Glass surface nanofabrication method based on friction-induced selective etching
A glass surface, nano-processing technology, applied in the process of producing decorative surface effects, nano-technology, metal material coating process, etc. The effect of improving processing efficiency and low processing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The first specific embodiment of the present invention is a method for nanofabrication of glass surfaces based on friction-induced selective etching, and its specific operation method is:
[0038] A. Install the scanning probe with a spherical tip on the atomic force microscope, fix the cleaned glass on the sample stage, start the atomic force microscope, and apply a load no higher than the critical load F to the probe c The fixed load F, and the probe scans the glass surface at a set scanning rate according to the square surface scanning trajectory, and the number of scanning cycles N is one.
[0039] B. Place the scanned glass in a HF solution with a mass concentration of 10%, and corrode it for 5 seconds.
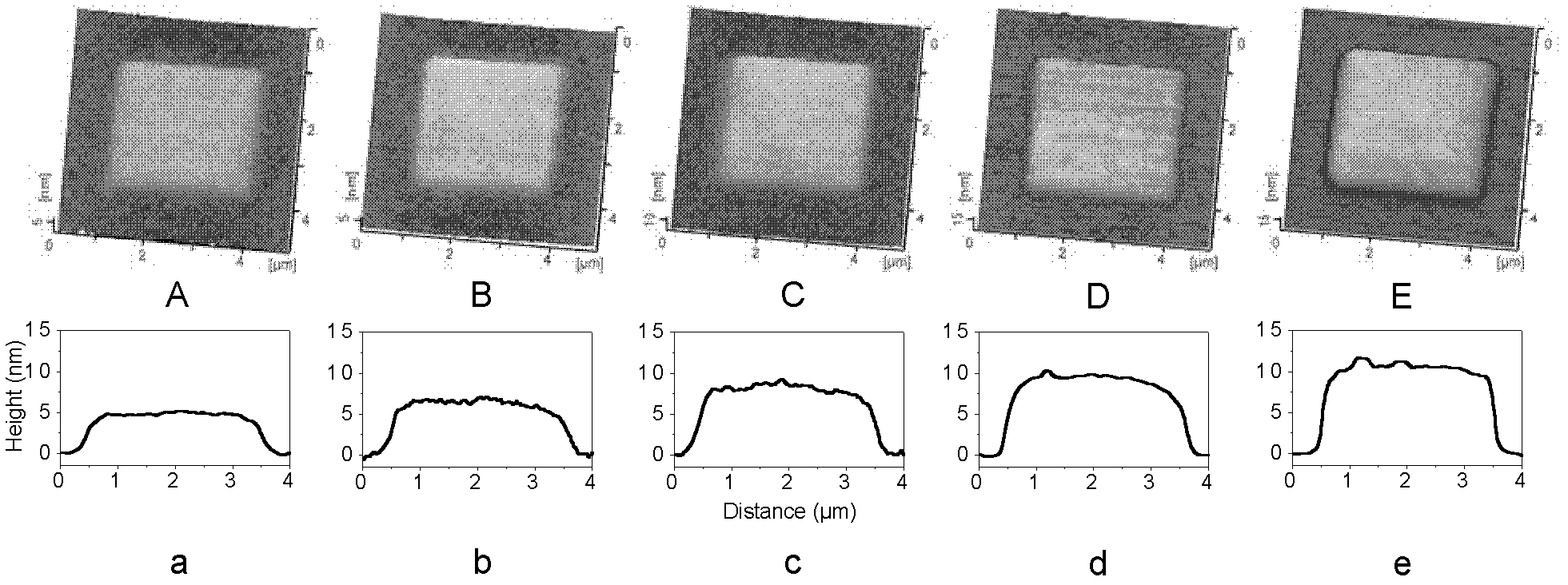
[0040] The following are the results of five specific processing tests carried out using the method of this example:
[0041] The scanning areas of the five specific processing tests are all 3 μm×3 μm, the scanning speed v is 12 μm / s, and the fixed load F is 5 μN...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The specific operation method is: a glass surface nano-processing method based on friction-induced selective etching, and the specific operation method is:
[0047] A. Install the scanning probe with a spherical tip on the atomic force microscope, fix the cleaned glass on the sample stage, start the atomic force microscope, and apply a load no higher than the critical load F to the probe c The fixed load F, and make the probe scan the glass surface according to the square surface scanning trajectory, and scan with the set number of cycles and the set scan rate v;
[0048] B. Place the scanned glass in an HF solution with a mass concentration of 20%, and corrode it for 5 seconds.
