Thermal treatment process of homogenizing and fine graining of steel carbide of hot die
A hot work die steel and carbide technology, applied in heat treatment equipment, heat treatment process control, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of uniform refinement gap, undisclosed refined carbide size, undisclosed heat treatment process, etc. Improved performance and service life, the effect of tissue performance optimization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1. 100 mm × 100 mm × 500 mm Dievar steel was placed in a furnace at room temperature and heated to 850 °C for 1 h, then directly raised to 1180 °C for 4 h, then cooled to 500 °C with the furnace, and then air-cooled to room temperature. Then install the furnace and heat it to 600 °C for 1 h, then raise it to 880 °C for 50 h, then cool it to 500 °C at a rate of 20 °C / h, and then cool it to room temperature with the furnace.
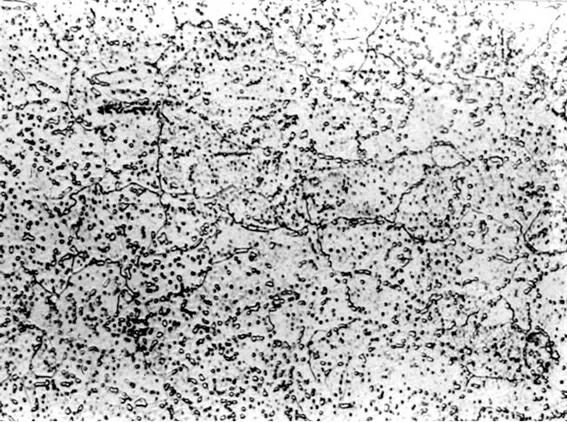
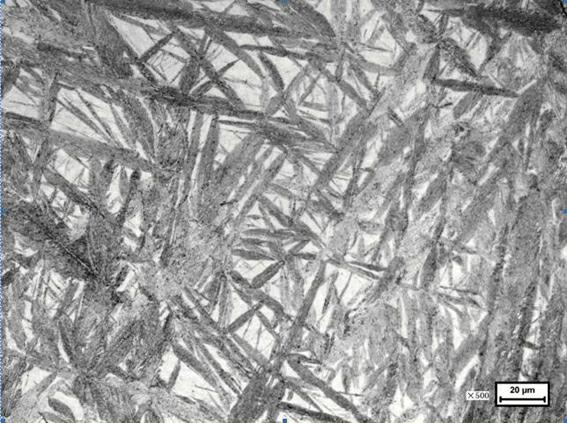
[0023] Among them, the metallographic structure diagram of martensite or bainite + austenite obtained after the first stage treatment is shown in image 3 , after the second stage of treatment, the metallographic structure diagram of uniform fine-grained carbides distributed on the ferrite matrix is obtained. Figure 4 , the carbide particles in the tissue were measured by SEM in the range of 200 nm to 1200 nm, and the measured hardness values were 153, 151, and 152 HB.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2. 200 mm×200 mm×500 mm Dievar steel was placed in a furnace at room temperature and heated to 600 °C and 850 °C for 1.5 h, respectively, and then raised to 1210 °C for 8 h, then cooled to 450 °C with the furnace and then air-cooled to room temperature. Afterwards, the furnace was heated to 600 °C and kept for 1.5 h, then raised to 900 °C and kept for 80 h, then cooled to 400 °C at a rate of 10 °C / h, and then cooled to room temperature with the furnace.
[0025] After heat treatment, the carbide particles in the tissue were measured by SEM in the range of 200 nm to 1200 nm, and the measured hardness values were 168, 172, and 160 HB.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Example 3. 150 mm × 150 mm × 400 mm Hotvar steel was installed at room temperature and then heated to 600 °C and 850 °C for 1.5 hours, respectively, and then heated to 1200 °C for 6 hours, then cooled to 400 °C with the furnace and then air-cooled to room temperature. Afterwards, the furnace was heated to 600 °C and kept for 1.5 h, then continued to heat up to 910 °C and kept for 70 h, then cooled to 450 °C at a rate of 15 °C / h, and then cooled to room temperature with the furnace.
[0027] The carbide particles in the tissue obtained after heat treatment were measured by SEM in the range of 200 nm to 1200 nm, and the measured hardness values were 143, 138, and 140 HB.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com