Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based growth factor gradient release microsphere stent as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of glycolic acid and growth factors, applied in medical science, prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of teratogenic incidence rate and lag in tissue engineering bone research, and achieve good gradient release performance, good cyst formation and film formation performance, and void space rate uniform effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] 1. Construction of homogeneous PLGA microspheres
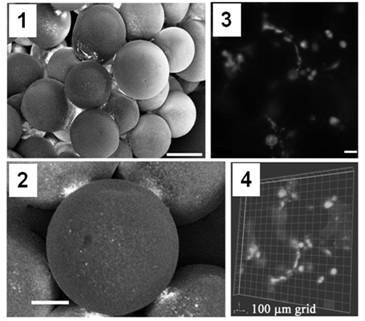
[0039] PLGA microspheres with a diameter of 50 μm were prepared. PLGA composition (lactic acid: glycolic acid with a molar ratio of 1:1, molecular weight of the polymer ~25,000) was randomly polymerized to make PLGA, and PLGA was dissolved in dichloromethane DCM (DCM 30% W / V, mass-volume ratio) to form PLGA Dissolving solution, wherein the mass percentage of PLGA in the PLGA dissolving solution is 3%, the polymer solution controls the waveform generator through an ultrasonic sensor, passes through a small coaxial spray needle, produces homogeneous polymer droplets, and flows into a solution containing 0.5 % (mass percentage content) in the beaker of PVA, form PLGA polymer droplet. Early PLGA polymer droplets were stirred for 3-4 hours, then hardened to form microspheres, filtered and distilled water (~1L) was used to remove residual PVA. Finally, the PLGA polymer microspheres were freeze-dried for 48 hours, stored at ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] 1. Construction of homogeneous PLGA microspheres
[0046] PLGA microspheres with a diameter of 100 μm were prepared. The composition of PLGA (lactic acid: glycolic acid with a molar ratio of 1:0.3, the molecular weight of the polymer is ~25,000) was randomly polymerized to make PLGA, and the PLGA was dissolved with DCM (dichloromethane) (DCM 30% W / V, mass volume ratio) Form a PLGA solution, wherein the mass percentage of PLGA in the PLGA solution is 1%. The polymer solution controls the waveform generator through an ultrasonic sensor, and passes through a small coaxial nozzle to produce homogeneous polymer droplets, which flow into the In a beaker containing 0.8% (mass percent) PVA, PLGA polymer droplets were formed. Early PLGA polymer droplets were stirred for 3-4 hours, then hardened to form microspheres, filtered and distilled water (~1L) was used to remove residual PVA. Finally, the PLGA polymer microspheres were freeze-dried for 50 hours, stored at -20°C, and the...
Embodiment 3
[0052] 1. Construction of homogeneous PLGA microspheres
[0053] PLGA microspheres with a diameter of 150 μm were prepared. The composition of PLGA (lactic acid: glycolic acid with a molar ratio of 1:2, the molecular weight of the polymer ~25,000) was randomly polymerized to make PLGA, and the PLGA was dissolved with DCM (dichloromethane) (DCM 30%W / V, mass-volume ratio) The PLGA solution is formed, wherein the mass percentage of PLGA in the PLGA solution is 5%. The polymer solution controls the waveform generator through an ultrasonic sensor, and passes through a small coaxial nozzle to produce homogeneous polymer droplets, which flow into In a beaker containing 1.0% (mass percent) PVA, PLGA polymer droplets were formed. Early PLGA polymer droplets were stirred for 3-4 hours, then hardened to form microspheres, filtered and distilled water (~1L) was used to remove residual PVA. Finally, the PLGA polymer microspheres were freeze-dried for 45 hours, stored at -20°C, and the di...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com