Detection of deformation of a wind turbine blade
A technology for wind power equipment and blades, which is used in the control of wind turbines, monitoring of wind turbines, and avoiding excessive deflection of blades. , the effect of significant savings potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
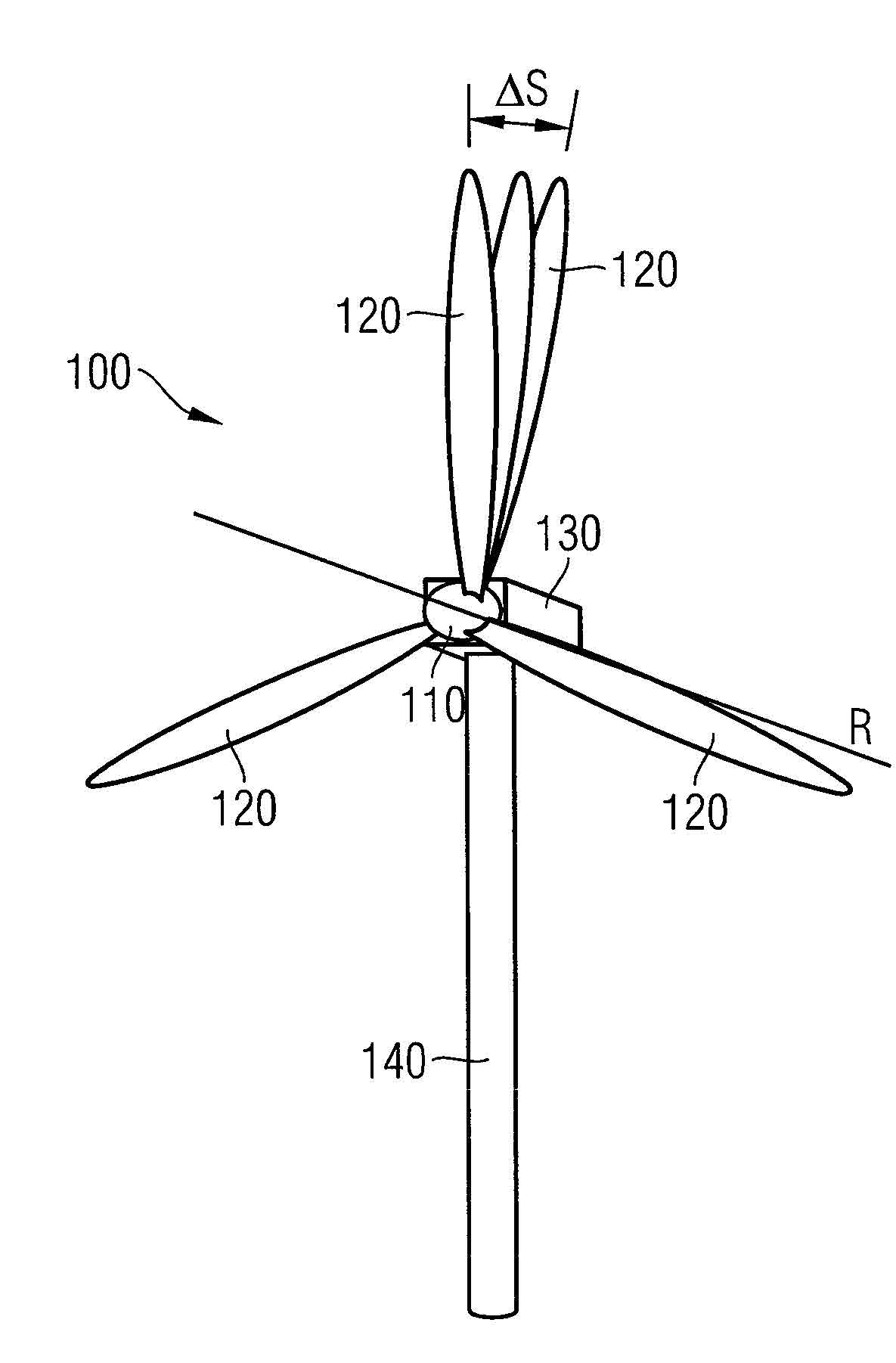
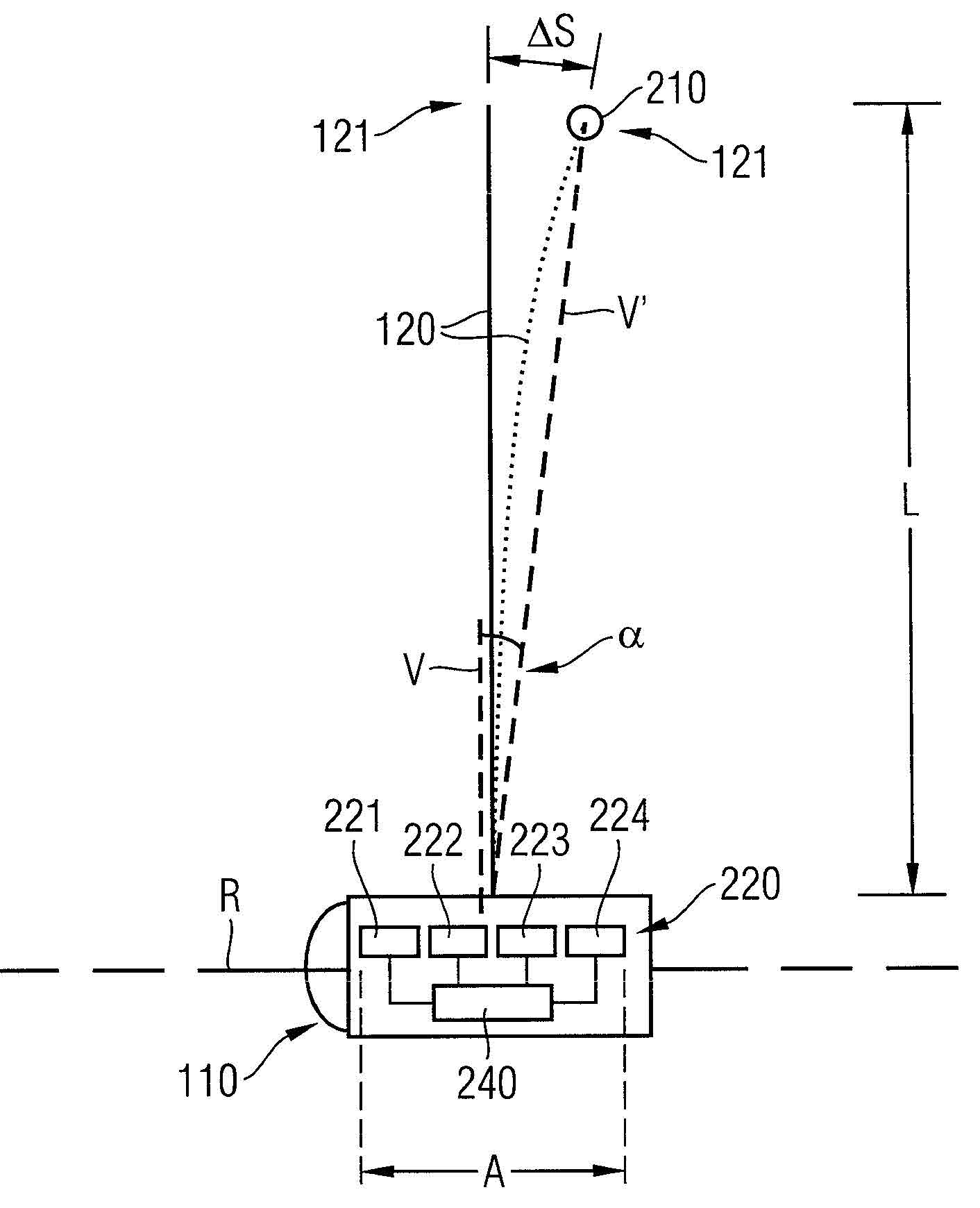
[0054] figure 1 A wind power installation 100 as known from the prior art is shown. The wind power plant 100 has a rotor 110 to which three blades 120 are fastened in the example shown. In the event of a wind load, the blades 120 are driven in a known manner, thereby setting the rotor 110 into rotation about the axis R of rotation. Furthermore, the wind power installation 100 has a nacelle 130 in which (not shown) the rotor 110 is mounted and a generator is arranged, with which the rotational energy of the rotor 110 is converted into electrical energy when a wind load occurs. (Other known components of such a wind power installation, such as the gangway fence etc. which are arranged outside the gondola, are not listed here in detail, but are generally assigned to the gondola 130 ). This is also well known. The nacelle 130 is fastened to a tower 140 of the wind power installation. The nacelle 130 is generally arranged rotatably about the longitudinal axis of the tower 140 o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com