Method for manufacturing gallium nitride compound semiconductor, and semiconductor light emitting element
A manufacturing method, gallium nitride-based technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the unrealistic characteristics of light-emitting elements, m-plane InGaN layer crystal defects and increased holes, Problems such as decreased crystallinity of the m-plane InGaN layer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0134] As follows, while referring to Figure 14 , while describing an embodiment in which a semiconductor light-emitting element is manufactured according to the method for manufacturing a gallium nitride-based compound semiconductor of the present invention.
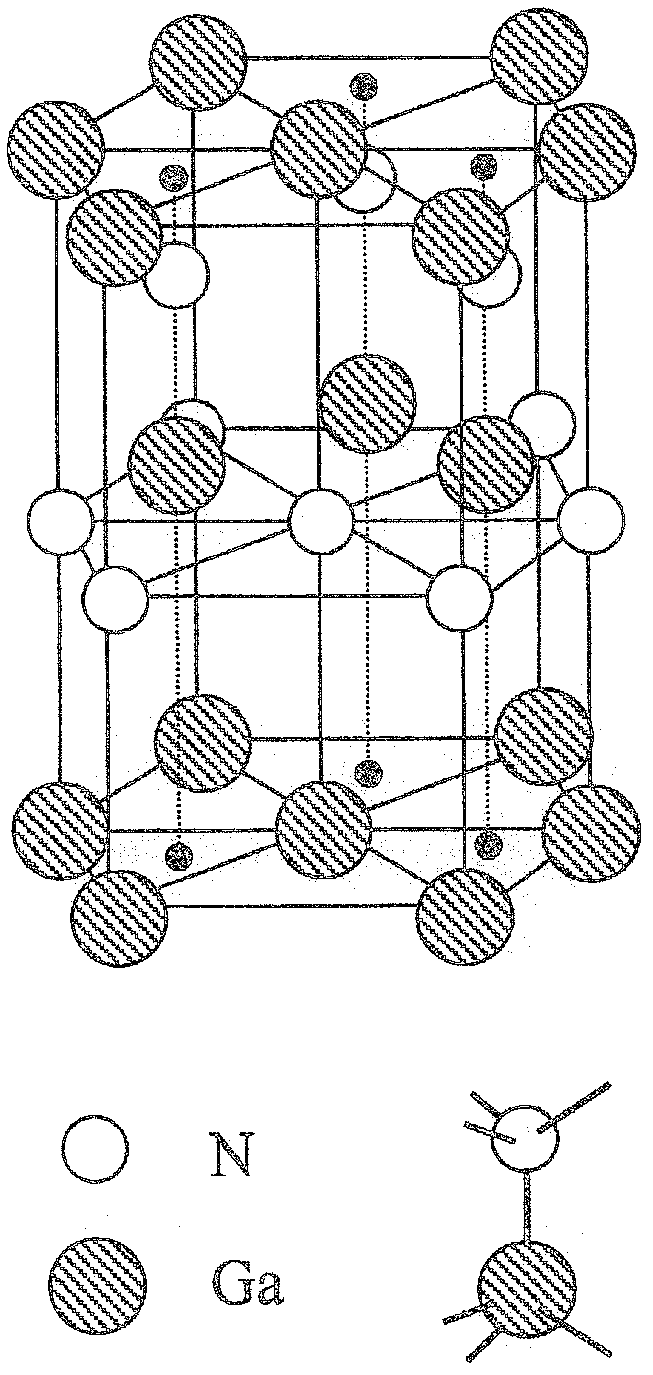
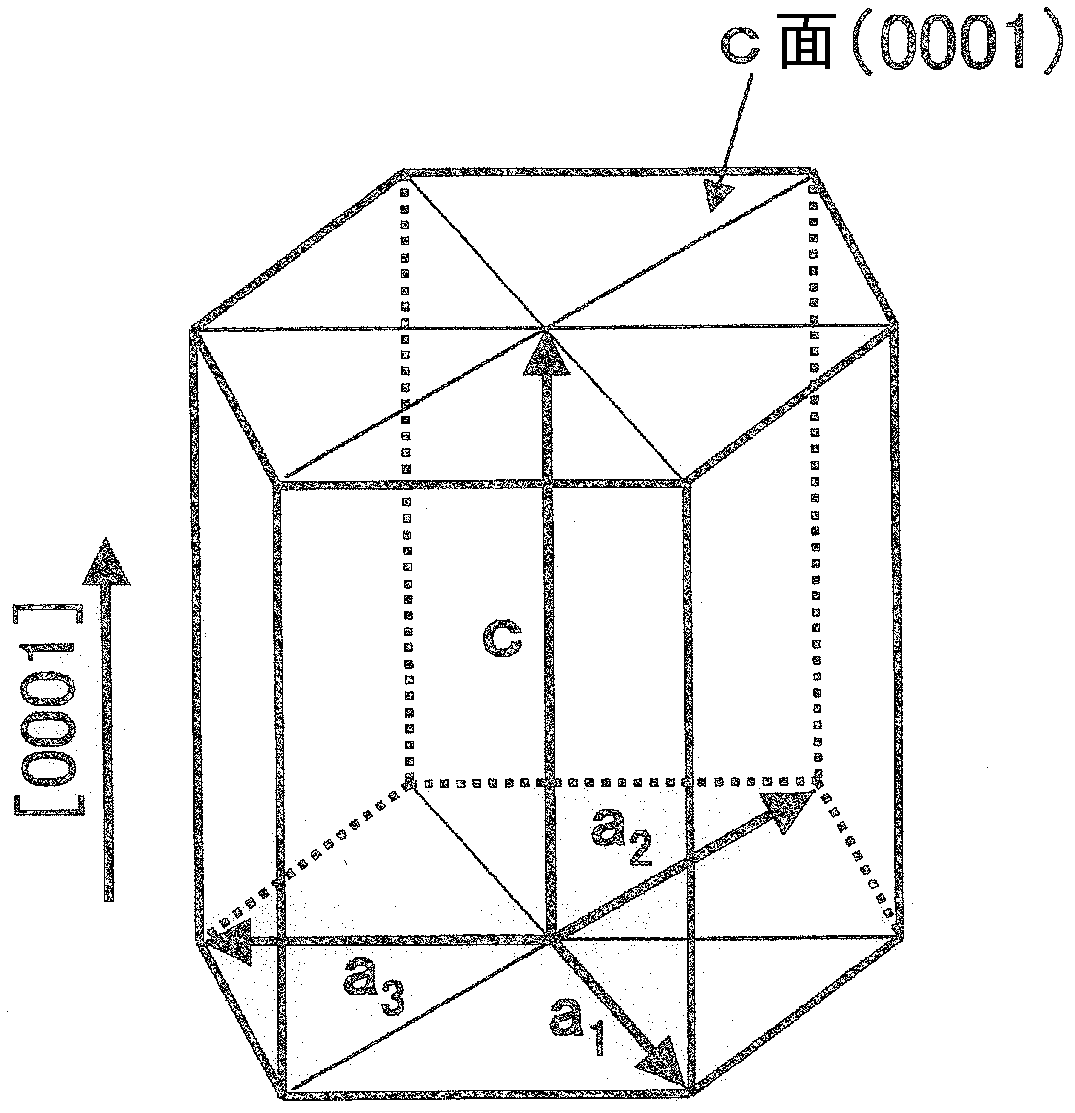
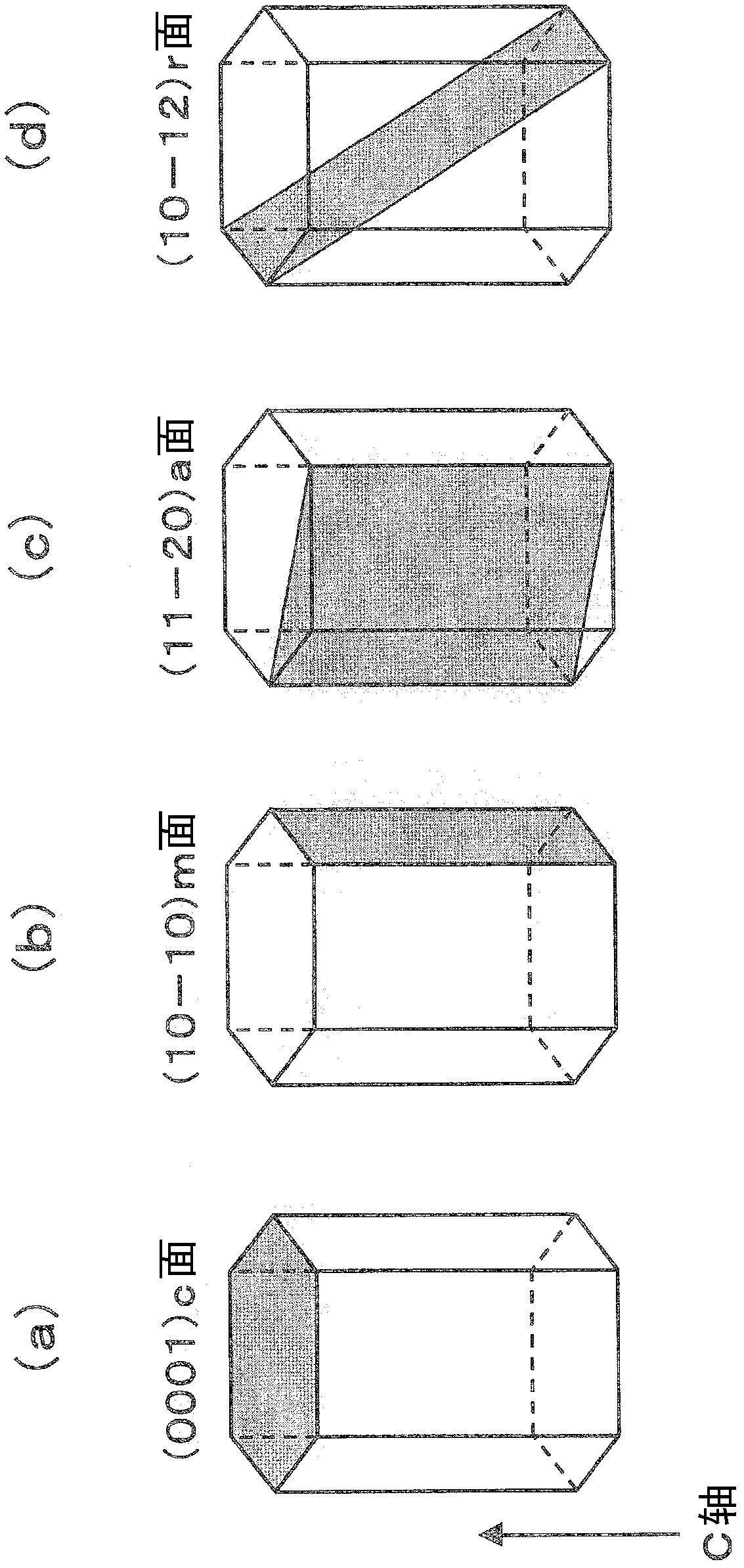
[0135] The substrate 101 for crystal growth used in this embodiment is a substrate on which gallium nitride (GaN) on the (10-10)m plane can grow. A self-supporting substrate of gallium nitride itself exhibiting an m-plane is most preferable, but a substrate exhibiting an m-plane in a 4H or 6H structure of silicon carbide (SiC) having a similar lattice constant may also be used. In addition, sapphire that also exhibits the m-plane may also be used. However, if a substance different from the gallium nitride-based compound semiconductor is used on the substrate, it is necessary to insert an appropriate intermediate layer or buffer layer between the gallium nitride-based compound semiconductor layer deposited on top.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com