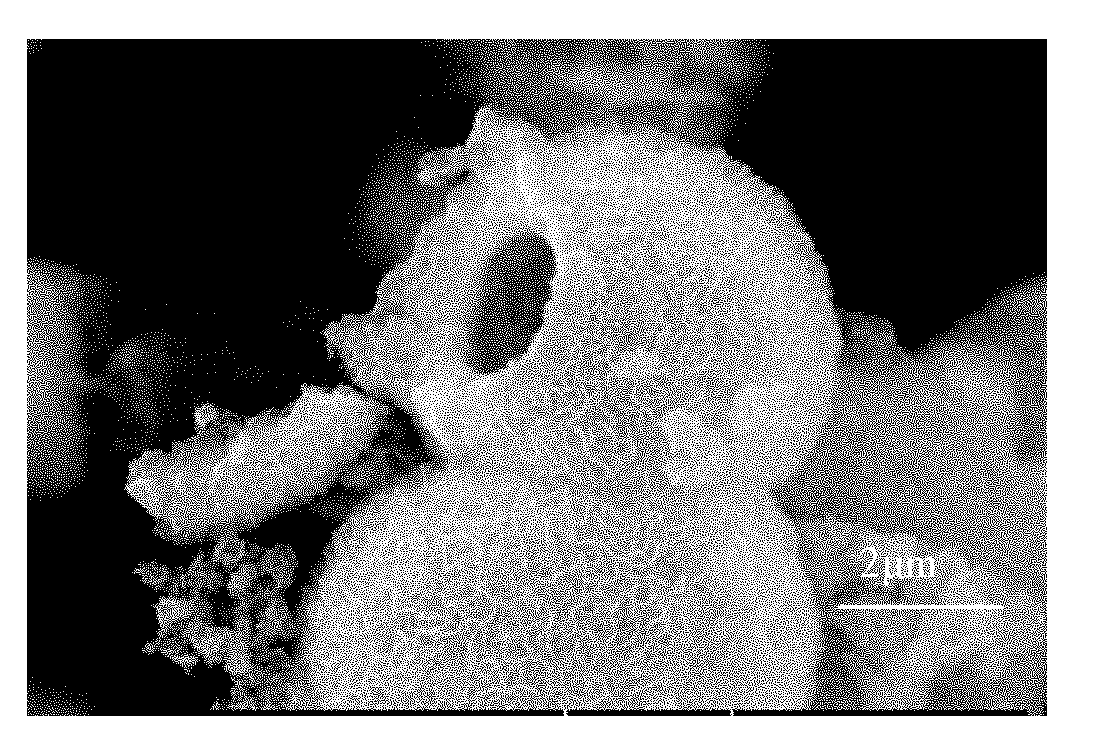
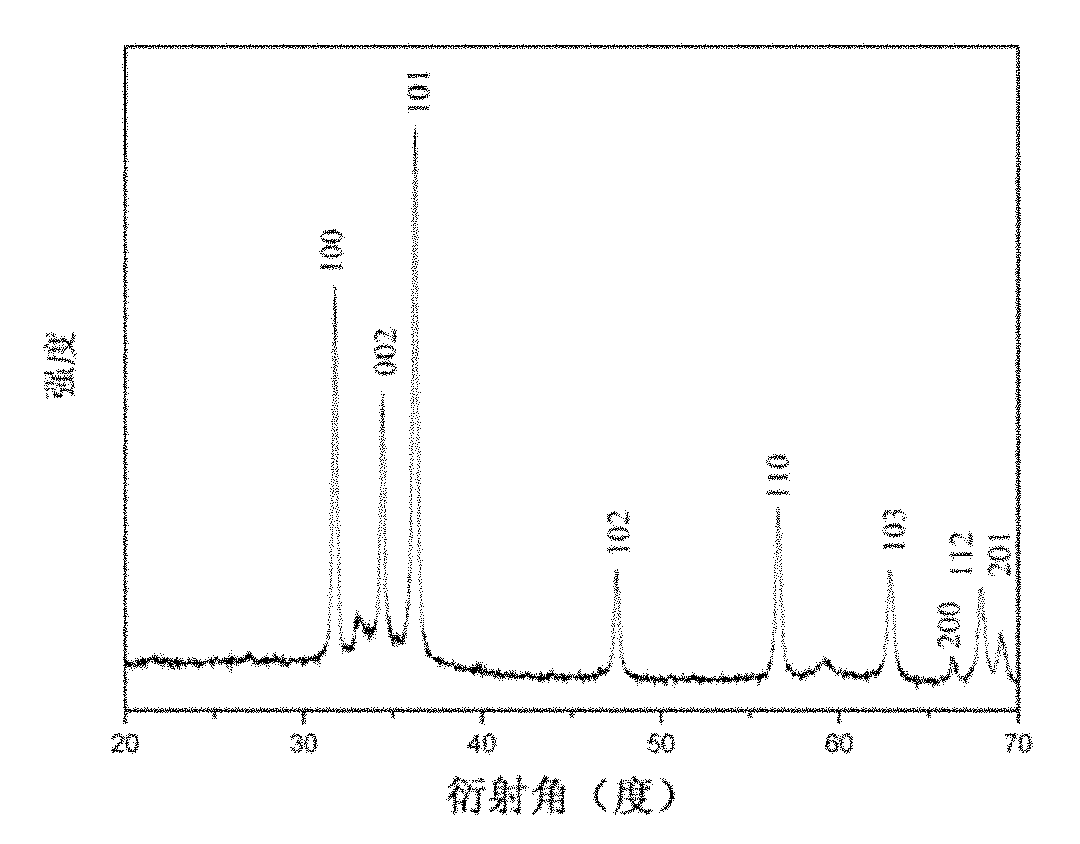
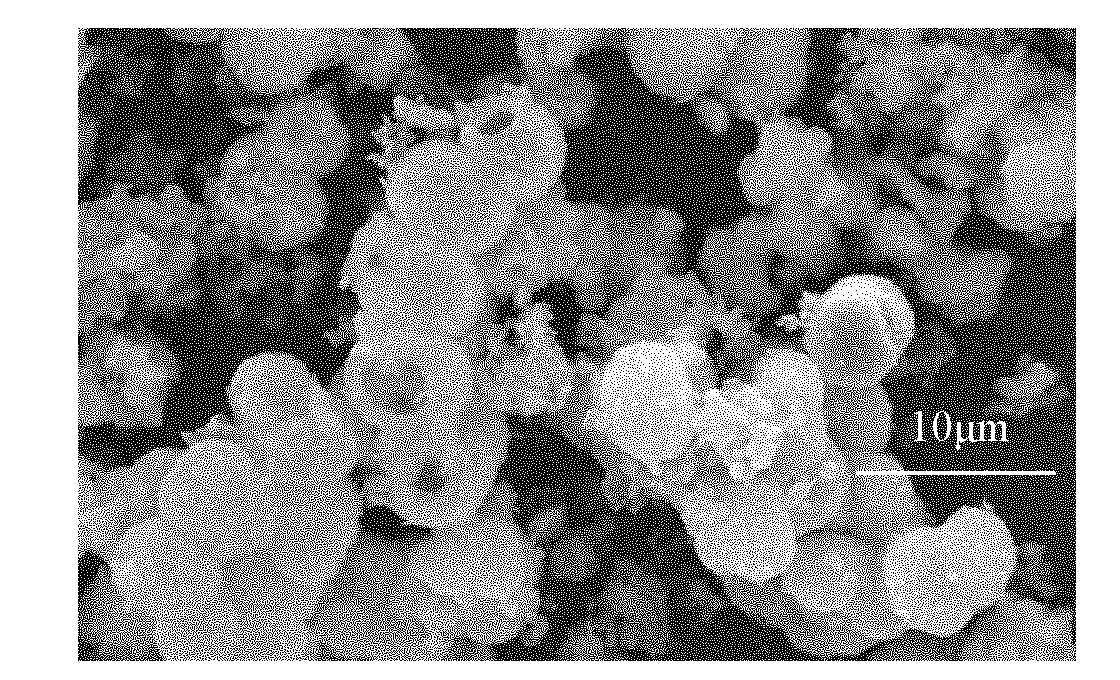Zinc oxide hollow microspheres and preparation method thereof
A technology of zinc oxide and microspheres, applied in the direction of zinc oxide/zinc hydroxide, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and energy consumption, complex process and other problems of thermal evaporation method, and achieve low sample dislocation density, wide application value and high output high rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] 1) Dissolve zinc nitrate hexahydrate and hexamethylenetetramine in deionized water, add sodium citrate while stirring at room temperature, and prepare a uniform transparent solution after stirring and dissolving, wherein zinc nitrate hexahydrate and hexamethylenetetramine The molar concentration of tetraamine is 1:2, and the volume of deionized water is 20mL. After fully stirring and dissolving, configure Zn 2+ A mixed solution with a molar concentration of 0.1mol / L and a sodium citrate concentration of 0.02mol / L;
[0018] 2) Put the mixed solution into a closed high-pressure reaction kettle, then put the high-pressure reaction kettle into an electric heating constant temperature blast drying oven, and conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 120°C for 2 hours;
[0019] 3) Cool down to room temperature naturally after the reaction, open the autoclave, filter the white precipitate, wash twice with deionized water, then wash twice with absolute ethanol, and dry at 50°C for 3 ho...
Embodiment 2
