Comprehensive recovery method for nickel-hydrogen waste battery
A technology of waste batteries and recycling methods, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of high recycling efficiency, lack of short recycling routes, etc., and achieve the effects of good recycling benefits, short recycling process routes, and less energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
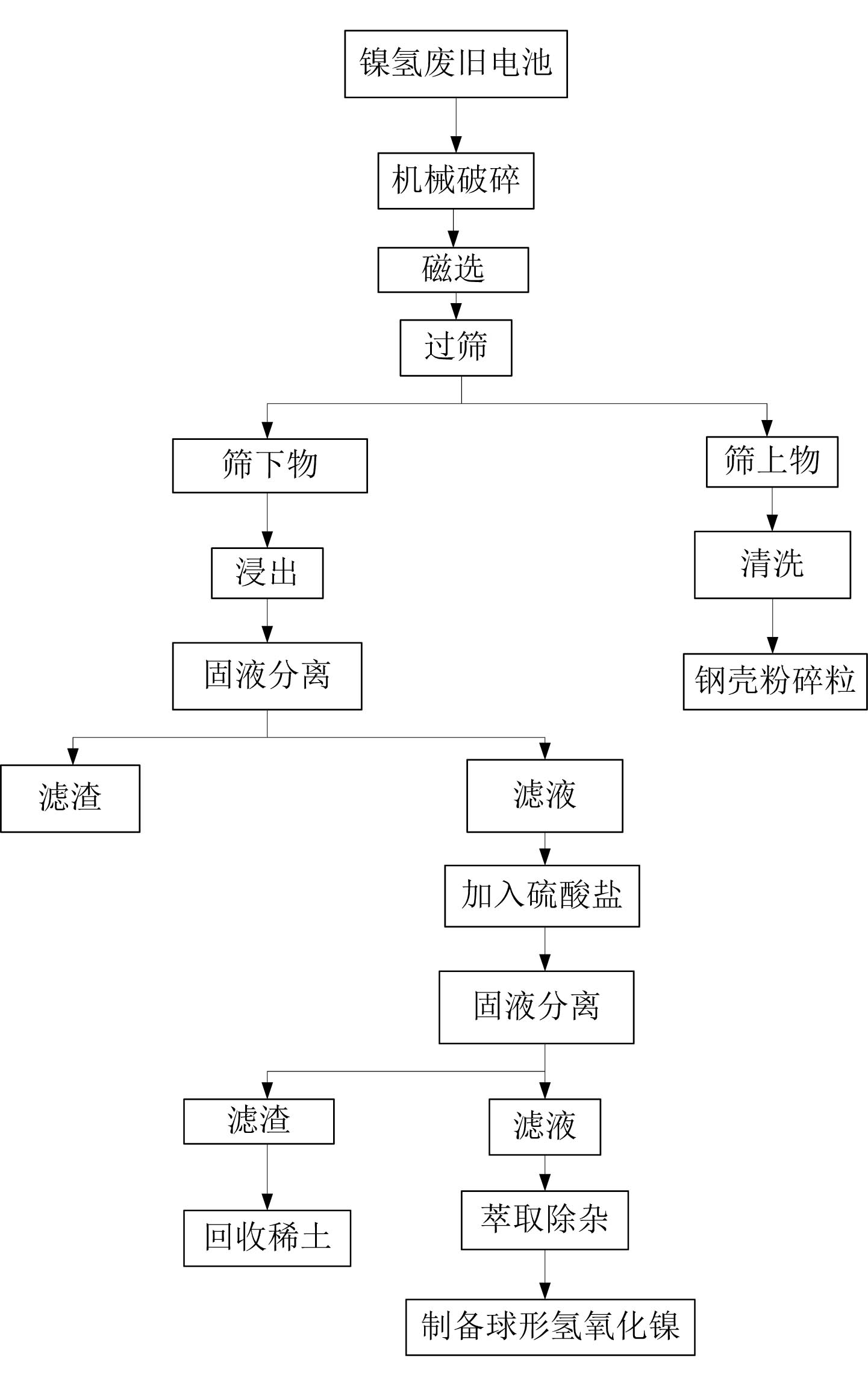
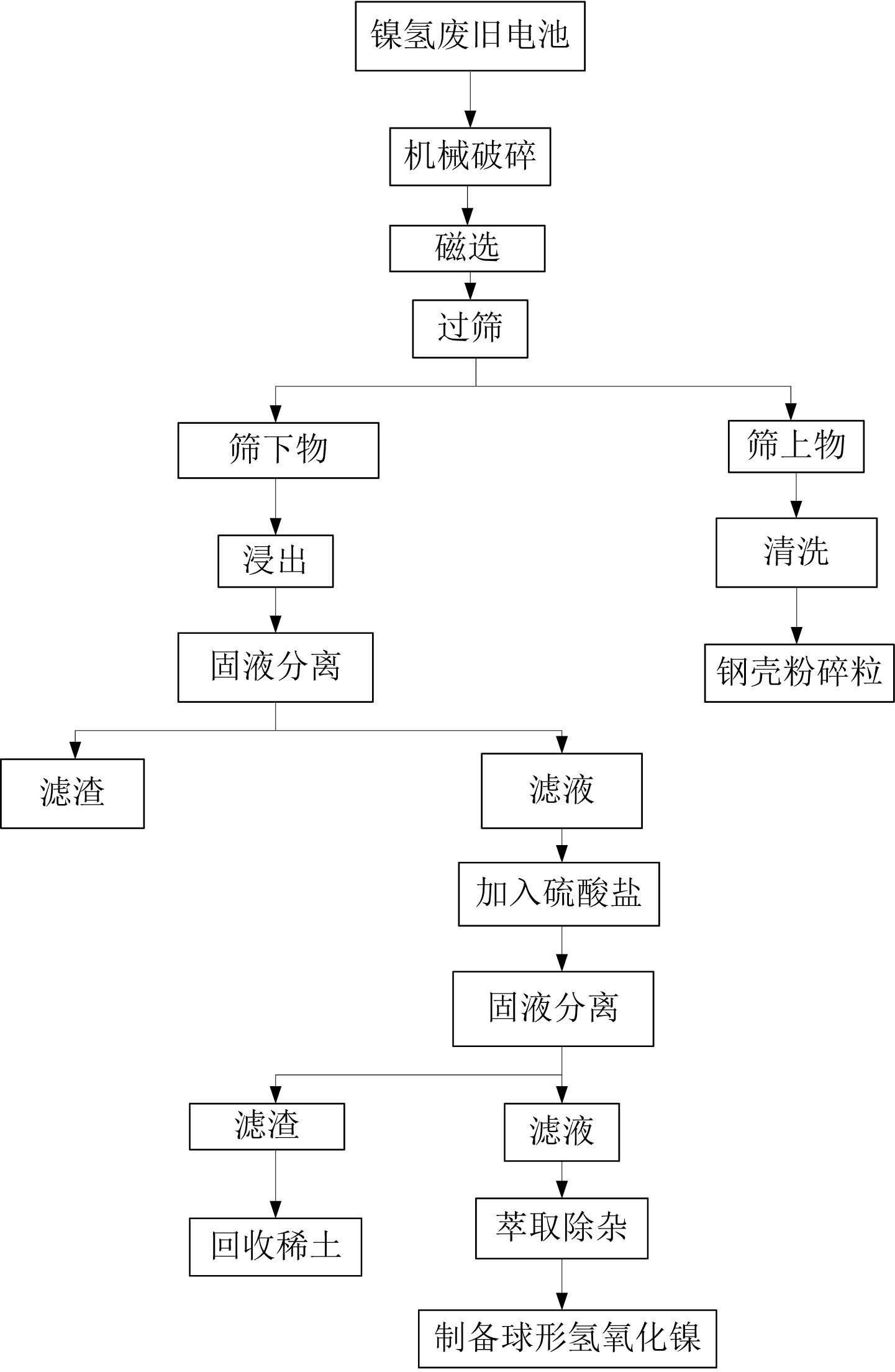
[0043] 1) Broken the waste Ni-MH batteries, sieved by magnetic separation, and separated the steel case from the rest of the waste Ni-MH batteries;
[0044] 2) Prepare leachate, the concentration of sulfuric acid in the leachate is 1mol / L, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide is 10%;
[0045] 3) Put the powder under the sieve into the leaching solution, powder: leaching solution = 1kg: 6L, heat up to 50°C, and leaching for 3 hours;
[0046] 4) Solid-liquid separation, adjust the pH value of the filtrate to 2, the temperature is 50°C, add 1.5 times the theoretical amount of sodium sulfate required for precipitation of rare earth elements, and precipitate the rare earth elements therein;
[0047] 5) Solid-liquid separation, adding extractant P204 to the filtrate to remove impurities to obtain a sulfate solution containing nickel and cobalt.
[0048] The recovery rate of nickel was 99.4%, that of cobalt was 99.9%, and that of rare earth elements was 97.9%.
Embodiment 2
[0050] 1) Broken the waste Ni-MH batteries, sieved by magnetic separation, and separated the steel case from the rest of the waste Ni-MH batteries;
[0051] 2) prepare leachate, the concentration of sulfuric acid in the leachate is 5mol / L, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide is 5%;
