Dissociation rate matching method and device
A technology for de-rate matching and de-interleaving, applied in the field of de-rate matching methods and devices, can solve the problems of bit-level processing efficiency, inability to be effectively improved, large input data volume, etc., and save time for reading data , Save the time of judging the address and improve the processing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
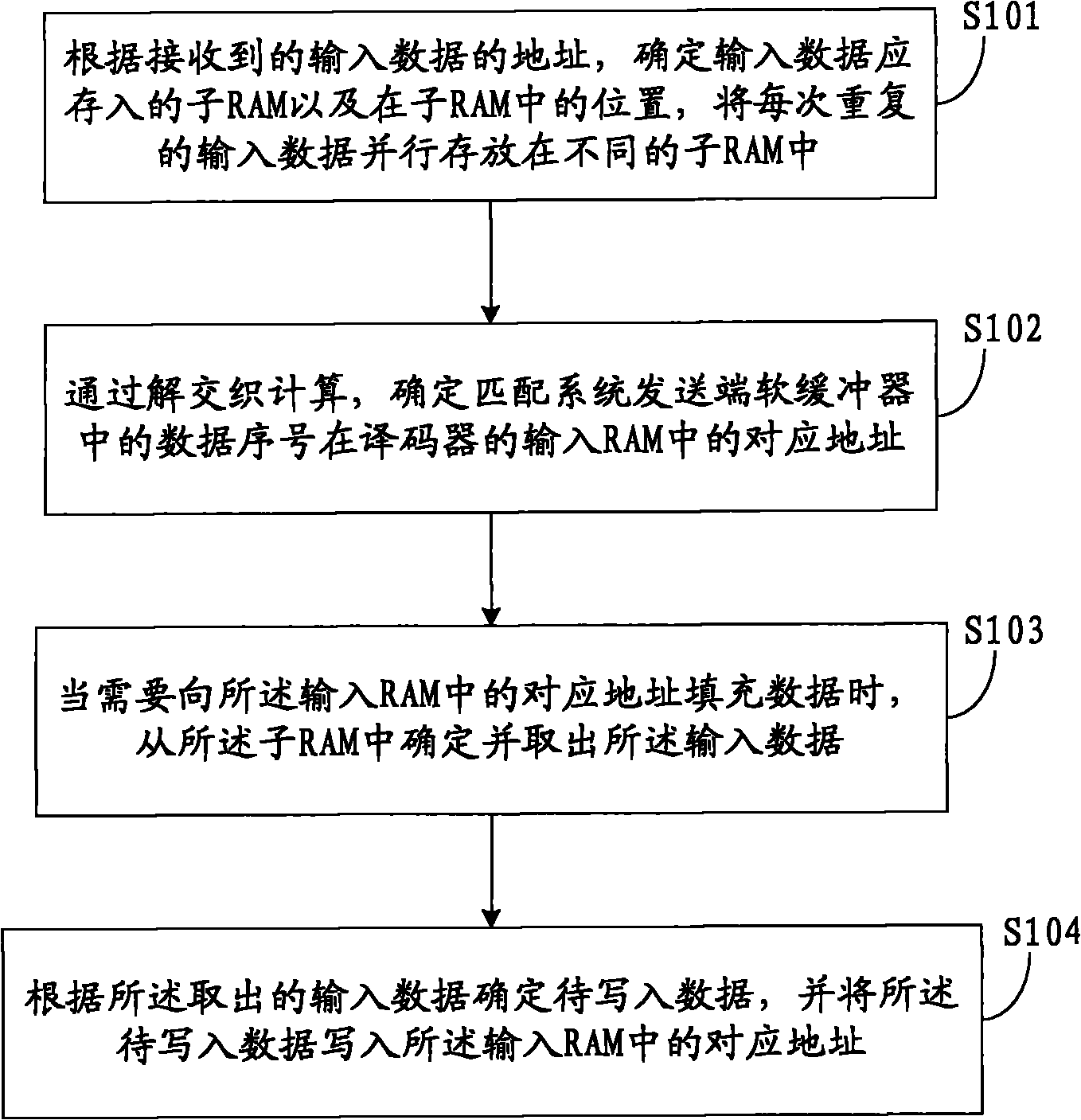
[0053] Embodiment 1. On the basis of the above-mentioned division of multiple sub-RAMs, refer to figure 1 , the method provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0054] S101: According to the address of