Method for amplifying and multiplying T cells with antigenic specificity
A specific, cellular technology, applied in animal cells, antibacterial drugs, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve the problem that the number of effective target cells is small, the treatment cannot be satisfied, and it is difficult for immunogenic antigens to stimulate the specific proliferation of immune cells, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of good amplification effect, low cost and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1, Preparation of bispecific T cells (anti-tumor specific and anti-influenza virus specific T cells)
[0034] 1. Preparation of packaging cell lines expressing recombinant virus (containing the gene encoding anti-melanoma gp100 TCR protein)
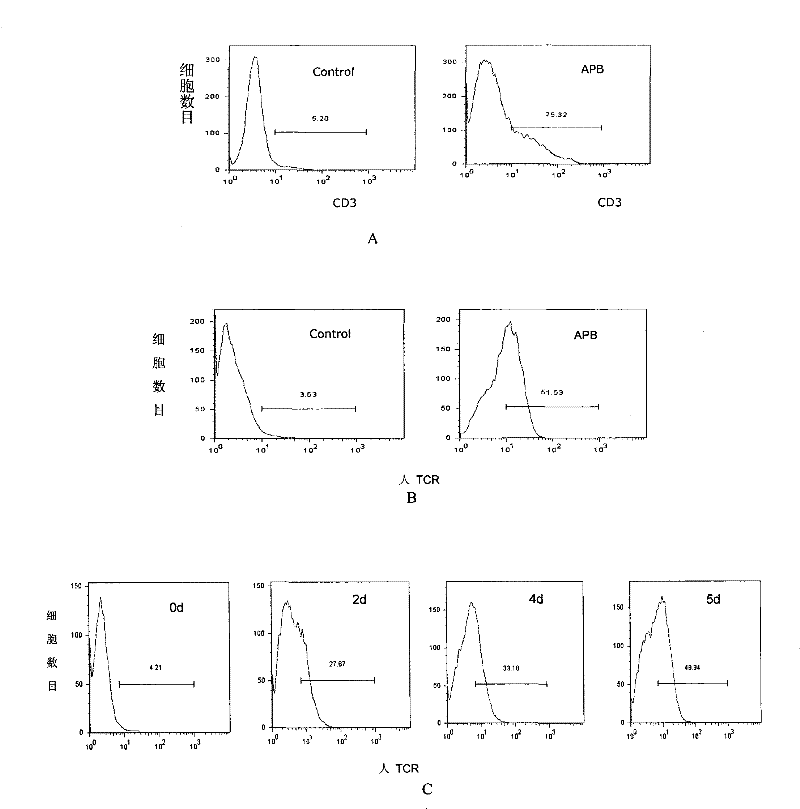
[0035] APB plasmids were used to transfect Phoenix-Eco cells, and the resulting virus supernatants were used to infect PT67 packaging cells. The infected monoclonal PT67 virus supernatants were respectively infected with the SupT1 human lymphoma cell line to detect the expression of human CD3. Any infected SupT1 human lymphoma cell line served as blank control. This method is used to select the packaging cell line that produces the highest virus titer.
[0036] The result is as figure 1 As shown in A, it shows that the screened PT67 packaging cell line produces the highest virus titer (that is, it can maximize the expression of human CD3 on the surface of SupT1 cells), and can be used as a packaging cell line for toxin pr...
