Lateral double-diffusion metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) device introducing local stress
A local stress and device technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable device drive capabilities, and achieve the effects of improving device drive capabilities, high withstand voltage characteristics, and reducing adverse effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
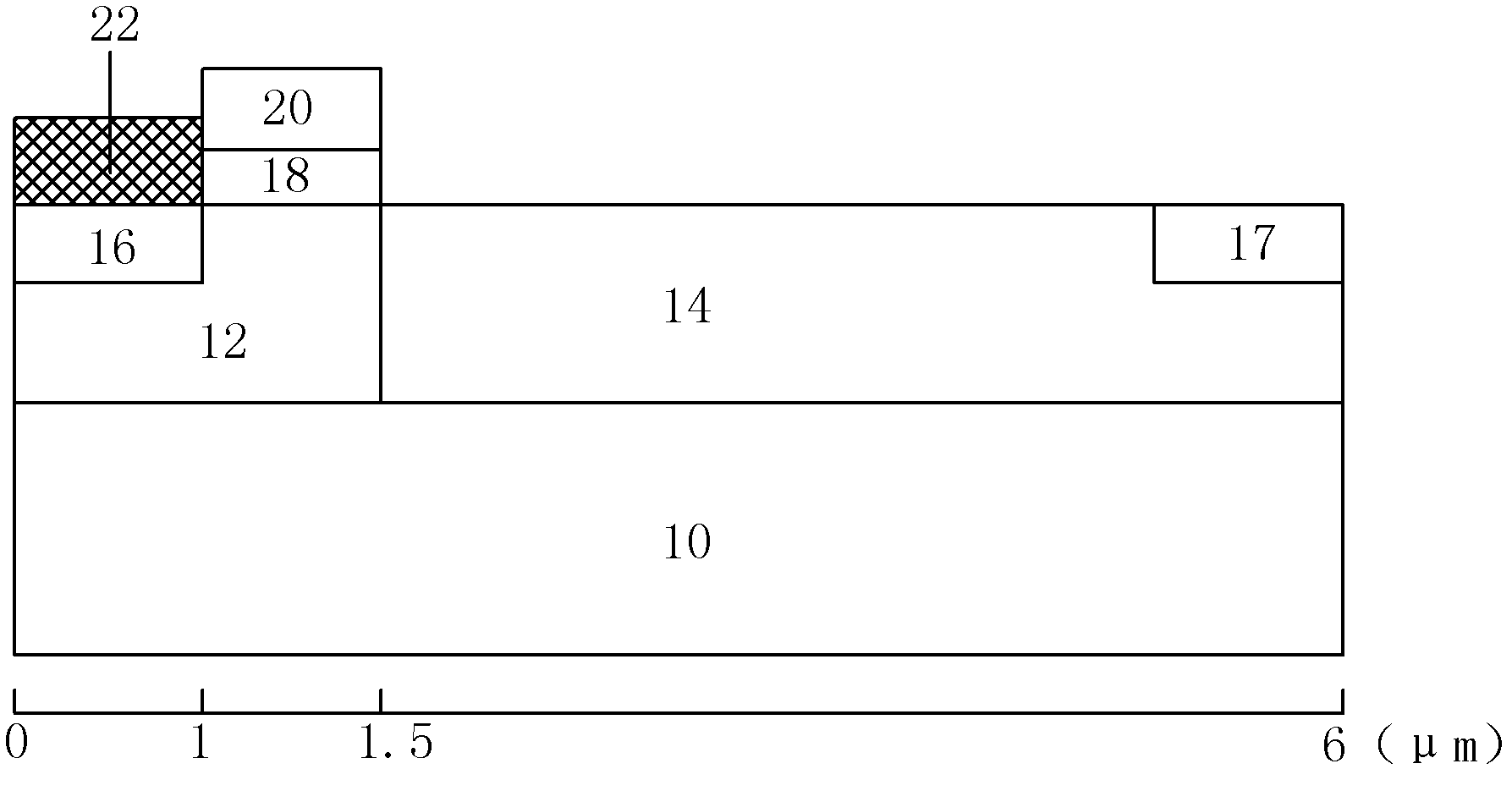
[0032] The cross-sectional structure of the LDMOS device in this example is as follows figure 1 shown. Including a bulk substrate 10, a well region 12 and a drift region 14 adjacent to each other are formed on the substrate 10, a source region 16 and a drain region 17 are respectively formed in the well region 12 and the drift region 14, and a source region 16 and a drain region 14 are formed in the well region 12 and the drift region 14 A gate oxide layer 18 is grown on the surface of the well region 12 between them, and a polysilicon gate 20 is grown on the gate oxide layer 18 . In this example, only the surface of the source region 16 is covered with silicon nitride (Si 3 N 4 ) film 22, using the intrinsic stress of the silicon nitride film 22 to introduce stress into the channel of the LDMOS device. Since the silicon nitride film 22 only exists on the surface of the source region 16 , the stress introduced by it only acts on the nearby channel, and basically does not af...
