Method for judging metallurgical quality of titanium alloy blade
A titanium alloy and blade technology, applied in the field of metallurgical quality judgment of titanium alloy blades, can solve the problems of engine reliability blind spots, streamlines and microstructures, mechanical properties and usable performance, etc., to achieve perfect technical standards and save costs , the effect of improving production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] This embodiment provides a method for judging the metallurgical quality of titanium alloy blades, characterized in that: the method for judging the metallurgical quality of titanium alloy blades includes, during the blade forming process, including: rod extrusion, upsetting, pre-forging, Isothermal forming, isothermal correction, heat treatment, mechanical processing, low power corrosion; vacuum heat treatment: double annealing, heating at 920℃, heat preservation, heat preservation time calculated according to the maximum cross section; cooling with argon gas; heating at 550℃, heat preservation for 2h, argon filling Air cooling; machining method: CNC machining; low-power corrosion bath: HF (42%) 120ML / L, HNO 3 (65%~68%)260ML / L, H 3 PO 4 (85%) 160ML / L, urea 25g / L, others are water;
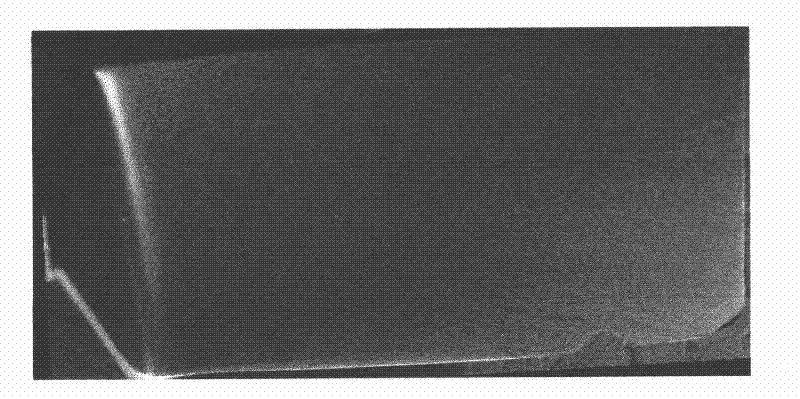
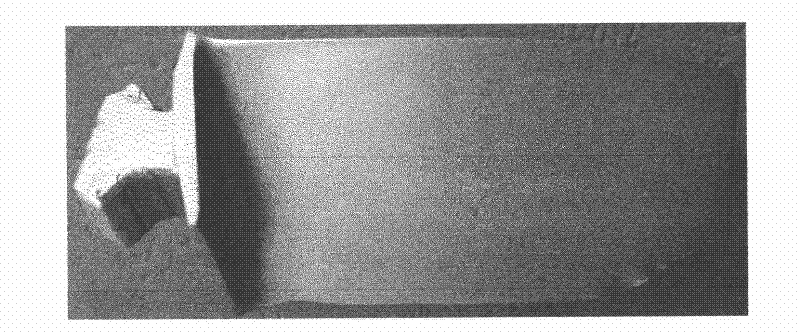
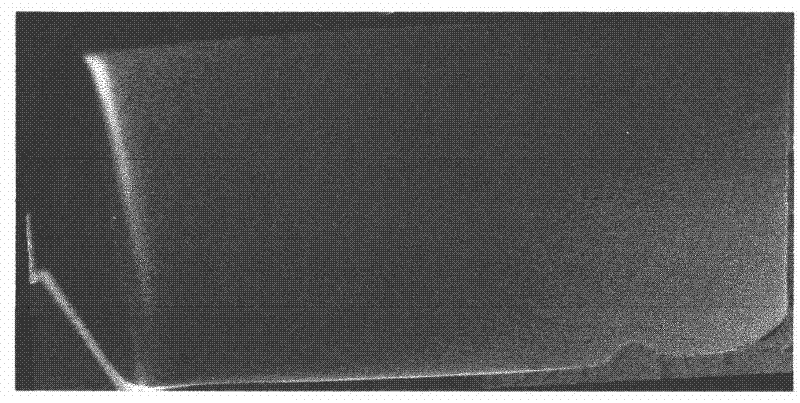
[0022] If the uniform equiaxed α-phase organization is the ideal organization, then the heterogeneous microstructures corresponding to the low-magnification morphologies of different color contr...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment provides a method for judging the metallurgical quality of titanium alloy blades, characterized in that: the method for judging the metallurgical quality of titanium alloy blades includes, during the blade forming process, including: rod extrusion, upsetting, pre-forging, Isothermal forming, isothermal correction, heat treatment, mechanical processing, low-power corrosion; vacuum heat treatment: double annealing, heating at 930℃, heat preservation, heat preservation time calculated according to the maximum cross section; cooling with argon gas; heating at 650℃, heat preservation for 4h, argon filling Air cooling; machining method: CNC machining; low-power corrosion bath: HF (42%) 120ML / L, HNO 3 (65%~68%)260ML / L, H 3 PO 4 (85%) 160ML / L, urea 25g / L, others are water;
[0034] If the uniform equiaxed α-phase organization is the ideal organization, then the heterogeneous microstructures corresponding to the low-magnification morphologies of different color contr...
Embodiment 3
[0045] This embodiment provides a method for judging the metallurgical quality of titanium alloy blades, characterized in that: the method for judging the metallurgical quality of titanium alloy blades includes, during the blade forming process, including: rod extrusion, upsetting, pre-forging, Isothermal forming, isothermal correction, heat treatment, mechanical processing, low power corrosion; vacuum heat treatment: double annealing, heating at 925℃, heat preservation, heat preservation time calculated according to the maximum cross section; cooling with argon gas; heating at 600℃, heat preservation for 3h, argon filling Air cooling; machining method: CNC machining; low-power corrosion bath: HF (42%) 120ML / L, HNO 3 (65%~68%)260ML / L, H 3 PO 4 (85%) 160ML / L, urea 25g / L, others are water;
[0046] If the uniform equiaxed α-phase organization is the ideal organization, then the heterogeneous microstructures corresponding to the low-magnification morphologies of different color contr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com