Novel metallurgical auxiliary material flux and preparation method thereof
A technology of flux and auxiliary materials, which is applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve problems such as environmental pollution, and achieve a stable effect of flux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] A metallurgical auxiliary material flux is composed of the following components by weight percentage:
[0020] Fe 2 o 3 : 60.0%; CaO: 35.0%;
[0021] The sum of impurity content ≤5.0%.
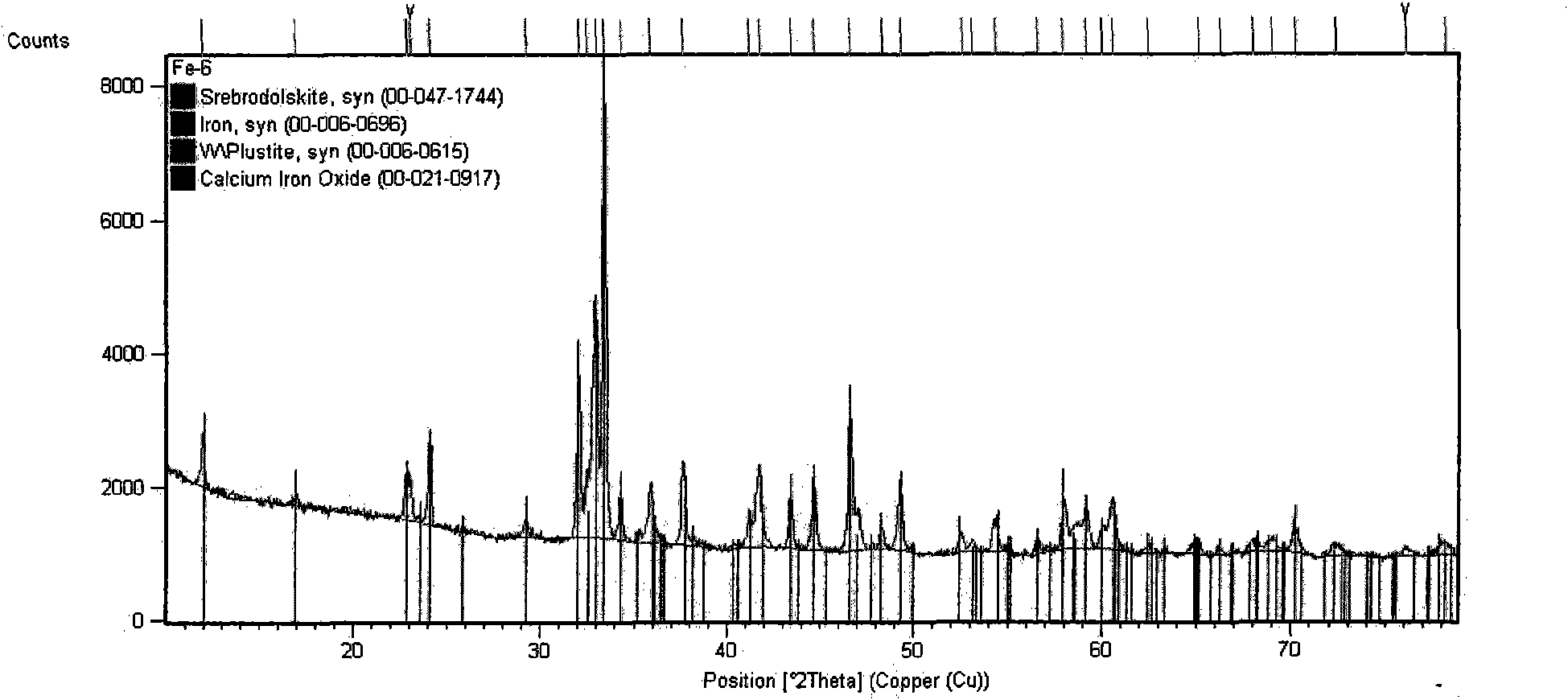
[0022] Its preparation method, the content is to crush the above components into particles with a particle size of ≤20mm, mix them evenly, and then melt at a high temperature of 1350-1400°C, and the phase structure of the melting reaction product is 2CaO·Fe 2 o 3 Lumpy material with main phase. After it is cooled, it is processed into a powder with a fineness of -200 mesh. Melting point: 1277°C. Phase composition (X-ray diffraction pattern) see figure 1 , and its main phase composition is shown in Table 1. In practice, the amount of calcium fluoride added to the metallurgical auxiliary flux is the same as 4.0%. The effect of its implementation is: the sinter cold ore drum index is increased by 5.2%; the reduction temperature of the molten iron reduction pellets in the converte...
