LED (Light-emitting Diode) device and wafer-level LED device as well as packaging structure of LED device and wafer-level LED device
A technology of LED devices and packaging structures, applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effects of improving reliability, preventing absorption and scattering, and improving production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a schematic structural diagram of an existing LED chip, which includes a conventional sapphire substrate 11, N-type gallium nitride 12, light emitting layer 13, P-type gallium nitride 14, P electrode bumps 16 and N electrode bumps 17 , before flip-chip, the LED chip is located on the side of the P-type gallium nitride, which is the upper surface in the usual sense.
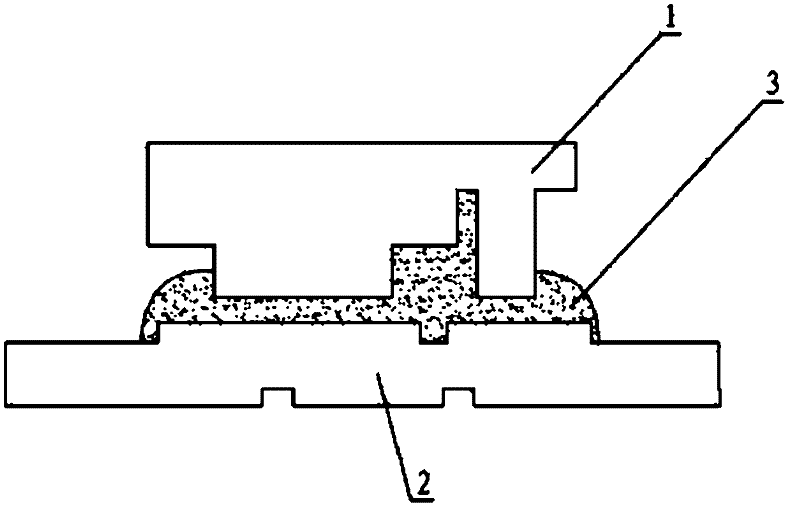
[0038] Such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment discloses an LED device, including an LED chip 1 and a substrate 2, the LED chip 1 is flip-chip mounted on the substrate 2, and the electrical connection between the LED chip 1 and the substrate 2 is realized through the ACF 3, so that the two The electrical connection between them is more reliable. Wherein, the ACF includes bonding materials and conductive particles, the bonding materials include thermosetting materials and thermoplastic materials; the conductive particles include any of the following metal flexor materi...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
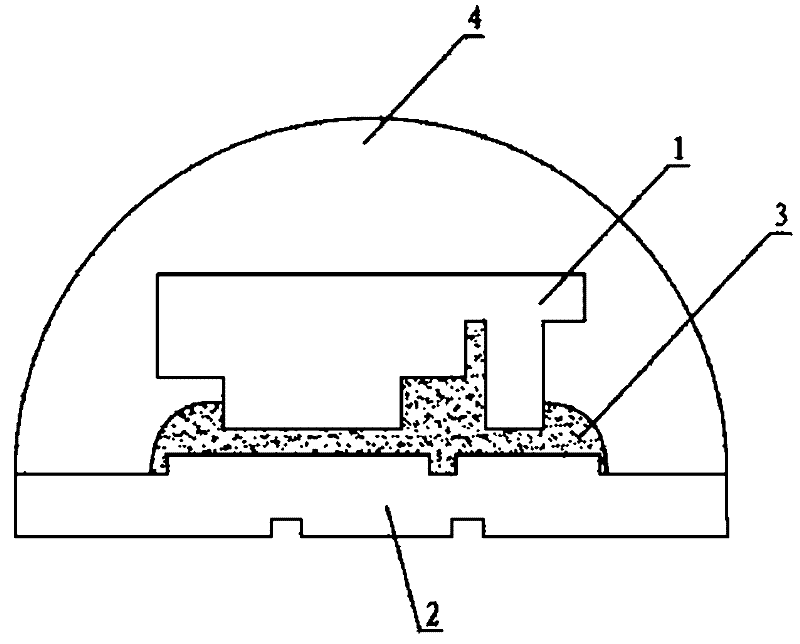
[0051] In this embodiment, gold flex wires 26 are used to connect the first gold flex electrode layer 22 and the second gold flex electrode layer 24 from the side to the bottom of the substrate 2, and the optical structure layer 42 in the outer packaging layer 4 has a square shape. The optical structure layer 42 is used for the adjustment of the external shape, which can realize the different optical type requirements of the packaging structure, and its material can be polycarbonate (PC), polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), silica gel (Silicone), poly One or more of propylene (EP), polyethylene phthalate (PET), and glass. The square shape structure can be made into a small volume and easy to form.
Embodiment 3
[0053] This embodiment also discloses an LED device. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the specific position of the reflective layer is slightly changed, such as Figure 8 Shown:
[0054] Its LED chip 1 includes a conventional sapphire substrate 11, N-type gallium nitride 12, light-emitting layer 13, P-type gallium nitride 14, P-electrode bumps 16 and N-electrode bumps 17; An ohmic contact layer 18 is grown on the P-type gallium nitride 14, and the conductive or non-conductive reflective layer 15 covers the outer surface of the ohmic contact layer on both sides of the P electrode bump of the LED chip. The P electrode bump 16 is directly electrically connected with the P-type gallium nitride 14 through the ohmic contact layer 18. At this time, the reflective layer 15 can be a distributed Bragg reflective layer (non-conductive reflective layer) composed of aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, and titanium dioxide. ), or the reflective layer 15 is a gol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com