Embodiment 2
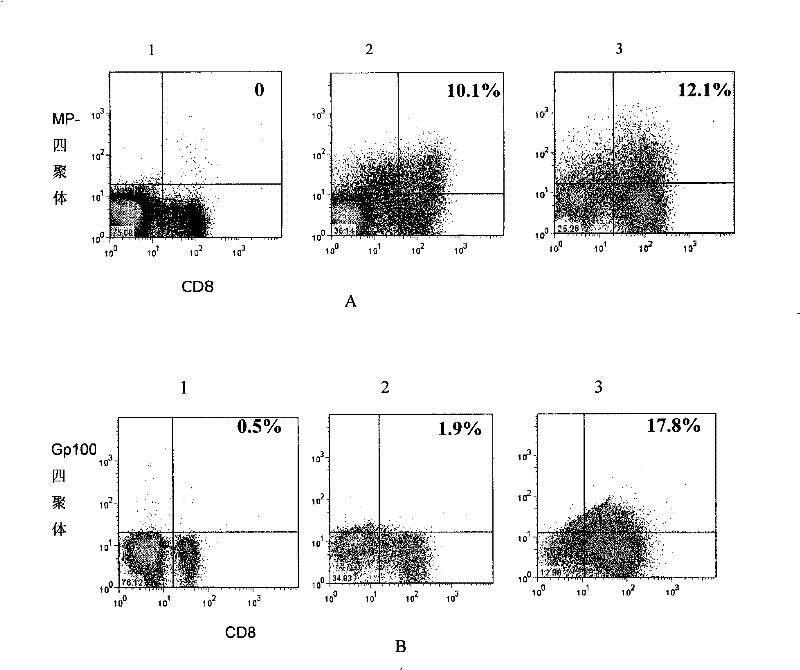
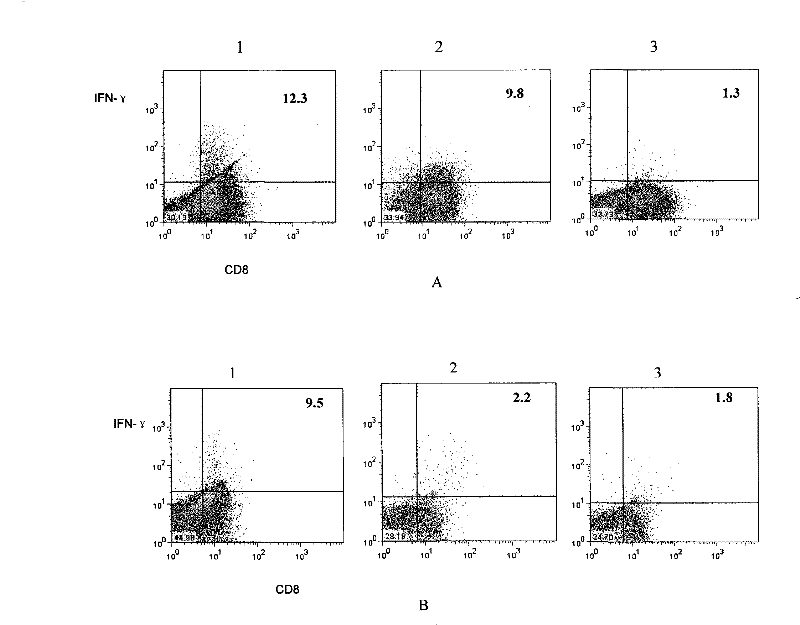
[0048] Example 2. Proliferation and function of bispecific T cells
[0049] The bispecific T cells obtained in Example 1 were subjected to the following experiments.
[0050] The tetramer of the melanoma antigen gp100 peptide was prepared according to the literature (Estcourt, M.J., A.J.McMichael, and T.Hanke, Altered primary CD8+T cell response to a modified virusAnkara(MVA)-vectored vaccine in the absence of CD4+T cell help . Eur J Immunol, 2005.35 (12): p.3460-7) described in the method of preparation.
[0051] According to the literature (Estcourt, M.J., A.J.McMichael, and T.Hanke, Altered primary CD8+T cell response to a modified virus Ankara(MVA)-vectored vaccine in the absence off CD4+T Cell help. EurJ Immunol, 2005.35 (12): p.3460-7).
[0052] FITC-labeled anti-mouse CD8 was purchased from BD, PharMingen, CA, USA;
[0053] Anti-mouse IFN-γ-PE was purchased from eBioscience, the catalog number is 12-7311-71;
[0054] Monensin was purchased from eBioscience, the prod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com