Wheat rhizosphere azotobacter for antagonism of various pathogenic fungi and application of wheat rhizosphere azotobacter
A technology of fungi and bacterial agents, applied in the field of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the wheat rhizosphere, to achieve broad application prospects, high nitrogenase activity, and good inoculation effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1, the isolation and identification of wheat rhizosphere nitrogen-fixing bacteria GD641
[0046] 1. Enrichment and isolation of wheat rhizosphere nitrogen-fixing bacteria GD641
[0047] Take 10g of soil sample (collected from Inner Mongolia, China) and shake it in 90ml of sterile water for 20 minutes to make a turbid solution. Take 5ml and put it into 30ml of nitrogen-fixing bacteria enrichment culture medium ACCC55, 100rpm, 28℃ for shaking culture, 72h Then replace with fresh medium to continue culturing. The nitrogen-fixing spores were isolated after repeating the culture for 3 times. Draw 1ml of the above-mentioned nitrogen-fixing bacteria enrichment culture and put it into 9ml sterile water to make 10 -1 Dilution, continue to dilute to make 10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 Bacterial suspensions of dilutions were heated in boiling water at 100°C for 10 minutes, and after cooling, 0.1ml of each dilution was spread on a nitrogen-fixing bacteria isolation medium...
Embodiment 2
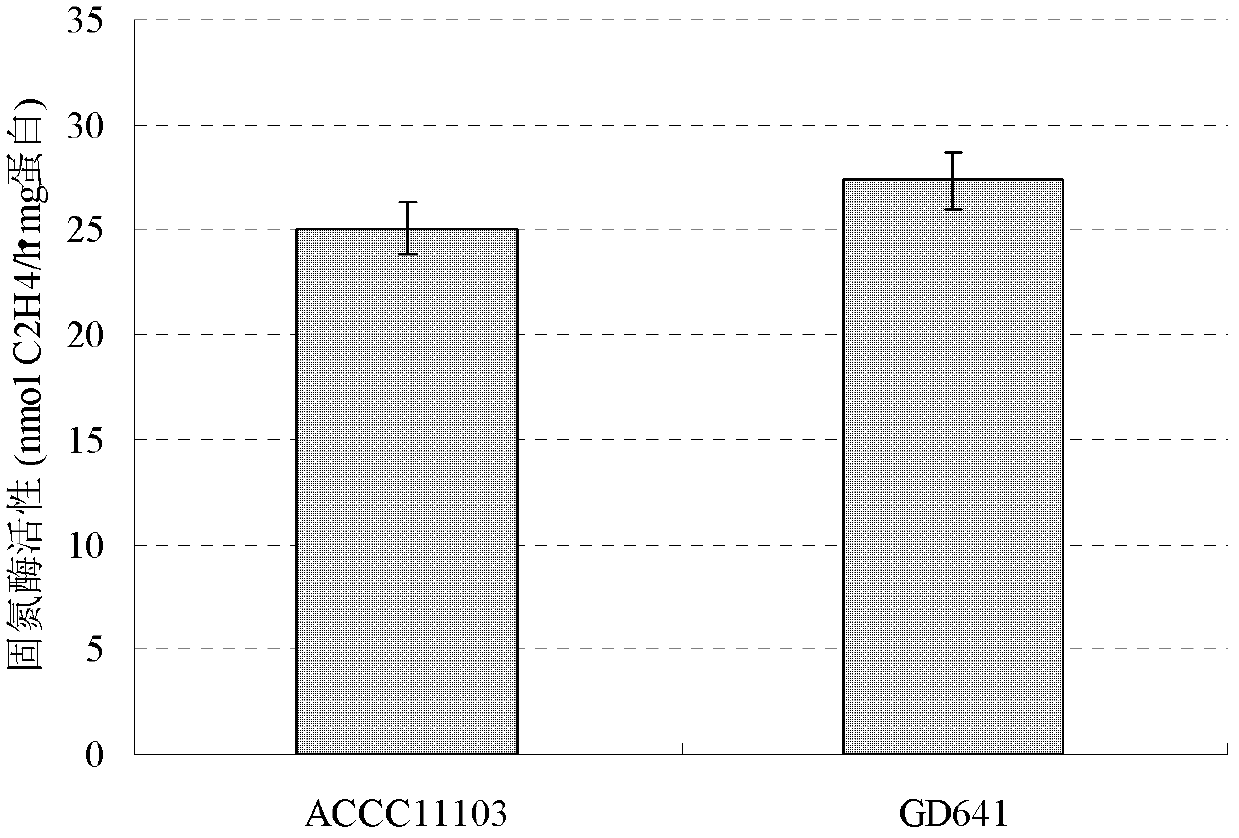
[0076] Example 2, Determination of Nitrogenase Activity of Paenibacillus sp. GD641 CGMCC No.5042
[0077] The Paenibacillus sp. (Paenibacillus sp.) GD641 CGMCC No.5042 obtained in Example 1 is carried out nitrogenase activity assay, and concrete method is as follows: in 15 * 150mm screw-top glass tubes, add 5ml improved nitrogen fixation medium and make inclined plane , inoculated with nitrogen-fixing bacteria and cultured at 28°C. Azotobacter chroococcum (Azotobacter chroococcum) ACCC11103, which is commonly used in the production of microbial fertilizers, was used as the positive control, and the blank slant without inoculation was used as the negative control, with 3 replicates. After culturing for 72 hours, replace the rubber stopper, inject acetylene gas to make the final concentration 10%, seal it with medical adhesive tape, continue culturing for 72 hours, take 100 μl of reaction gas, measure the amount of ethylene produced by gas chromatography, and calculate Paenibaci...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Embodiment 3, Paenibacillus sp. (Paenibacillus sp.) GD641 CGMCC No.5042 antagonizes pathogenic fungus inhibition rate determination
[0081] Adopt the two-point confrontation method to carry out the antagonism pathogenic fungus bacteriostatic rate measurement to the Paenibacillus sp. (Paenibacillus sp.) GD641 CGMCC No.5042 that embodiment 1 obtains, concrete operation is as follows: on the PDA plate apart from two points of center 2cm Inoculate crops with Gibberella zeae (or Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, or Verticillium dahliae) and Paenibacillus sp. GD641 CGMCC No.5042 on each screening treatment Three repetitions were performed, and the plate inoculated with pathogenic fungi but not nitrogen-fixing bacteria was used as a control. Incubate at a constant temperature at 28°C, and after 15 days, use a millimeter scale to measure the colony radius r of the pathogenic fungi on the confrontation plate along the direction of the tested Paenibacillus sp. GD641 CGMCC No.5042 1 , a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com