Method for designing adjustable frequency domain filter based on smooth curve
A filter design, smooth curve technology, applied in color TV parts, TV system parts, TV and other directions, can solve the problem of no filter, larger cutoff frequency fluctuation, ringing and other problems, to achieve robustness Strong, enhance the effect of image quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
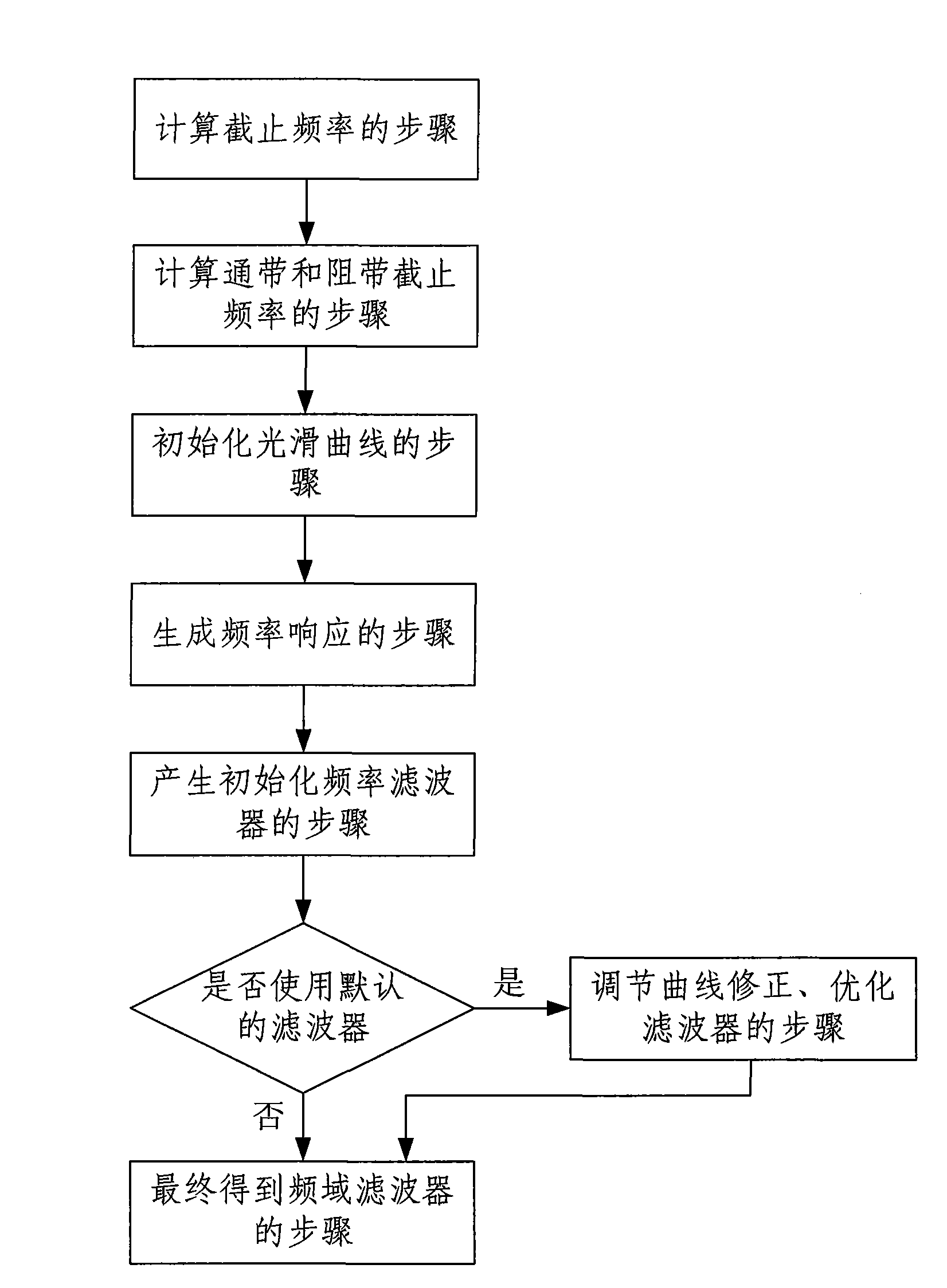
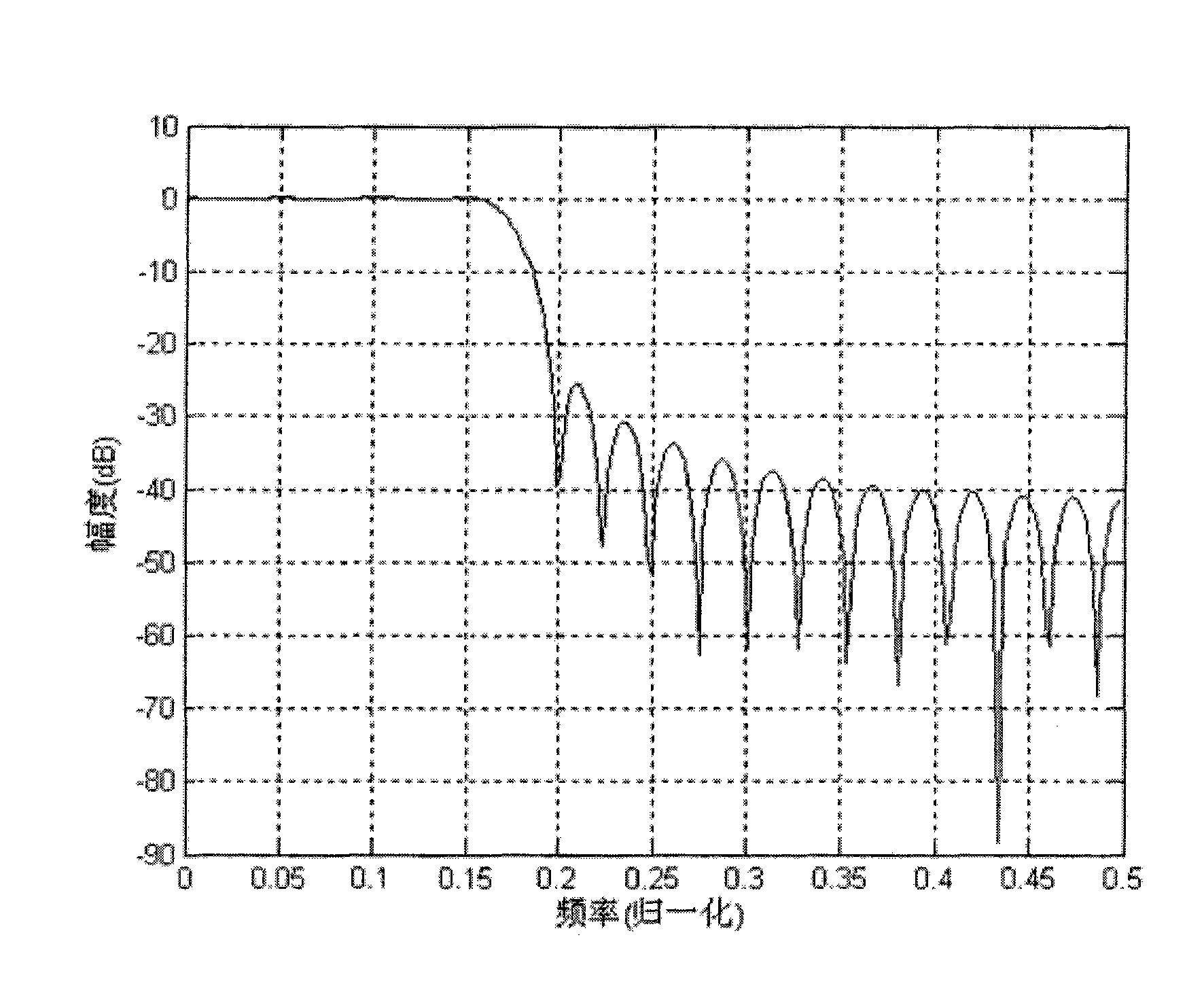
[0025] This embodiment is an adjustable smooth curve-based frequency domain filter design method. In this embodiment, the pass-band cut-off frequency and the stop-band cut-off frequency are adaptively calculated by changing the sampling rate of the signal, and then, between the pass-band and the stop-band, a transition band is generated by smooth curve fitting, which solves the problem of the distribution of sample points in the transition band. On this basis, the frequency response is designed and generated, and finally the frequency response is sampled at equal intervals in the frequency domain to obtain the final frequency domain filter. The frequency response of the filter is plotted as figure 2 As shown, the curve is defined piecewise. where the x-axis is the frequency axis, the y-axis is the amplitude axis, and ω p is the passband cutoff frequency, ω s is the stopband cutoff frequency, in the interval [0, ω p ) is called the passband, [ω p , ω s ) is called the tr...
Embodiment 2