Embodiment 2
[0025] A metallurgical auxiliary material flux is composed of the following components by weight percentage:
[0026] Fe 2 o 3 65.0%; CaO 30.0%;
[0027] The sum of impurity content ≤5.0%.
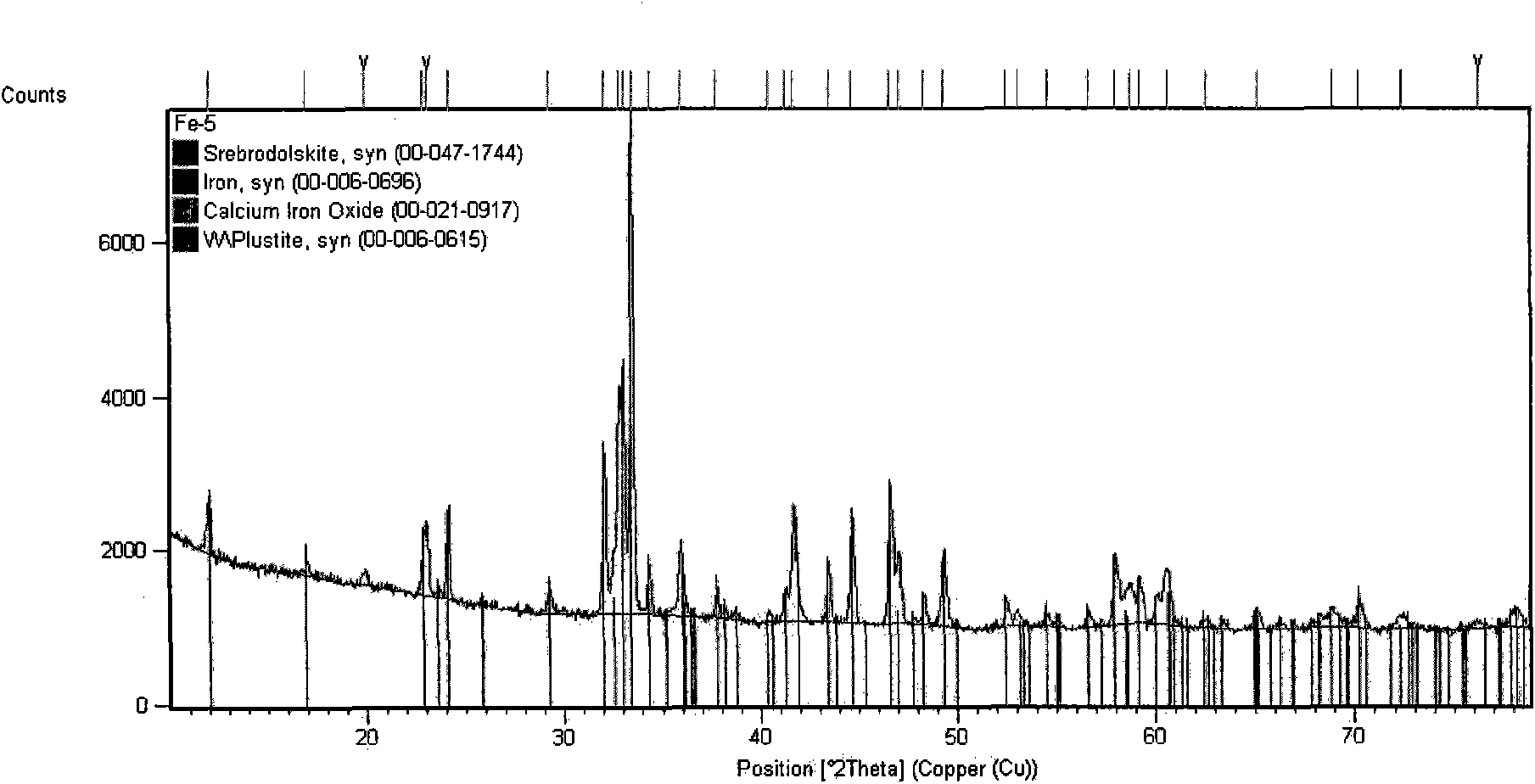
[0028] Its preparation method is to crush the above components into particles with a particle size of 20mm, mix them evenly, and then melt at a high temperature of 1350-1400°C, and the phase structure of the melting reaction product is 2CaO·Fe 2 o 3 Lumpy material with main phase. After it is cooled, it is processed into a powder with a fineness of -200 mesh. Melting point: 1262°C. Phase composition (X-ray diffraction pattern) see figure 2 , and its main phase composition is shown in Table 1. In practice, the amount of calcium fluoride added to the metallurgical auxiliary flux is the same as 4.5%. The implementation effect is as follows: the sinter cold ore drum index is increased by 6.5%; the reduction temperature of the molten iron reduction pellets in the converter is 1395°C...
