Vector control apparatus and motor control system
A vector control, motor technology, applied in vector control system, motor control, motor generator control and other directions, can solve the problem of not being able to correctly estimate the shaft error and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0067] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
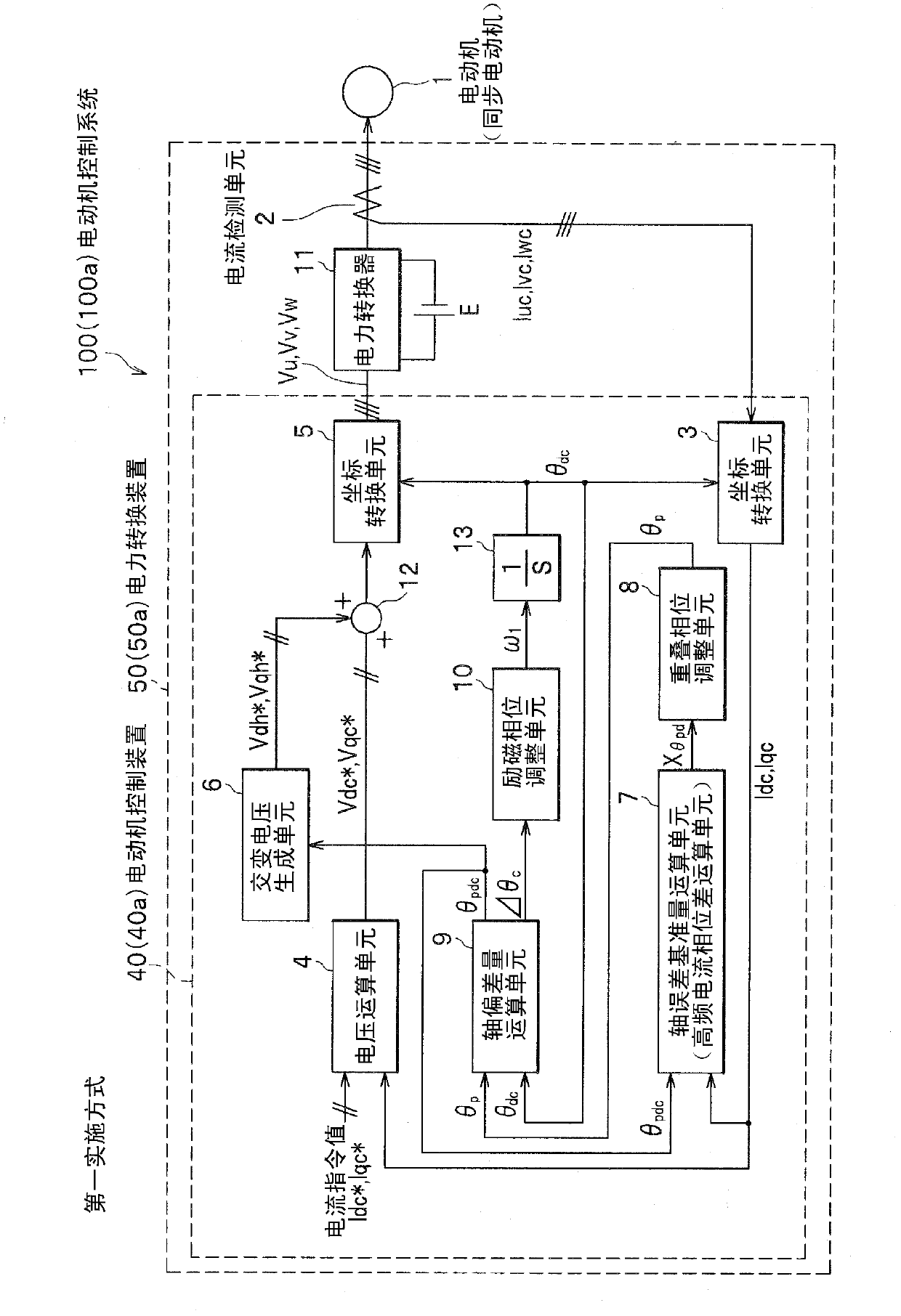
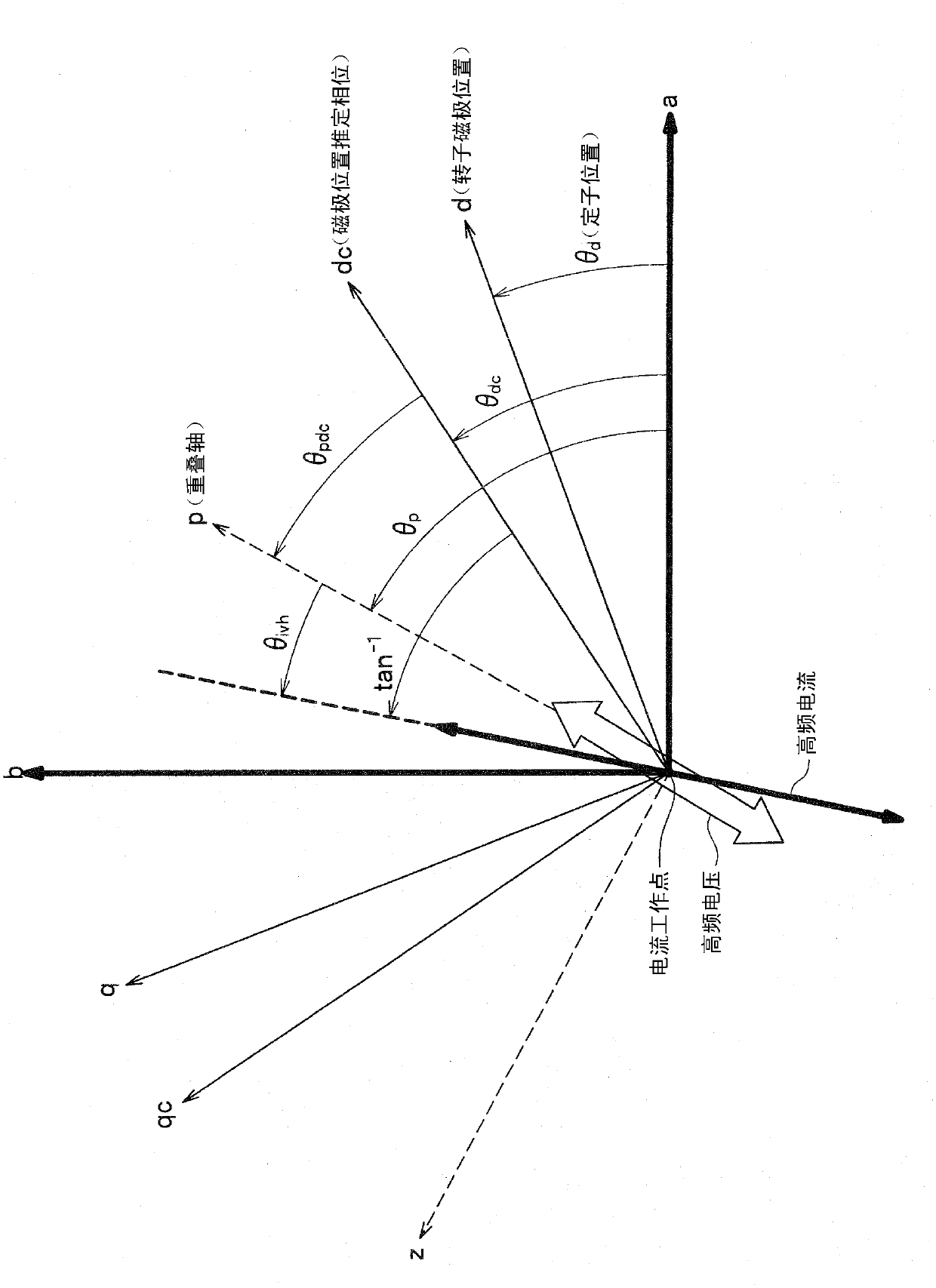
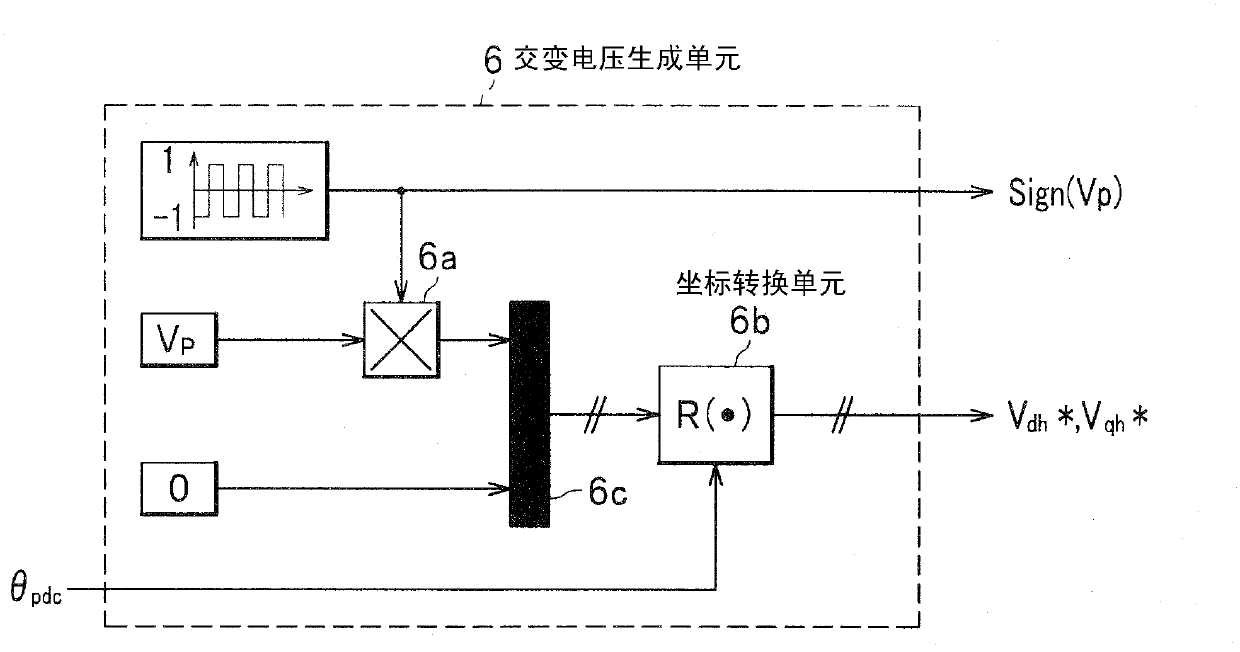
[0068] figure 1 is a configuration diagram of a motor control system according to the first embodiment of the present invention; figure 2 It is a diagram showing the definition of the coordinate system and symbols used in motor control.
[0069] exist figure 1 Among them, the motor control system 100 has a power conversion device 50 and a motor 1 , and the power conversion device 50 ( 50 a ) has a motor control device 40 ( 40 a ), a power converter 11 and a current detection unit 2 .