[0052] 3) Put the powder under the sieve into the leaching solution, powder: leaching solution = 1kg: 1L, heat up to 100°C, and leaching for 1 hour;
[0053] 4) Solid-liquid separation, adjust the pH value of the filtrate to 2, and the temperature is 90°C, add sodium sulfate 3 times the theoretical amount required for precipitation of rare earth elements, and precipitate the rare earth elements therein;
[0054] 5) Solid-liquid separation, adding extractant P204 to the filtrate to remove impurities to obtain a sulfate solution containing nickel and cobalt.
[0055] The recovery rate of nickel was 99.2%, that of cobalt was 99.8%, and that of rare earth elements was 98.6%.
Embodiment 3
[0057] 1) Broken the waste Ni-MH batteries, sieved by magnetic separation, and separated the steel case from the rest of the waste Ni-MH batteries;
[0058] 2) prepare leachate, the concentration of sulfuric acid in the leachate is 3mol / L, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide is 8%;
[0059] 3) Put the powder under the sieve into the leaching solution, powder: leaching solution = 1kg: 3L, heat up to 70°C, and leaching for 1.5 hours;
[0060] 4) Solid-liquid separation, adjust the pH value of the filtrate to 3, the temperature is 65 ° C, add sodium sulfate twice the theoretical amount required for precipitation of rare earth elements, and precipitate the rare earth elements;
[0061] 5) Solid-liquid separation, adding extractant P204 to the filtrate to remove impurities to obtain a sulfate solution containing nickel and cobalt.
[0062] The recovery rate of nickel was 99.7%, that of cobalt was 99.6%, and that of rare earth elements was 98.2%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com