Low tin-copper alloy contact wire for electric railway and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of electrified railways and tin-copper alloys, which is applied in the direction of cable/conductor manufacturing, electrical components, metal/alloy conductors, etc., can solve the problems of non-compliance with national policies, poor machinability, short service life, etc., and achieve obvious economic value and social value, good processability and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Low tin copper alloy contact wire for electrified railway and its manufacturing method:
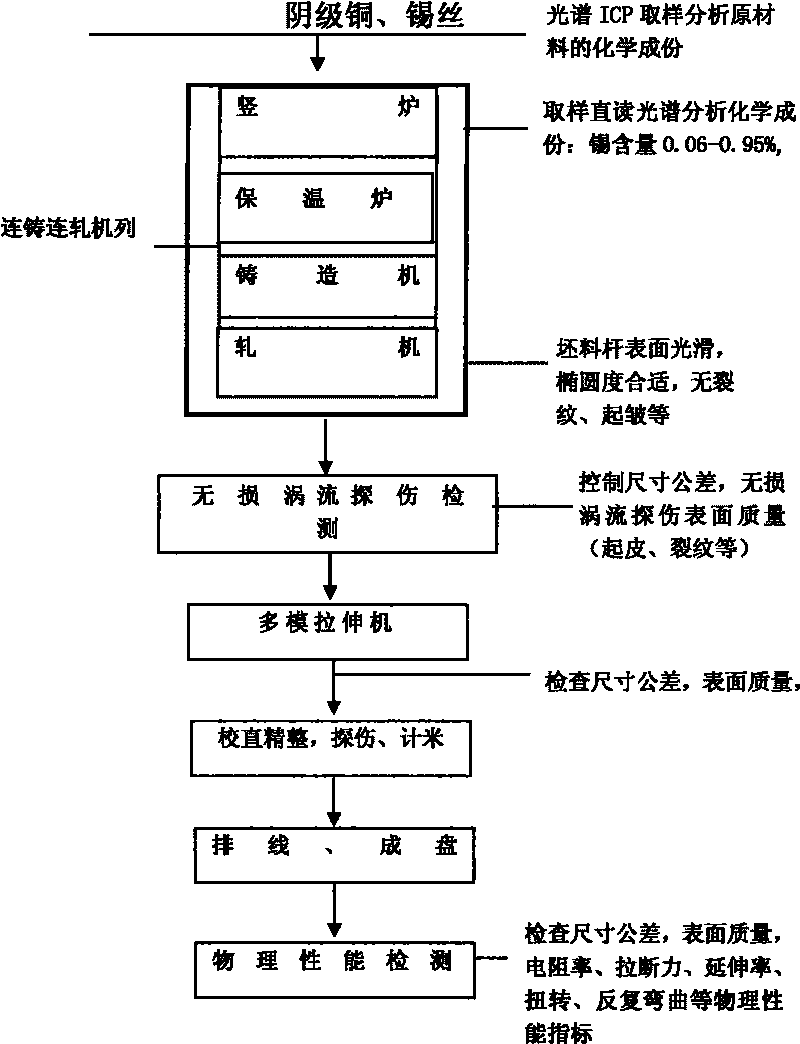
[0028] The continuous casting and rolling process is used to produce a low-tin-copper alloy contact wire blank rod with a diameter of Φ28mm. Among them, tin is added to the upper part of the lower flow tank by a quantitative adding device with a diameter of Φ6mm. Finally, the cross section is 2300mm after hot rolling 2 The cast bar is hot-rolled to a Φ28mm billet rod, and the hot working pass can be 4-8 times, the pass processing rate is 18.5% to 23.5% per pass, the total hot working rate is 73.26%, and the hot rolling temperature is 750-830 ℃, the grain size is 0.015~0.018mm, hot rolling has enough to change the as-cast grain size of alloy metal, but it is a good foundation for the subsequent cold working rate to improve the performance index.
[0029] The high-purity cathode copper is put into the vertical melting furnace, the fuel is natural gas, the temperature of the copper liquid...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Put 35 tons of high-purity cathode copper into the vertical melting furnace. When the temperature of the holding furnace rises to 1140℃~1150℃, ensure that the atmosphere in the furnace is slightly reduced and start production. The molten liquid metal flows into the ladle continuously through the lower chute. In the lower chute, the wire feeding method is used to control the weight percentage to add the metal tin wire at 0.097%, and the adding amount is synchronized with the casting speed. Sampling and analysis, after the tin content is qualified, start casting and rolling, the ladle temperature is controlled at 1100~1120℃, the casting speed is 750rpm, the cooling water pressure is 0.08~0.25Mpa, the casting slab is obtained after cooling and solidification, and the casting section is trapezoidal. Section area 2300mm 2 . The cast slab is fed into a rolling mill with a running speed of 750 rpm for continuous rolling four passes, and the rolling temperature is controlled to ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The continuous casting and rolling process is used to produce a low-tin-copper alloy contact wire blank rod with a diameter of Φ28mm. Among them, tin is added to the upper part of the lower flow tank by a quantitative adding device with a diameter of Φ6mm. Finally, the cross section is 2300mm after hot rolling 2 The cast bar is hot-rolled to a Φ28mm billet rod, the hot working pass is 4-8 times, the pass processing rate is 18.5-23.5%, the total hot working rate is 73.26%, and the hot rolling temperature is 750-830℃. The grain size is 0.015~0.018mm. Hot rolling is enough to change the as-cast grain size of alloy metals, but it provides a good foundation for the subsequent cold working rate to improve performance indicators.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com