Nitride semiconductor light-emitting device
A technology of nitride semiconductors and light-emitting elements, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of light output reduction and absorption ratio increase of light-emitting elements, so as to prevent light output reduction, suppress heat generation, and increase current Effects of Diffusion and Light Uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
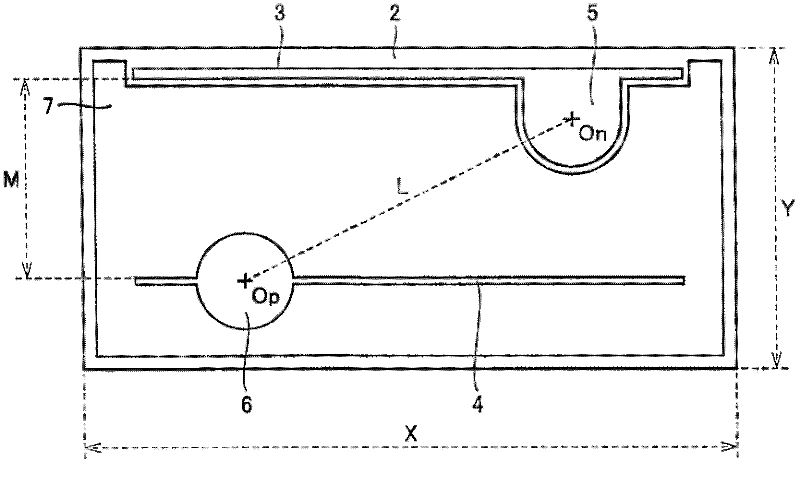
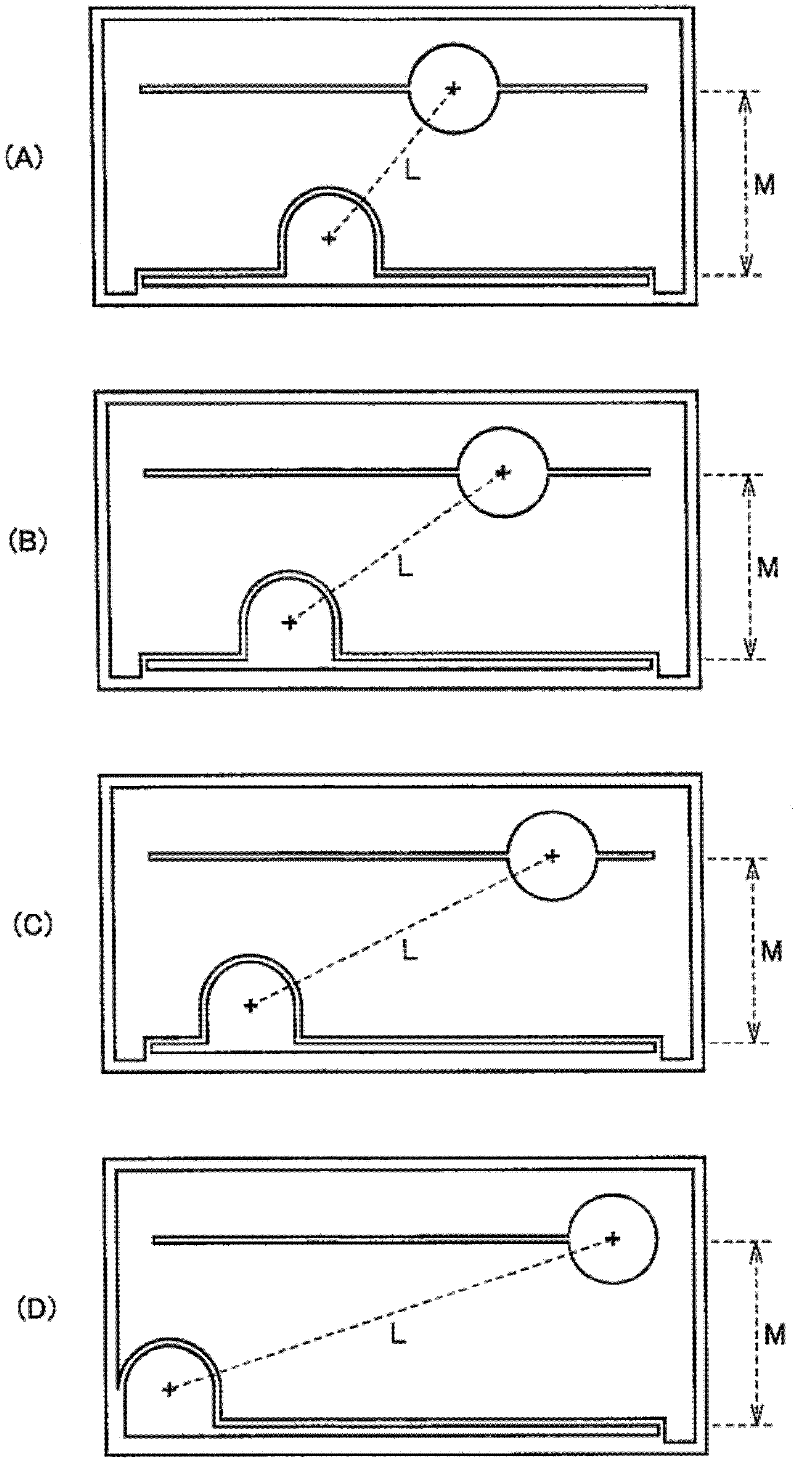
[0044] In embodiment 1 of the present invention, make and figure 1 and figure 2 A light-emitting element similar to the light-emitting element schematically illustrated in . image 3 (A) is a schematic plan view showing the light-emitting element of the first embodiment.
