Photon counting full-spectrum direct reading fluorescence spectrometer
A fluorescence spectrometer and photon counting technology, applied in the new fluorescence spectrometer field, can solve the problems of high production and operation cost, complex structure and high sensitivity, and achieve the effect of low production and operation cost, large linear dynamic range and good operation stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
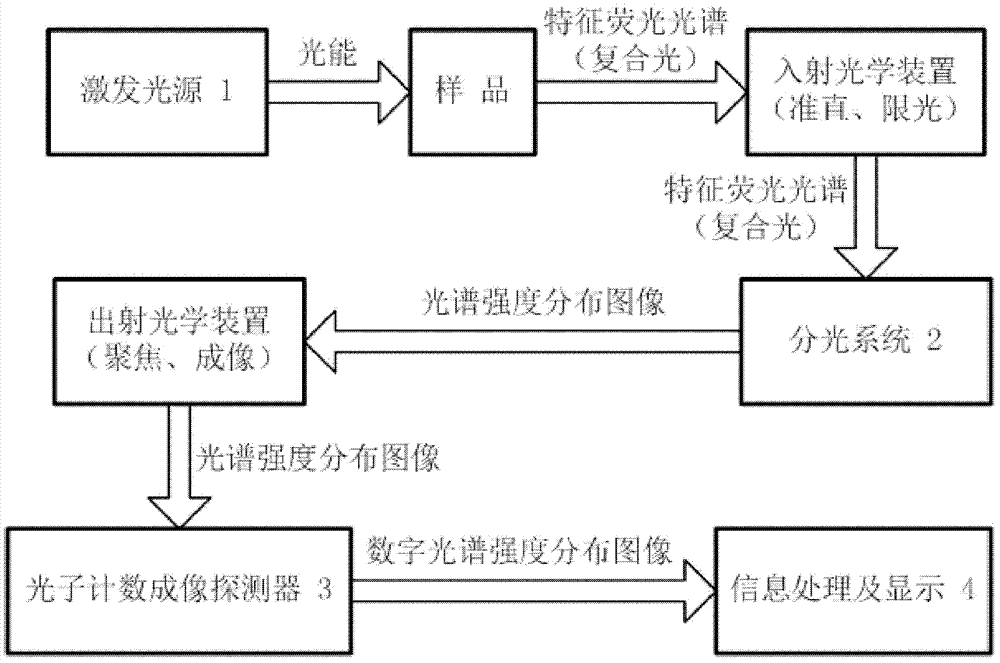
[0065] Such as figure 1 As shown, a photon counting full-spectrum direct-reading fluorescence spectrometer is mainly composed of an excitation light source 1, a spectroscopic system 2, a photon counting imaging detector 3, and information processing and display 4:
[0066] The excitation light source 1 is a light source device capable of providing light energy to excite the sample to generate a characteristic fluorescence spectrum;
[0067] Spectroscopic system 2 is a dispersion spectroscopic device capable of dispersing composite light into monochromatic light or spectral intensity distribution images;
[0068] The photon counting imaging detector 3 is an image sensor capable of position-sensitive detection and photon counting;
[0069] Information processing and display 4 is used to receive and process optical images, and express the processing and analysis results in various graphic forms that are easy for people or machines to understand;
[0070] The optical connections...
Embodiment 2
[0088] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that: on the basis of the photon counting imaging detector 3 described in Embodiment 1, a semiconductor layer can be added between the MCP output terminal and the position-sensitive anode, and the MCP There is a gap between the output terminal and the semiconductor layer, the semiconductor layer is plated on the insulating substrate, and the DC high-voltage power supply is electrically connected to the semiconductor layer through high-voltage leads or conductive electrodes (such as Figure 4shown). At this time, the above step S540, that is, the physical process of collecting the electron cloud by the position-sensitive anode, evolves into: the electron cloud first crosses to the semiconductor layer under the action of the accelerating bias electric field, and then is induced to the position-sensitive anode through charge induction.
Embodiment 3
[0090] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that: on the basis of the fluorescence spectrometer described in Embodiment 1, the excitation light source 1 can use a variety of different types of light source devices, either a continuous light source or a continuous wavelength Or discretely tunable lasers, sharp-line light sources or fixed-wavelength lasers (preferably continuous light sources) can also be used, from which a variety of photon counting full-spectrum direct-reading fluorescence spectrometers based on different excitation light sources can be derived.
[0091] For example: a continuous light source can use a high-intensity short-arc xenon lamp. At this time, a variety of characteristic fluorescence spectra and multiple characteristic fluorescence spectral lines produced by various material components can be analyzed; a sharp-line light source can use a high-intensity hollow cathode lamp. At this time It can analyze multiple characteristic flu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com