the received input data, determine the sub-RAM where the input data should be stored and the position in the sub-RAM, and store each repeated input data in parallel in different sub-RAMs;
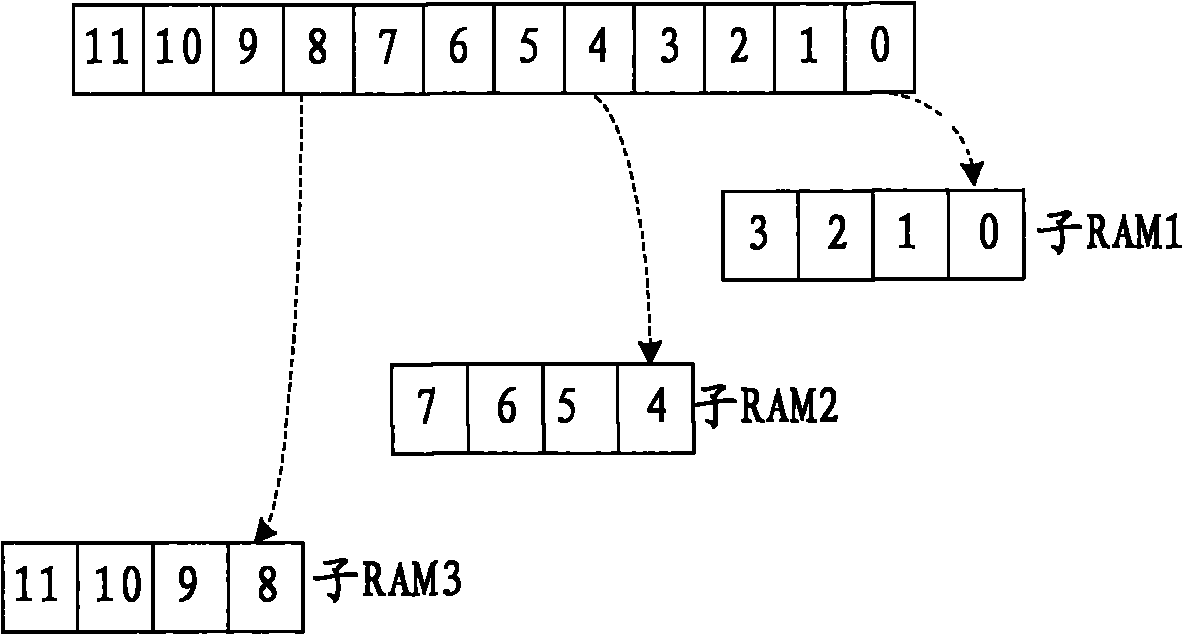
[0055] Through this step, it is possible to store repeated data in different sub-RAMs, and since each bit of data should be stored in which sub-RAM and where it should be stored in the sub-RAM can be determined, therefore, it can be parallelized Store data into each sub-RAM. Wherein, the sub-RAM where the input data should be stored and the location in the sub-RAM can be determined according to the length of the data and the number of times of repeated sending.