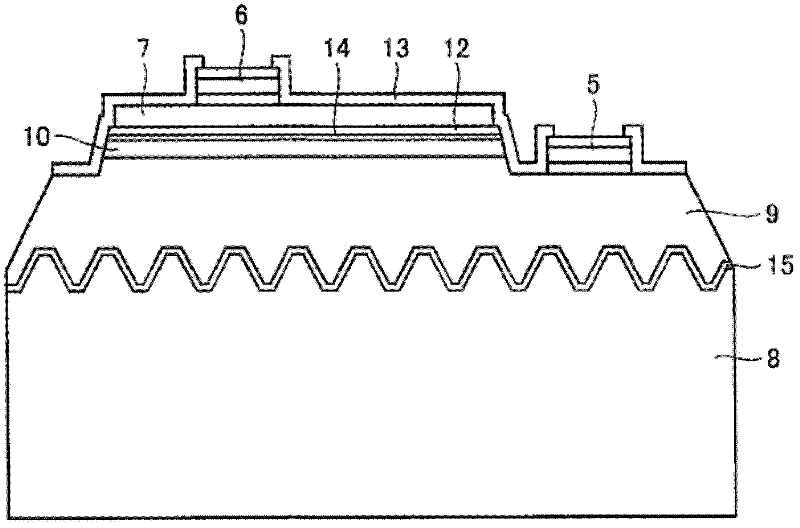
[0045] Such as figure 2 As schematically shown, in the light-emitting element of Example 1, an n-type nitride semiconductor layer 9 is deposited via an AlN buffer layer 15 on a sapphire substrate 8 having a main surface in the (0001) plane direction. The n-type semiconductor layer 9 includes: a GaN base layer with a thickness of 9 μm and a Si-doped n-type GaN contact layer with a thickness of 2 μm deposited at a substrate temperature of about 1000° C., with a carrier concentration of about 6×10 18 cm -3 .
[0046] A nitride semiconductor active layer 10 is deposited on the n-type semiconductor layer 9 . The active layer 10 has a multiple quantum well structure. On the basis of a substrate temperatur...
Embodiment 2
[0066] image 3 (B) is a plan view schematically showing the light-emitting element of Example 2 of the present invention. Compared with Example 1, the light-emitting element of this Example 2 is only different in the value of the ratio M / L. In Example 2, the distance M between the branch electrodes and the distance L between the centers of the p-side and n-side electrode pads The ratio M / L was reduced to 0.7. By comparison image 3 (A) and image 3 (B) just can see clearly the change of M / L value in embodiment 1 and embodiment 2.
[0067] From Figure 6 (B) and Figure 6 (C) It can be seen that in the case of driving the light-emitting element with a current of 100mA, wherein the current density>90A / cm 2 , current injection area: 1.10×10 -3 cm 2 , the light output Po (mW) and power efficiency WPE (%) of the light emitting element (M / L=0.70) of Example 2 were the highest.
Embodiment 3
[0069] image 3(C) is a plan view schematically showing a light-emitting element according to Example 3 of the present invention. Compared with the other embodiments, the light-emitting element of Example 3 is only different in the value of the ratio M / L, and the ratio M / L of the distance M between the branch electrodes to the distance L between the centers of the p-side and n-side electrode pads is further improved. Reduced to 0.5.
[0070] Figure 7 An optical photograph taken with a CCD camera (HAMAMATSU C8000-20) of the light emitting state of the light emitting element is shown. The optical photographs attached here are shown as black and white shaded photographs, but the original optical photographs are shown in red, orange, yellow, green, light blue, blue, and navy in order from areas with more light to areas with less light. A color photograph of wavelength variation. When the color photo is converted into a black and white photo, green at an intermediate wavelengt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com