[0022] 1) Dissolve zinc nitrate hexahydrate and hexamethylenetetramine in deionized water, add sodium citrate while stirring at room temperature, and prepare a uniform transparent solution after stirring and dissolving, wherein zinc nitrate hexahydrate and hexamethylenetetramine The molar concentration of tetraamine is 1:1, and the volume of deionized water is 24mL. After fully stirring and dissolving, configure Zn 2+ A mixed solution with a molar concentration of 0.2mol / L and a sodium citrate concentration of 0.04mol / L;
[0023] 2) Put the mixed solution into a closed high-pressure reaction kettle, then put the high-pressure reaction kettle into an electric constant temperature blast drying oven, and perform a hydrothermal reaction at 140°C for 7 hours;
[0024] 3) Cool down to room temperature naturally after the reaction, open the autoclave, filter the white precipitate, wash twice with deionized water, then wash twice with absolute ethanol, and dry at 55°C for 4 hours to o...
Embodiment 3
[0026] 1) Dissolve zinc nitrate hexahydrate and hexamethylenetetramine in deionized water, add sodium citrate while stirring at room temperature, and prepare a uniform transparent solution after stirring and dissolving, wherein zinc nitrate hexahydrate and hexamethylenetetramine The molar concentration of tetraamine is 2:1, and the volume of deionized water is 28mL. After fully stirring and dissolving, configure Zn 2+ A mixed solution with a molar concentration of 0.3mol / L and a sodium citrate concentration of 0.06mol / L;
[0027] 2) Put the mixed solution into a closed high-pressure reaction kettle, then put the high-pressure reaction kettle into an electric heating constant temperature blast drying oven, and conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 160°C for 12 hours;
[0028]3) Cool down to room temperature naturally after the reaction, open the autoclave, filter the white precipitate, wash twice with deionized water, then wash twice with absolute ethanol, and dry at 60°C for 5 ho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com