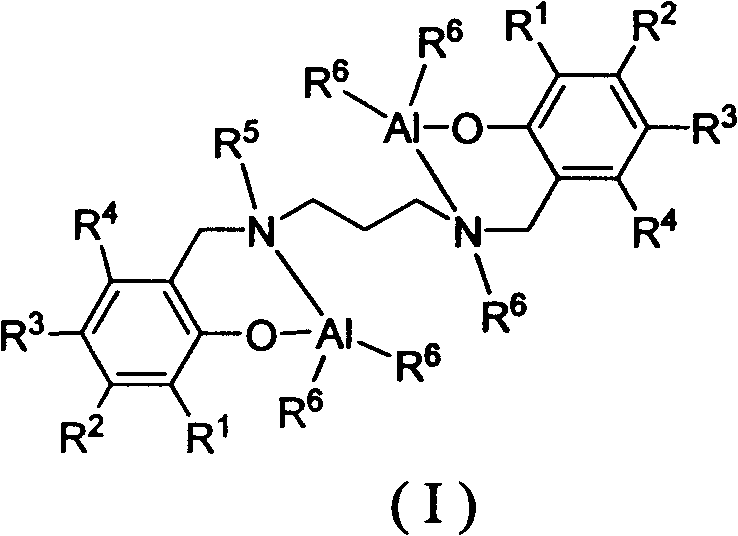
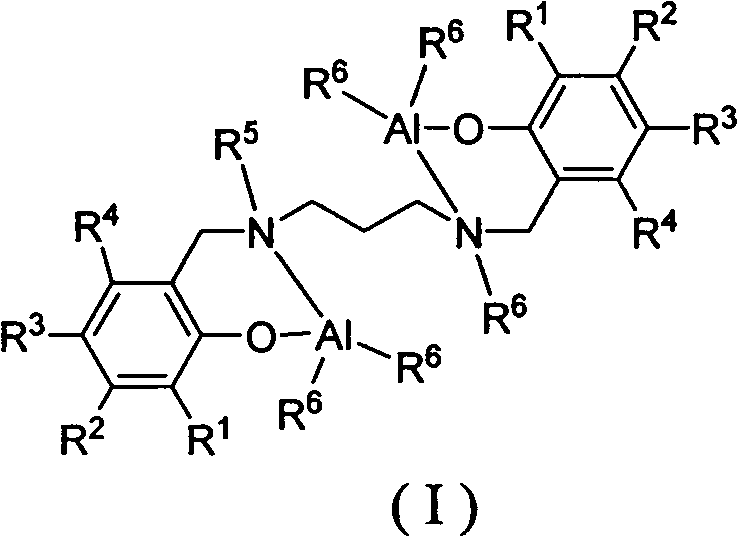
Lactide-epsilon-caprolactone copolymerization catalyst and copolymerization method
A technology of co-polymerization catalyst and lactide, which is applied in the field of lactide/ε-caprolactone co-polymerization catalyst, can solve the problems such as uncontrollable microstructure, and achieve the effects of microstructure controllability, simple reaction method and high catalytic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
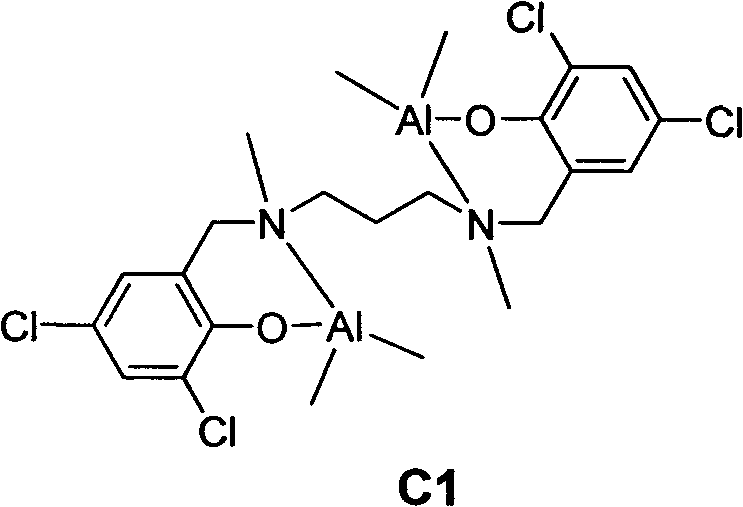
[0027] C1-catalyzed copolymerization of racemic lactide and ε-caprolactone to form block copolymers
[0028]
[0029]Under the protection of argon, add racemic lactide (0.432g, 3.0mmol) into the polymerization bottle, dissolve it with 3.0mL of toluene, weigh 0.030mmol of aluminum catalyst C1 and 0.090mmol of n-dodecyl alcohol into the polymerization bottle for 70 °C for 24 hours. Weigh ε-caprolactone (0.456 g, 4.0 mmol) into a polymerization bottle, control the reaction temperature to 90° C., react for 2 hours, and add petroleum ether to terminate the reaction. The solvent was removed, the residue was dissolved in dichloromethane, and methanol was added to precipitate the polymer. Vacuum dried for 24h. Caprolactone conversion: 66%, lactide conversion: 100%, M n =7.1×10 3 g / mol, molecular weight distribution PDI=1.35.
Embodiment 2
[0031] C2-catalyzed copolymerization of racemic lactide and ε-caprolactone to form block copolymers
[0032]
[0033] Under the protection of argon, add ε-caprolactone (0.342g, 3.0mmol) into the polymerization bottle, dissolve it with 3.0mL toluene, weigh 0.030mmol of aluminum catalyst C2 and 0.060mmol of isopropanol into the polymerization bottle and polymerize at room temperature 1 Hour. Racemic lactide (0.288 g, 2.0 mmol) was weighed and added into a polymerization bottle, the reaction temperature was controlled at 70° C., and the reaction was carried out for 20 hours, and petroleum ether was added to terminate the reaction. The solvent was removed, the residue was dissolved in dichloromethane, and methanol was added to precipitate the polymer. Vacuum dried for 24h. Caprolactone conversion: 100%, lactide conversion: 90%, M n =1.0×10 4 g / mol, molecular weight distribution PDI=1.16, polymer glass transition temperature and crystallization temperature: 30°C and 98°C, po...
Embodiment 3
[0035] C3 Catalyzed Copolymerization of L-Lactide and ε-Caprolactone to Block Copolymers
[0036]
[0037] Under the protection of argon, add ε-caprolactone (0.342g, 3.0mmol) into the polymerization bottle, dissolve it with 3.0mL toluene, weigh 0.010mmol of aluminum catalyst C3 and 0.010mmol of amyl alcohol, add it to the polymerization bottle and polymerize at room temperature for 4 hours . Weighed L-lactide (0.432g, 3.0mmol) into a polymerization bottle, controlled the reaction temperature to 100°C, reacted for 48 hours, and added petroleum ether to terminate the reaction. The solvent was removed, the residue was dissolved in dichloromethane, and methanol was added to precipitate the polymer. Vacuum dried for 24h. Caprolactone conversion: 100%, lactide conversion: 82%, M n =6.5×10 4 g / mol, molecular weight distribution PDI=1.22.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com