[0070] The current detection unit 2 detects three-phase currents Iu, Iv, and Iw flowing in the motor 1, and outputs three-phase current signals Iuc, Ivc, and Iwc. Power converter 11 converts DC power from DC power supply E into three-phase AC power based on three-phase command voltages Vu, Vv, and Vw generated by motor control device 40 , and supplies the three-phase AC powe...
no. 2 approach
[0133] Figure 10 It is a configuration diagram of a motor control system according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0134] and figure 1 Compared with the configuration of the motor control system 100c of this embodiment, the second shaft deviation calculation unit 101 that estimates the shaft deviation Δθ (= θpd) from the induced voltage of the motor 1 is added, and the excitation phase adjustment unit 10 is changed to give Either one of the axis deviation calculation unit 9 and the second shaft deviation calculation unit 101 is selected as the excitation phase switching adjustment unit 102 for the switching function of the shaft deviation. Since the axis deviation amount after switching is Δθh, the symbol of the output signal of the axis deviation amount calculating means 9 is changed to Δθh. The second axial misalignment calculation unit 101 estimates the axial misalignment Δθemf by (Formula 10) using the characteristic parameters of the electric motor. ...
no. 3 approach
[0145] In each of the embodiments described above, although a synchronous motor was used as the motor, an induction motor can also be used.
[0146] Figure 13 It is a configuration diagram of a motor control system as a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0147] The motor control system 100 d is different from the first and second embodiments in that an induction motor 131 is used instead of the motor 1 and a slip compensation unit 132 and an adder 14 are added.
[0148] In the case of the induction motor 131, although there is no saliency due to the shape of the rotor, the saliency of the inductance is equivalently exhibited due to the magnetic saturation phenomenon caused by the secondary magnetic flux excited by the induced current on the primary side Therefore, the method of the first embodiment can be used. That is, since the rotor (not shown) of the induction motor has no magnets, the phase adjustment unit 8 ( Figure 5 ) only needs to make the d-axis follow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com