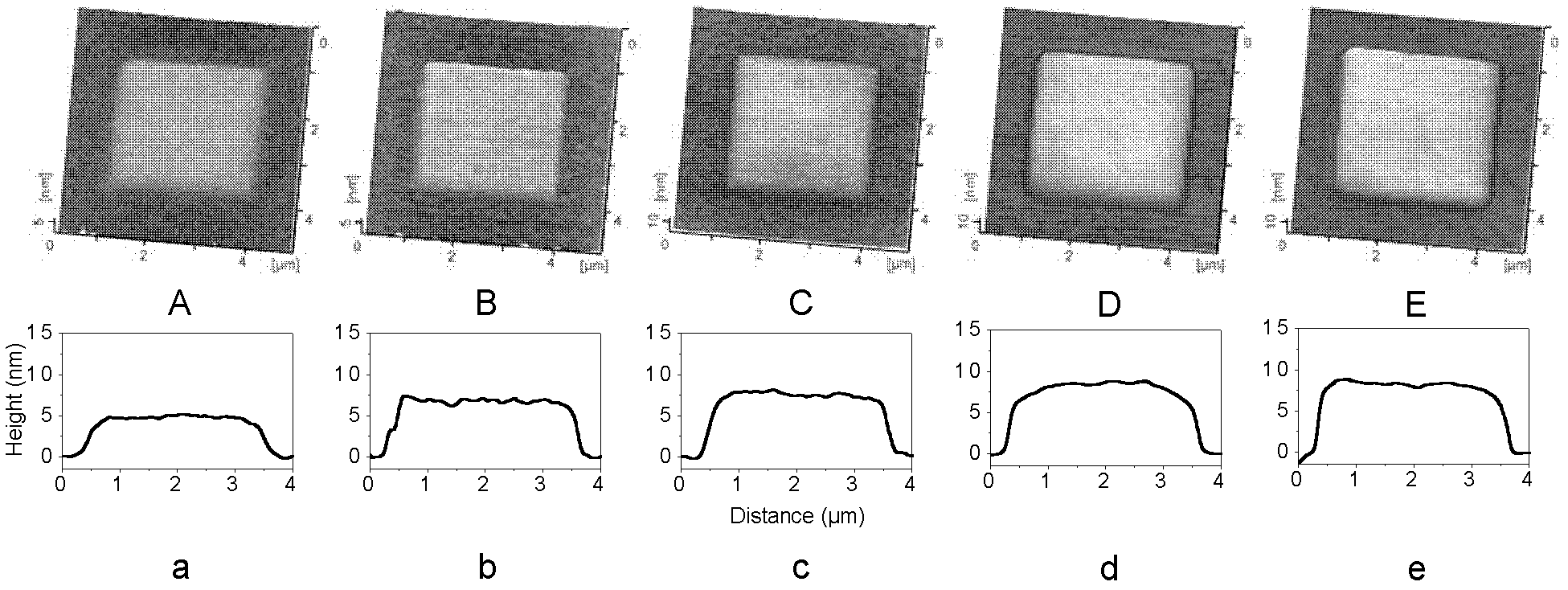
[0049] The following are the results of five specific processing tests carried out using the method of this example:
[0050] The specific scanning area of each specific processing test is 3 μm×3 μm, the applied constant load F is 5 μN, and the set scanning rate v is 12 μm / s; the set scanni...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Its specific operation method is:
[0055] A. Install the scanning probe with a spherical tip on the atomic force microscope, fix the cleaned glass on the sample stage, start the atomic force microscope, and apply a load no higher than the critical load F to the probe c The fixed load F, and the probe follows the scanning trajectory of the square surface scanning, and scans the glass surface at a set scanning rate with the number of cycles N being 1.
