every day.
Embodiment 3
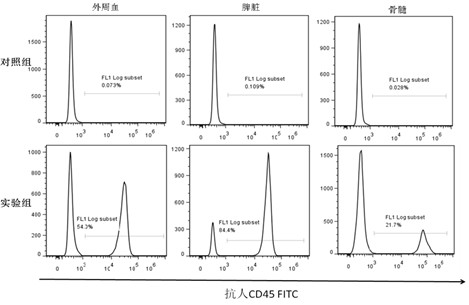
[0024] Example 3 Implantation detection of mouse human leukocyte quantity and content
[0025] 1. Take 1ml of heparin anticoagulated mouse blood, or 1ml of splenocyte suspension (the total number of cells is 10 6 ), add ammonium chloride solution (NH4Cl: 8.99g / L, KHCO3: 1g / L, Na4-EDTA: 0.037g / L) 3ml lysed red blood cells, mix well, act at 37°C for 10 minutes, centrifuge at 300g for 5 minutes, discard clear;
[0026] 2. Resuspend the cells in 40 μl of 1× phosphate buffer, add 20 μl of anti-CD45 FITC monoclonal antibody, mix well, and incubate at 4°C in the dark for 30 minutes;
[0027] 3. Wash twice with 2 ml of 1× phosphate buffer solution, pour out the liquid at the mouth of the tube with filter paper after each wash;
[0028] 4. Add 500 μl of 1× phosphate buffer solution to resuspend the cells, and perform flow cytometry detection on the machine; use CELL-QUEST software to obtain 10,000 cells per tube, and use human CD45 positivity as the phenotype characteristic of human ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com