Low-temperature fused salt clean smelting method for tin
A low-temperature molten salt and molten salt technology, applied in the field of non-ferrous metal metallurgy, can solve the problems of air, land and water pollution, difficulty in separation of tin and iron, and difficulty in separation of tin and iron, and achieve the purpose of reducing temperature, promoting technological progress, and simplifying smelting. Effects of Tin Process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
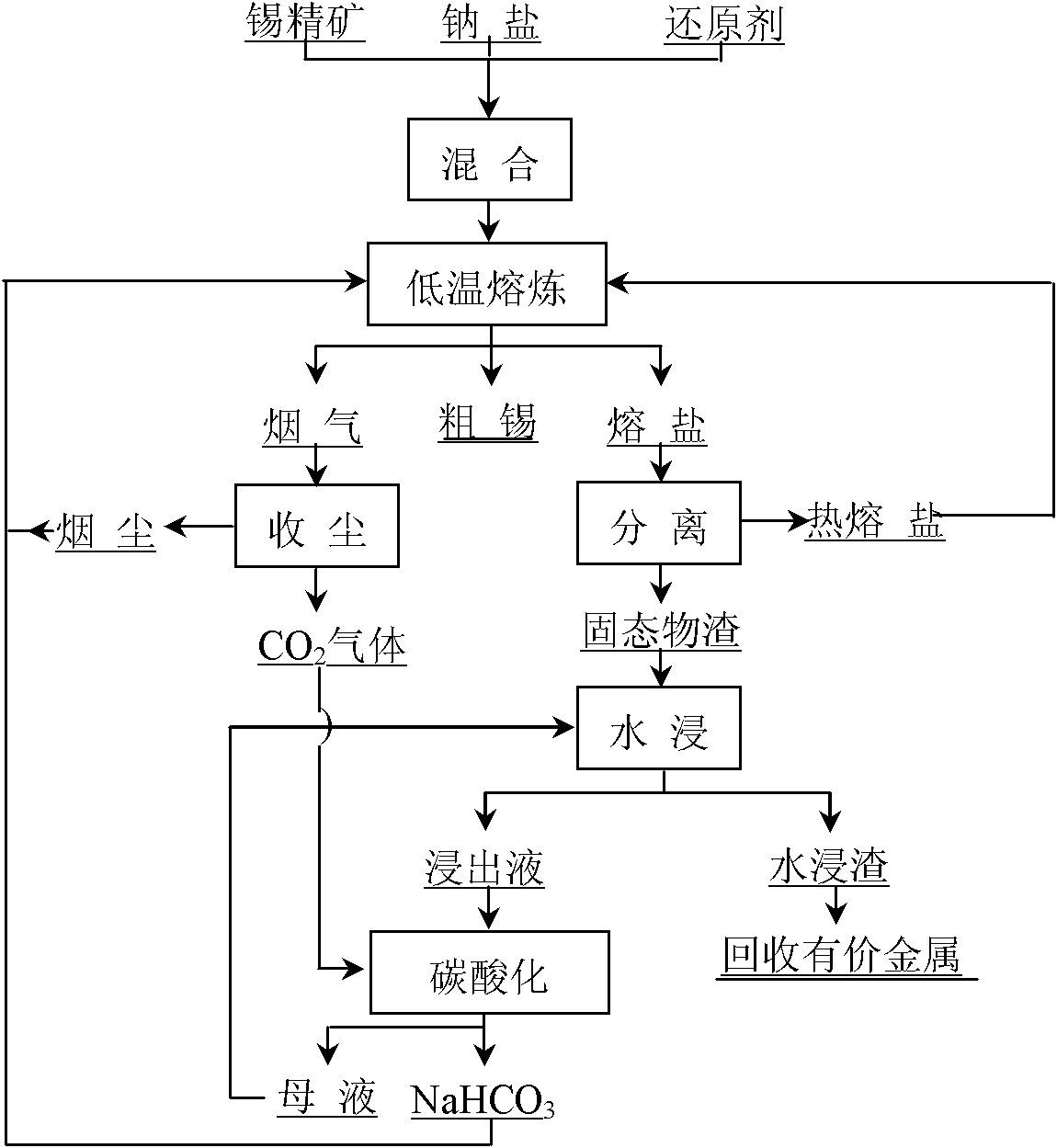
[0040] The chemical composition of tin concentrate A is (%): Sn 69.1%, As 0.01%, S 0.34%, Fe 1.12%, Cu0.07%, Pb 0.035%, SiO 22.17%. Weigh 100g of tin concentrate, 32g of pulverized coal, 310g of industrial grade sodium carbonate and 10g of industrial grade caustic soda and mix them evenly, and put the mixture into a graphite crucible. Push the graphite crucible into the resistance furnace, melt at 850°C for 2.5 hours, and produce 68.4g of crude tin containing 98.86% tin, and the direct yield of tin reaches 99.0%; the hot molten salt clarifies and separates the solid to obtain molten sodium 287g of salt and 35.6g of solid slag bonded with a small portion of sodium salt were leached with 200mL of tap water at a temperature of 75°C for 3 hours to obtain 19.7g of dry leaching residue, and the volume of the filtrate and washing liquid was 220mL. Into CO 2 , co-precipitating NaHCO 3 18.6g.
Embodiment 2
[0042] The chemical composition of tin concentrate B is (%): Sn 41.0%, As 1.6%, S 1.3%, Fe 22.3%, Cu 0.13%, Pb 4.5%, Bi0.11%, CaO 0.30%, SiO 2 4.12%. Weigh 100g of tin concentrate B, 26g of pulverized coal, 3.6g of zinc oxide, 300g of industrial grade sodium chloride and 15g of industrial grade caustic soda and mix evenly, and put the mixture into a graphite crucible. Push the graphite crucible into a resistance furnace, melt at 900°C for 2 hours, and produce 44.5g of crude tin containing 90% tin, and the direct yield of tin reaches 98.0%; hot molten salt clarifies and separates solids to obtain molten sodium salt 280g and 80g of solid slag bonded with a small portion of sodium salt were leached with 400mL of tap water at a temperature of 80°C for 3 hours to obtain 47.5g of dry leaching residue. The volume of the filtrate and washing liquid was 620mL, and CO 2 , co-precipitating NaHCO 3 28.2 g.
Embodiment 3
[0044] A kind of tin hydroxide slag produced by treating tin anode slime is used as raw material, the tin content is 60%, and it also contains a small amount of lead, antimony and sodium chloride; it is reduced with coke powder containing 82% C and 10% ash agent. Weigh 1000g of tin slag, 250g of coke powder and 1000g of industrial sodium carbonate and mix evenly respectively. After the mixture is loaded into a graphite crucible, 694g of molten sodium carbonate returned in Example 1 and Example 2 and 40g of NaHCO recovered are covered on the surface of the material . Then push the graphite crucible into the resistance furnace, melt at 800°C for 3 hours, and produce 612.4g of crude tin containing 96.5% Sn, and the direct yield of tin reaches 98.5%; the hot molten salt is filtered and separated by -200 mesh stainless steel mesh After the solid matter, 1510.6 g of molten sodium salt and 212 g of solid slag bonded with a small portion of sodium salt were obtained, and leached with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com