Embodiment 3
[0031] A metallurgical auxiliary material flux is composed of the following components by weight percentage:
[0032] Fe 2 o 3 65.0%; CaO 30.0%;
[0033] The sum of impurity content ≤5.0%.
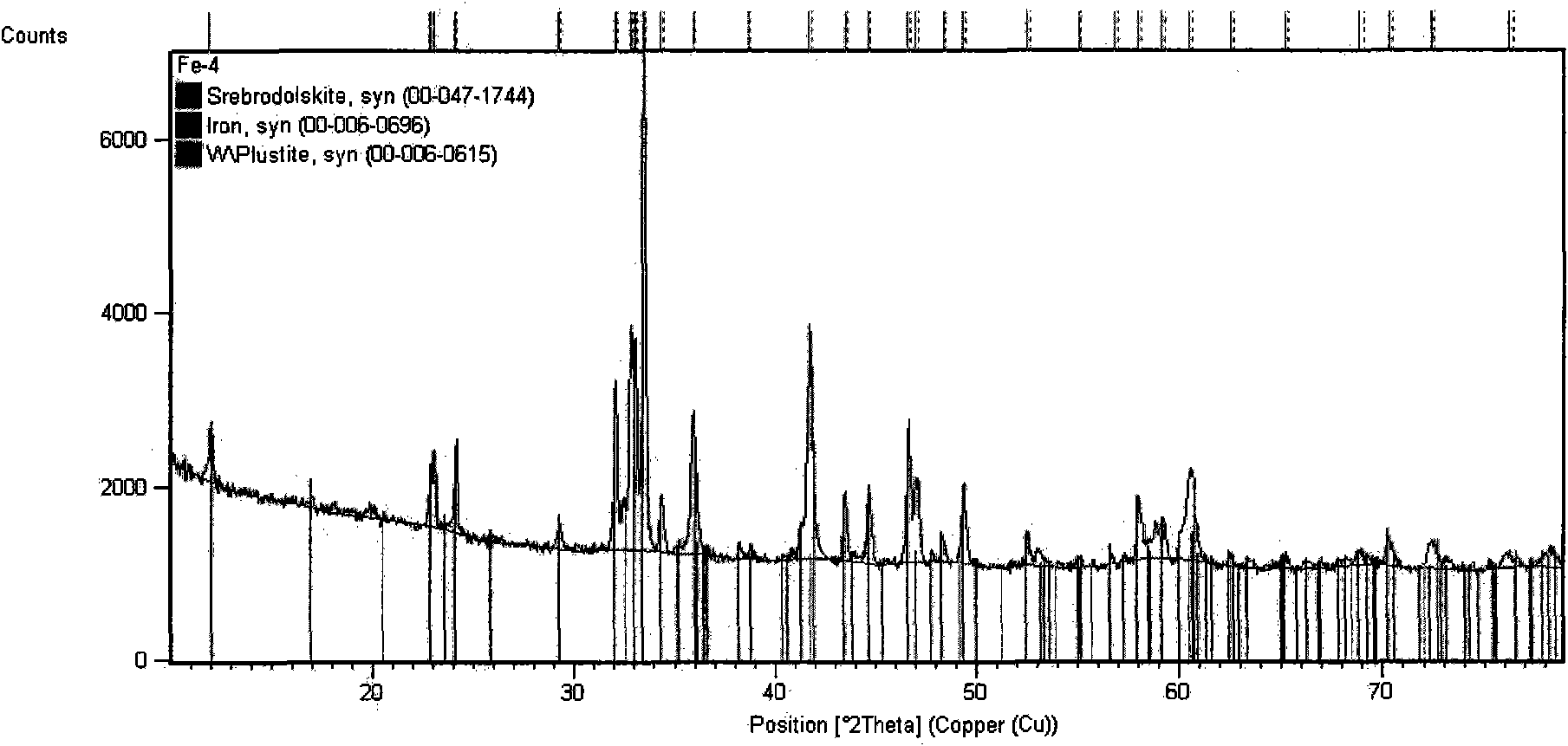
[0034] Its preparation method is to break the above components into particles with a particle size of ≤20mm, mix them evenly, and then melt at a high temperature of 1350-1400°C, and the phase structure of the melting reaction product is 2CaO·Fe 2 o 3 Lumpy material with main phase. After it is cooled, it is processed into a powder with a fineness of -200 mesh. Melting point: 1258°C. Phase composition (X-ray diffraction pattern) see image 3 , and its main phase composition is shown in Table 1. image 3 .In practice, the amount of calcium fluoride added to the metallurgical auxiliary flux is the same as 5.0%. The effect of its implementation is: the sinter cold ore drum index increases by 7.8%; the reduction temperature of the converter molten iron reduction pellets is 1410°C. M...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com