[0056] B. Place the scanned glass in an HF solution with a mass concentration of 15%, and corrode it for 10 seconds.
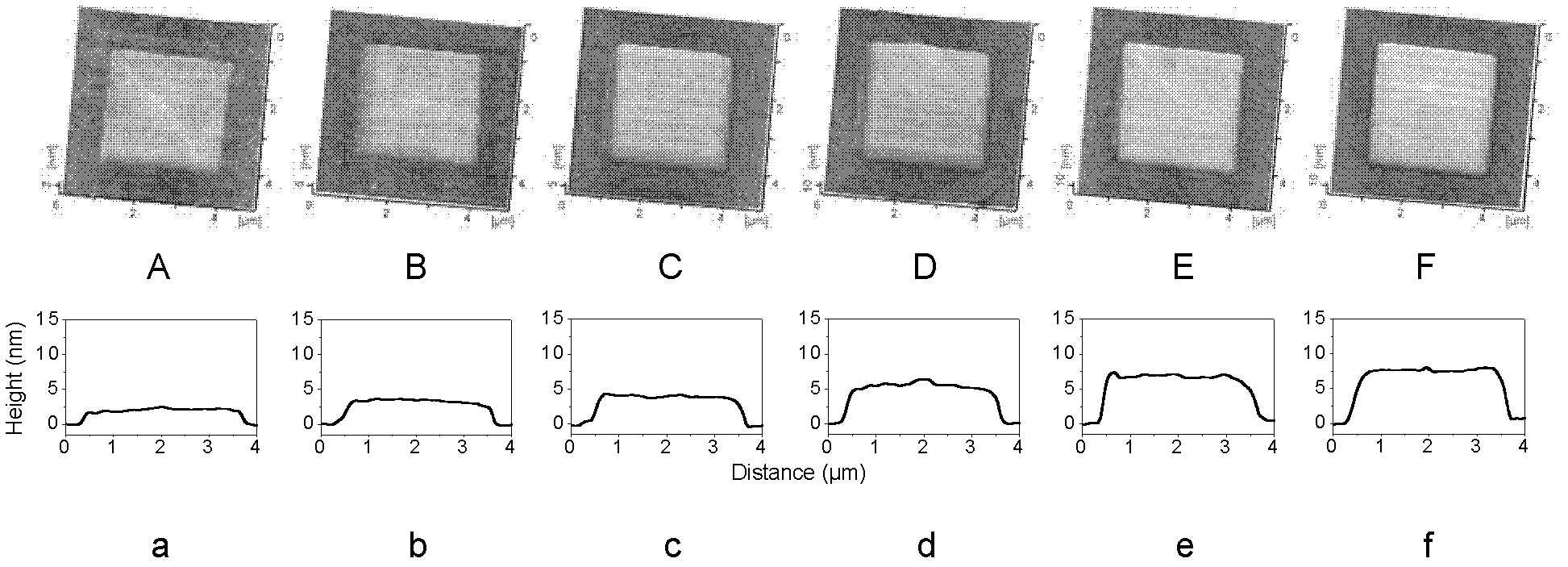
[0057] The following are the results of six specific processing tests carried out using the method of this example:
[0058] The specific scanning area of the six specific processing tests is 3μm×3μm, the fixed load F is 5μN, and the scanning speed v is 90μm / s, 30μm / s, 12μm / s, 6μm / s, 3μm / s, 1.2μm / s.
[0059] image 3 It is the (silicon nitride probe scanning) topography diagram of the glass obtaine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com