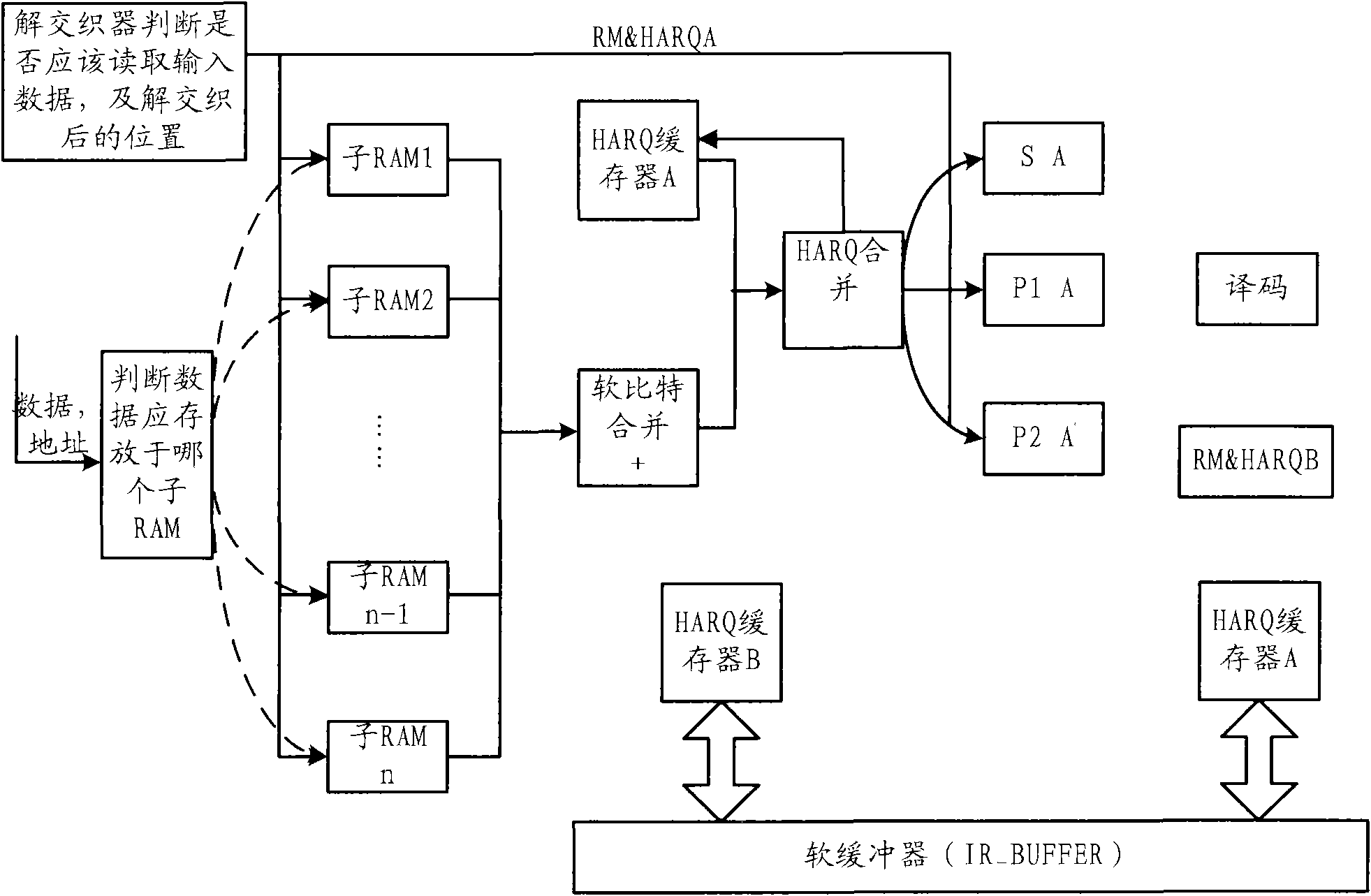
[0056] see figure 2 , which is a schematic diagram of the implementation structure of...
Embodiment 2
[0073] In practical applications, if the receiving end finds that the received input data has errors, it may perform HARQ (Hybrid-ARQ, hybrid automatic retransmission operation), that is, it needs to request the sending end to resend the data. Note that the concept of resending data here is different from the concept of repeatedly sending data described above. The repeated transmission mentioned above refers to increasing the length of data for subsequent symbol-level processing during one transmission; and retransmission means that if an error is found during one transmission, the sending end performs the same operation as the first The operation of the same configuration in the first transmission, that is, when the data is resent after receiving the HARQ request each time, a string of data needs to be repeatedly sent multiple times.
[0074] In order to improve the accuracy of the received data, the data received again after the HARQ request can often be combined with the da...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Since the process of de-rate matching is from the k in the soft buffer (IR_BUFFER) of the current code block 0 After reaching the last value of the soft buffer, it increases from position 0 until k in the soft buffer 0 -1 position end, iterate over all positions in the soft buffer. For the data outside the soft buffer after interleaving, it is discarded during the rate matching encoding, and these discarded data need to be filled with zeros to replace the rate matching solution, which requires the process of solving the rate matching to process three bit streams All data of (systematic bit, parity bit 1, parity bit 2) (total (3*32* interleaving matrix row number=K w ) data) to traverse. In downstream processing, the soft buffer size per code block That is N cb always less than or equal to K w , and in some cases the difference between these two values is very large, for example: in LTEFDD system, when the number of code blocks is 20, N IR / C is 7733, while K w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com