Mixed carbon material and negative electrode for nonaqueous rechargeable battery
A carbon material, mixed carbon technology, applied in secondary batteries, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in generating air-blocking pores, reduced high-temperature storage characteristics, and reduced storage characteristics, and achieve damage suppression and high-temperature storage. The effect of excellent characteristics and high electrode density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~5, comparative example 1~3
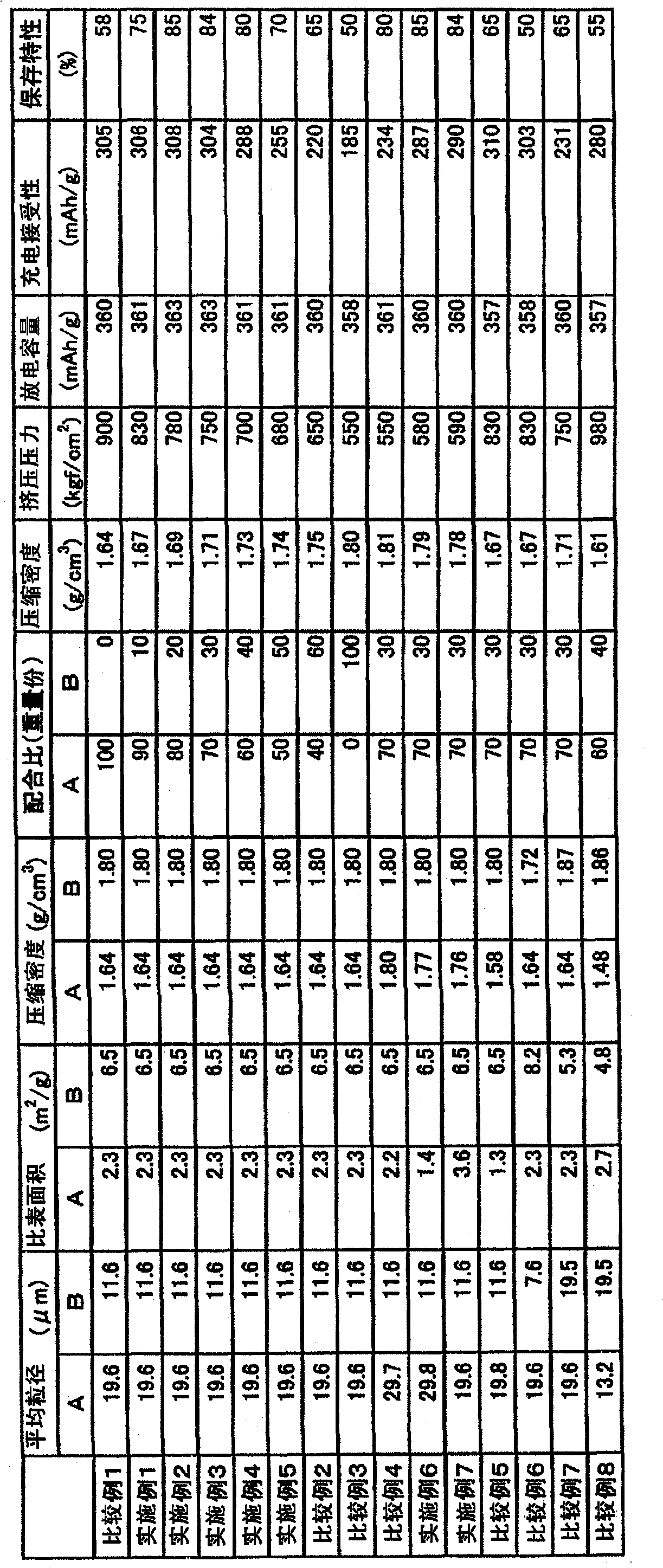
[0097] The carbon materials A and B obtained by the following production method were mixed according to the compounding ratio (parts by mass) shown in Table 1 to obtain the negative electrode material. In addition, in each of the Examples and Comparative Examples, the compressed densities of the carbon materials A, B, and the mixed carbon materials were measured by the above-mentioned method, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0098] (1) Carbon material A
[0099] Spheroidized flaky natural graphite powder by solid mixing method using a V mixer. The average particle size is 19.5 μm and the specific surface area (S1) is 5.3 m. 2 100 parts / g of graphite powder and 5 parts of coal-based pitch powder with an average particle size of 35 μm and a softening point of 85° C. were mixed.
[0100] The obtained mixed powder was placed in a heating furnace, under nitrogen flow, heat-treated at 1000° C. for 1 hour, and then allowed to cool to obtain a carbon material with turbostratic...
Embodiment 6
[0104] The carbon materials A and B obtained by the following production method were mixed according to the compounding ratio (parts by mass) shown in Table 1 to obtain the negative electrode material. In addition, the compressed densities of the carbon materials A, B and the mixed carbon materials were measured by the above-mentioned method, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0105] (1) Carbon material A
[0106] The flake natural graphite powder was spheroidized by solid mixing using a V mixer. The average particle size is 29.5 μm and the specific surface area (S1) is 3.6 m. 2 100 parts of graphite powder per g and 5 parts of coal-based pitch powder with an average particle size of 35 μm and a softening point of 85° C. were mixed.
[0107] The obtained mixed powder was placed in a heating furnace, under nitrogen flow, heat-treated at 1000° C. for 1 hour, and then allowed to cool to obtain a carbon material with turbostratic carbon formed by carbonization of pitch adher...
Embodiment 7
[0111] The carbon materials A and B obtained by the following production method were mixed according to the compounding ratio (parts by mass) shown in Table 1 to obtain the negative electrode material. In addition, the compressed densities of the carbon materials A, B and the mixed carbon materials were measured by the above-mentioned method, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0112] (1) Carbon material A
[0113] Spheroidized flaky natural graphite powder by solid mixing method using a V mixer. The average particle size is 19.5 μm and the specific surface area (S1) is 5.3 m. 2 100 parts / g of the same graphite powder as in Example 1 and 2 parts of coal-based pitch powder with an average particle diameter of 35 μm and a softening point of 85° C. were mixed.
[0114] The obtained mixed powder was left still in a heating furnace, and was heat-treated at 1000° C. for 1 hour under nitrogen flow, and then allowed to cool to obtain a carbon material with turbostratic carbon for...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com