Embodiment 2
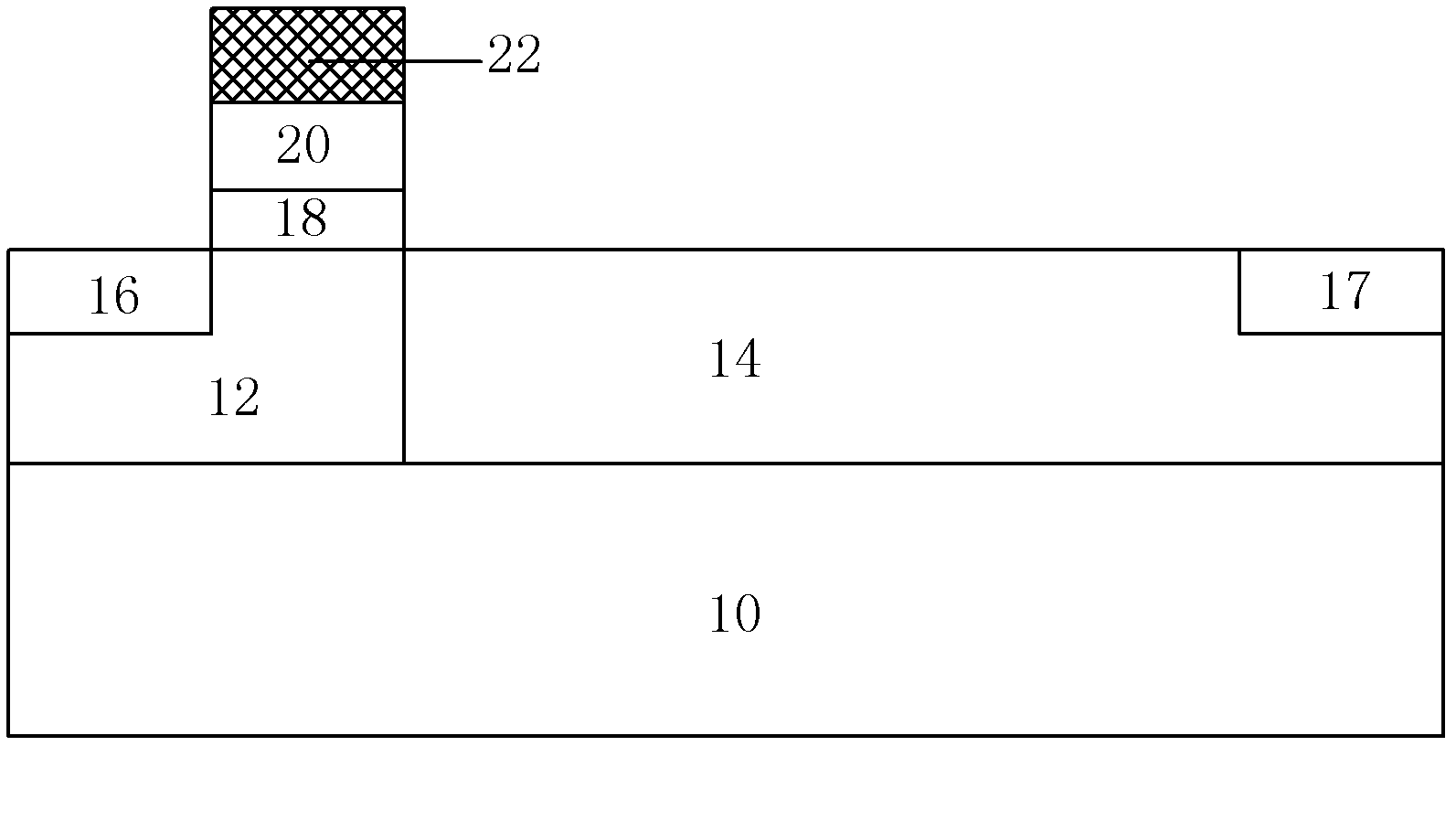
[0034] image 3It is a schematic diagram of the structure of an LDMOS device covered with a silicon nitride film 22 on the surface of the source region 16 and the gate 20 . The manufacturing process of the device of this example is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the manufacturing of the device body is completed according to the traditional CMOS device manufacturing process, including the preparation of the substrate 10, the formation of the well region 12, the growth of the gate oxide layer 18, the growth of the polysilicon gate 20, the trench ion implantation, drift region 14 ion implantation, source region 16 and drain region 17 ion implantation, and then chemical vapor deposition process is used to deposit nitride with a thickness of 120nm and a tensile stress of 2GPa on the surface of source region 16 and gate 20 Silicon film (22). Next, the fabrication of the entire device is completed through traditional process steps such as local interconnection. The device st...
