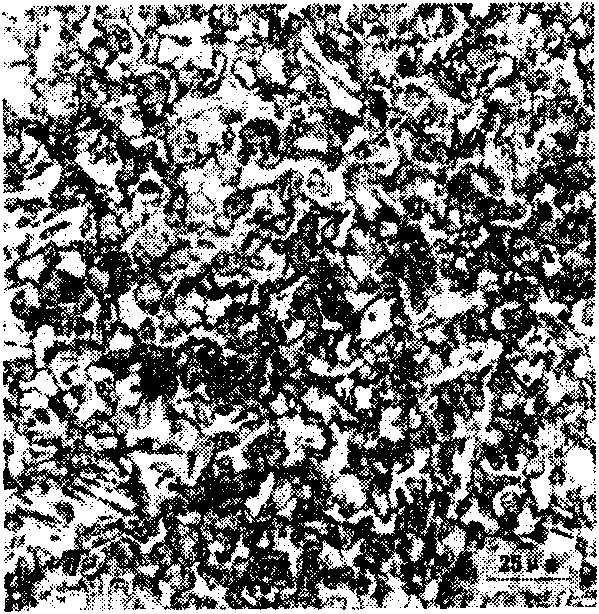Method for improving low-temperature impact toughness of high strength thick steel plate
A low-temperature impact toughness and high-strength technology, applied in the direction of temperature control, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, low production efficiency, and low yield, and achieve uniform and stable impact toughness, increase processing time, and reduce dependence.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
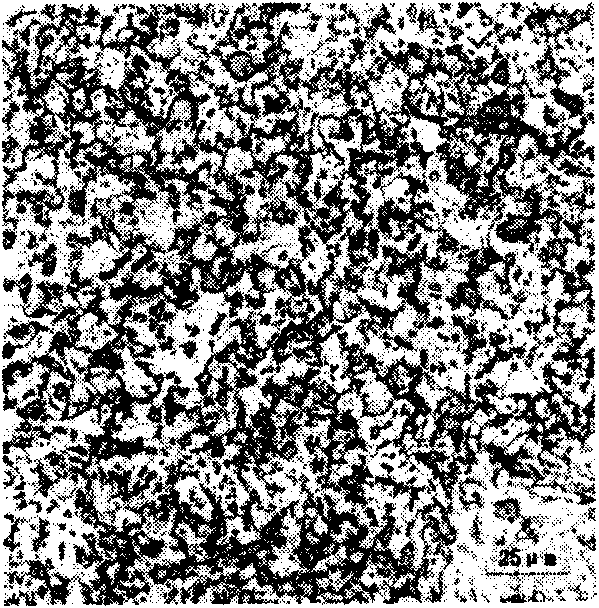
[0023] C≤0.15% in the chemical composition of the slab used in the present invention. The slab with a thickness of 250mm is cooled after being directly rolled on a medium and heavy plate rolling mill. The thickness of the steel plate after rolling is 80mm, and the compression ratio of the steel plate is 3.13. The rolled steel plate was quenched at 930°C, then quenched for the second time at 880°C, and tempered at a medium temperature of 550°C in a normalizing furnace. The structure of the surface and core of the steel plate after sub-temperature quenching is as attached figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the surface and core of the tempered steel plate are as attached image 3 , Figure 4 shown.
[0024] Table 1 shows the properties of 40mm steel plates produced by normal production process using slabs of the same composition and thickness. The mechanical properties of the 80mm steel plate treated by the above process are shown in Table 2.
[0025] Table 240mm steel plate me...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2 On the basis of Embodiment 1, the compression ratio of the steel plate is further reduced, and a 150 mm thick steel plate is manufactured by using a 320 mm thick steel billet. C≤0.15% in the chemical composition of the billet. The steel billet is rolled to a thickness of 150mm at one time by direct rolling method on the plate rolling mill, and the compression ratio is 2.13. The steel plate was stacked and cooled for 48 hours after rolling, and the level I flaw detection was all qualified, indicating that the steel plate had no obvious internal defects. The 150mm thick steel plate is heated to 930°C for high-temperature quenching, then heated to 850°C for the second quenching, and finally high-temperature tempering at 650°C in a normalizing furnace. Figure 5 , Figure 6 , Figure 7 It is the structure of the surface, thickness 1 / 4 and core of the steel plate after sub-temperature quenching. Table 3 shows the mechanical properties of the 150mm steel plate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com