[0035] This embodiment is an improvement of the first embodiment, and is a refinement of the step of calculating the cutoff frequency in the first embodiment. The source signal and the target signal in the step of calculating the cutoff frequency described in this embodiment include: a video image signal and an audio digital signal.
[0036] In fact, the filter designed in the present invention can generate a one-dimensional filter, can also generate a two-dimensional filter, and can even generate an n-dimensional filter by extension. Without loss of generality, when the present invention is used to generate an n-dimensional filter, the frequency responses corresponding to n different directions (dimensions) are all generated by the steps described in the first embodiment. While the audio signal is actually a one-dimensional signal, the video image signal is actually a two-dimensional signal. As long as the pass-band cut-off frequency and the stop-band cut-off frequency are c...
Embodiment 3
[0038] This embodiment is an improvement of the first embodiment, and is a refinement of the step of initializing the smooth curve in the first embodiment. The smooth curve in the step of initializing the smooth curve in this embodiment includes: an ellipse and a parabola.
[0039] In fact, a smooth curve between the passband cutoff frequency and the stopband cutoff frequency can be fitted with a variety of curves. Simpler curves are elliptic lines and parabolas, using elliptic line fitting to generate transition bands such as Figure 4 shown. The following example illustrates the process of using an ellipse to fit the transition zone. The ellipse equation is expressed as
[0040] x 2 a 2 + y 2 b 2 = 1 - - - ( 1 ) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com