Soil or settlement soluble iron in-situ sampling device and in-situ sampling and testing method thereof
A sampling device and sediment technology, which is applied in the direction of sampling device, material analysis by observing the influence of chemical indicators, and analysis by making materials undergo chemical reactions, can solve the problem of low accuracy of measurement results, inability to be stable at the same time, Large destructive problems, to avoid valence changes, improve accuracy, and save time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
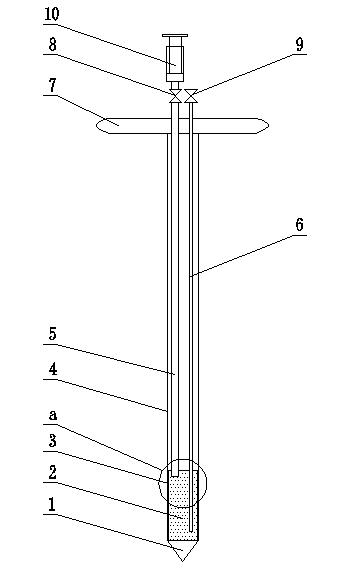
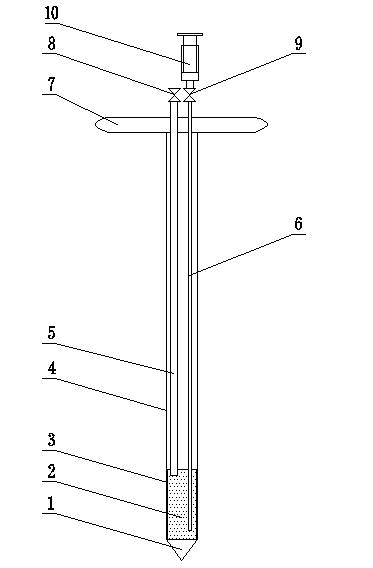
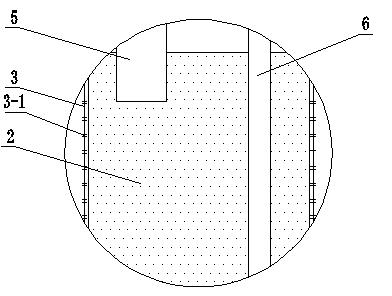
[0019] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1-Figure 3 Describe this embodiment mode, a kind of in-situ sampling device of soil or sediment soluble iron in this embodiment mode consists of a stainless steel drill bit 1, a pottery clay water collection pipe 2, a first stainless steel pipe 3, a second stainless steel pipe 4, a plastic suction pipe 5, a plastic The suction pipe 6, the handle 7, the suction pipe interface valve 8, the suction pipe interface valve 9 and the suction device 10, the stainless steel drill bit 1 is fixedly installed on the lower end surface of the pottery clay water collection pipe 2, and the second stainless steel pipe 4 is fixedly installed On the upper end surface of the clay water collecting pipe 2, a plurality of water inlet holes 3-1 are evenly opened on the pipe wall of the first stainless steel pipe 3, and the first stainless steel pipe 3 is coated on the outer wall of the clay water collecting pipe 2, so that Said rotary handle 7 i...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0021] Specific implementation mode two: combination Figure 1-Figure 3 To illustrate this embodiment, the steps of a method for in-situ sampling and determination of soil or sediment soluble iron in this embodiment are:
[0022] Step 1. Press the rotary handle 7 at the sample point to be tested, and the stainless steel drill bit 1 cooperates with the clay water collection pipe 2 to drill into the soil or sediment to a certain depth; the specific depth depends on the sampling depth when the sample is taken. For example, the depth is 5cm, 10cm, 20cm or 40cm;
[0023] Step 2, close the suction pipe interface valve 9, connect the aspirator 10 with the plastic suction pipe 5 through the suction pipe interface valve 8, and extract the air in the clay water collection pipe 2 to obtain negative pressure;
[0024] Step 3, close the valve 8 of the suction pipe interface, and collect 40-50 mL of pore water in the soil or sediment;
[0025] Step 4, respectively configuring EDTA and BPD...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com