Embodiment 3
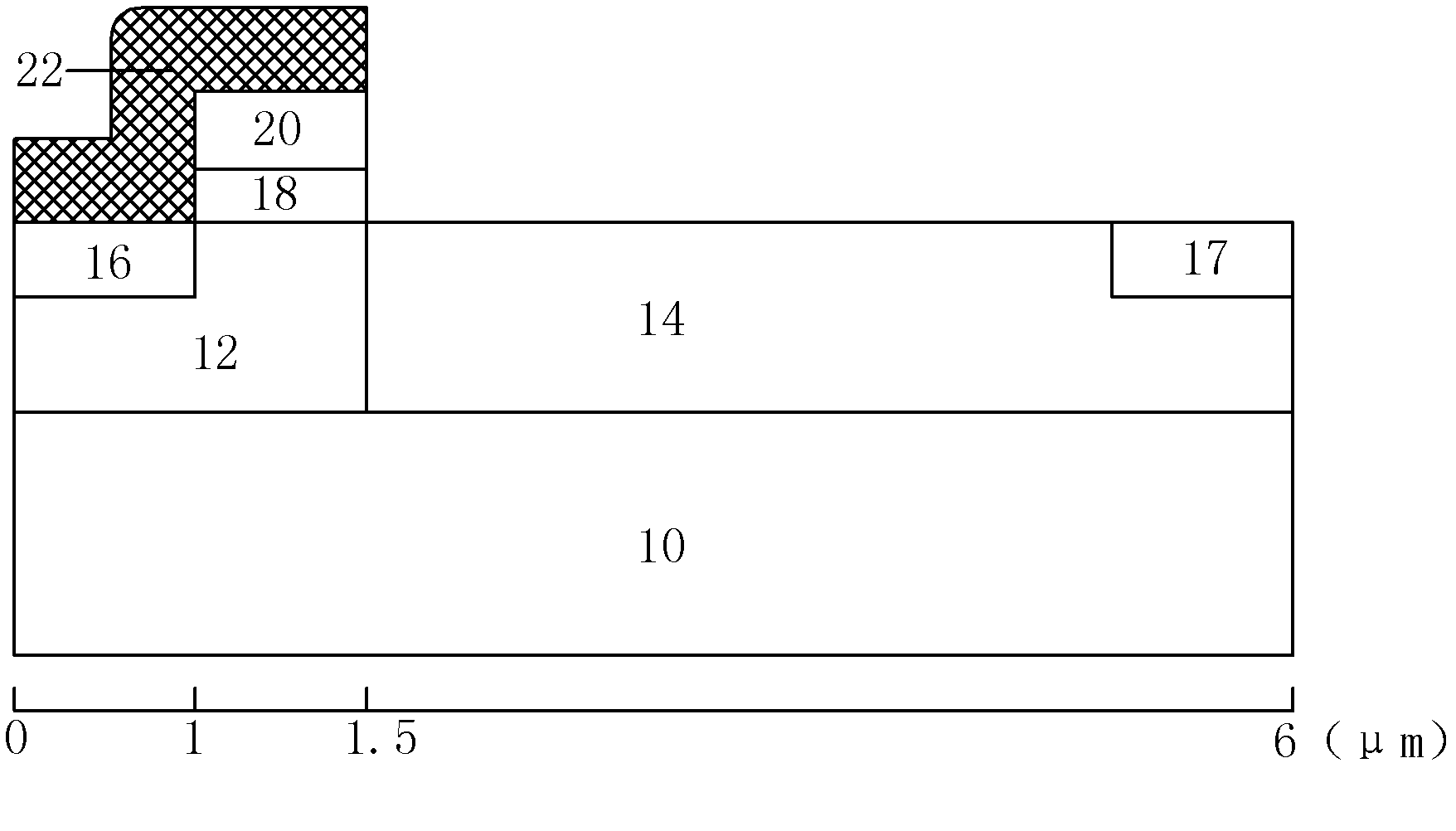
[0036] Figure 4 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the device in this example. The device source region 16 and gate 20 of this example are covered with a silicon nitride film 22, and there is a layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2) between the source region 16 and the silicon nitride film 22. 2 ) film 24. The main function of the silicon dioxide film 24 is to buffer the stress introduced by the silicon nitride covering the surface, so that the stress distribution in the channel region (1-1.5 μm) is relatively uniform. Refer to the description of the above-mentioned embodiment for the manufacturing process of the device body of this example. The manufacturing process of the silicon nitride film 22 of this example is to grow a layer of 20nm thick silicon dioxide film (24) on the surface of the source region 16 first, and then use chemical vapor deposition. A silicon nitride film (22) with a thickness of 120nm and a tensile stress of 2GPa is deposited on the surface of the silic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com